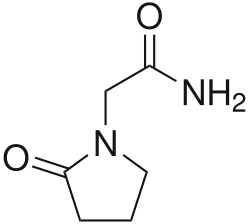
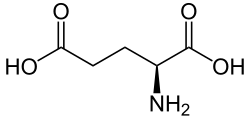
Mechanism
There is no universally accepted mechanism of action for racetams. Racetams generally show negligible affinity for common central nervous system receptors, but modulation of central neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine and glutamate, has been reported. Although aniracetam and nebracetam show some affinity for muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, only nefiracetam demonstrates nanomolar interactions with neurotransmitter receptors. Modification of membrane-located mechanisms of central signal transduction is another hypothesis. [3]
Like some ampakines, some racetams, such as piracetam and aniracetam, are positive allosteric modulators of the AMPA receptor. [7]
Racetams are understood to work by allosterically modulating glutamate receptors, specifically AMPA receptors, leading to Ca2+ influx that is excitatory. [8] Racetams are posited to enhance memory through interaction with glutamate receptors in the central nervous system.
Phenylpiracetam, unique among racetams in being a phenethylamine and stimulant, is an atypical dopamine reuptake inhibitor. [9] [10] [11] [12]
Anticonvulsant racetams, including levetiracetam, brivaracetam, and seletracetam, act as synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A (SV2A) ligands. [6] A newer analogue of these agents, padsevonil, is no longer a racetam itself but is much more potent in comparison and interacts with not only SV2A but also synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2B (SV2B) and synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2C (SV2C). [6]
Methylphenylpiracetam, a derivative of phenylpiracetam, is a positive allosteric modulator of the sigma σ1 receptor. [10] [13] [15] It is currently the only racetam known to possess this action. [10]
Cofactors
In studies with aged rats, marked improvement has been observed in cognitive tasks in experimental groups given piracetam. Performance was further increased when piracetam was combined with choline. Evidence in studies with rats has indicated that the potency of piracetam is increased when administered with choline. [16]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.