Salvinorins are a group of natural chemical compounds and their structural analogs. Several salvinorins have been isolated from Salvia divinorum . They are classified as diterpenoid furanolactones. Salvinorin A is a hallucinogen with dissociative effects.
Contents
Several salvinorins have been isolated and characterized.
| Name | Structure | R1 | R2 | Chemical formula | Molar mass | CAS number | PubChem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salvinorin A | 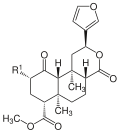 | –OCOCH3 | − | C23H28O8 | 432.46 g·mol−1 | 83729-01-5 | CID 128563 from PubChem |
| Salvinorin B | –OH | − | C21H26O7 | 390.43 g·mol−1 | 92545-30-7 | CID 11440685 from PubChem | |
| Salvinorin C | 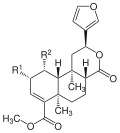 | –OCOCH3 | –OCOCH3 | C25H30O9 | 475.29 g·mol−1 | 385785-99-9 | – |
| Salvinorin D [1] | –OH | –OCOCH3 | C23H28O8 | 432.47 g·mol−1 | 540770-13-6 | – | |
| Salvinorin E [1] | –OCOCH3 | –OH | C23H28O8 | 432.47 g·mol−1 | 540770-14-7 | – | |
| Salvinorin F [1] | –H | –OH | C21H26O6 | 374.43 g·mol−1 | 540770-15-8 | – | |
| Salvinorin G | =O | –OCOCH3 | C23H26O8 | 430.45 g·mol−1 | 866622-54-0 | – | |
| Salvinorin H | –OH | –OH | C21H26O7 | 390.43 g·mol−1 | 872004-62-1 | – | |
| Salvinorin I |  | – | – | C21H28O7 | 392.45 g·mol−1 | 917951-71-4 | – |
| 17α-Salvinorin J | 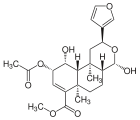 | – | – | C23H30O8 | 434.49 g·mol−1 | 1157894-83-1 | – |
| 17β-Salvinorin J |  | – | – | C23H30O8 | 434.49 g·mol−1 | 1157894-85-3 | – |