 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H23NO3 |
| Molar mass | 253.34 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Arnolol is a beta blocker. [1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H23NO3 |
| Molar mass | 253.34 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Arnolol is a beta blocker. [1]
The international nonproprietary name (INN) is an official generic and non-proprietary name given to a pharmaceutical drug or an active ingredient. INNs make communication more precise by providing a unique standard name for each active ingredient, to avoid prescribing errors. The INN system has been coordinated by the World Health Organization (WHO) since 1953.
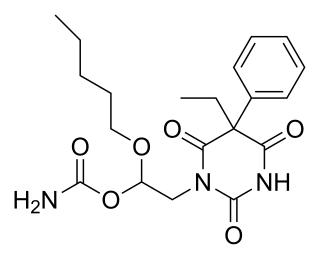
Febarbamate, also known as phenobamate, is an anxiolytic and tranquilizer of the barbiturate and carbamate families which is used in Europe by itself and as part of a combination drug formulation called tetrabamate.
Adaprolol is a beta blocker.

Alfurolol is a beta blocker.

Ancarolol is a beta blocker.
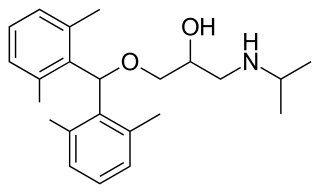
Xipranolol is a beta blocker.

Xibenolol is a beta blocker.

Etolorex is an anorectant of the amphetamine class. It was never marketed.
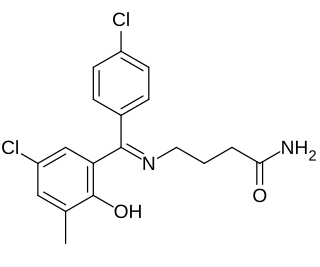
Tolgabide is a drug which was patented by Synthélabo as an anticonvulsant but was never marketed. It is an analogue of progabide and acts similarly to it as a prodrug of GABA, and therefore as an indirect agonist of the GABA receptors.

Pentabamate (S-109) is a tranquilizer of the carbamate family.
Cyclarbamate, also known as cyclopentaphene, is a muscle relaxant and tranquilizer of the carbamate family which has been marketed by Cassenne in France since 1961.

Nisobamate is a tranquilizer of the carbamate family which was never marketed.
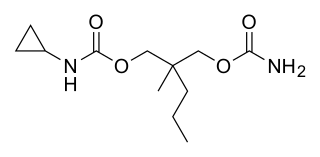
Lorbamate is a muscle relaxant and tranquilizer of the carbamate family which was never marketed.
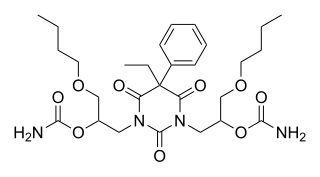
Difebarbamate (INN) is a tranquilizer of the barbiturate and carbamate families which is used in Europe as a component of a combination drug formulation referred to as tetrabamate.

Tetrabarbital is a barbiturate derivative used as a hypnotic.

Drug nomenclature is the systematic naming of drugs, especially pharmaceutical drugs. In the majority of circumstances, drugs have 3 types of names: chemical names, the most important of which is the IUPAC name; generic or nonproprietary names, the most important of which are the International Nonproprietary Names (INNs); and trade names, which are brand names. Generic names for drugs are nowadays constructed out of affixes and stems that classify the drugs into different categories and also separate drugs within categories. A marketed drug might also have a company code or compound code.

Furostilbestrol (INN), also known as diethylstilbestrol di(2-furoate) or simply as diesthylstilbestrol difuroate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol that was never marketed. It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol and was described in the literature in 1952.
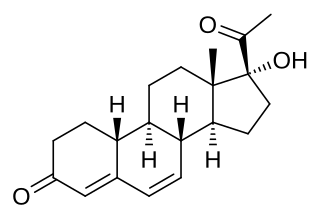
Gestadienol (INN), also known as 6-dehydro-17α-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-norprogesterone group that was never marketed.

Cismadinone (INN), also known as 6α-chloro-17α-hydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione or 6α-chloro-δ1-dehydro-17α-hydroxyprogesterone, is a steroidal progestin closely related to the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone derivatives that was never marketed. An acetylated form, cismadinone acetate, also exists, but similarly to cismadinone, was never marketed.

Clomegestone (INN), or clomagestone, also known as 6-chloro-17α-hydroxy-16α-methylpregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione, is a steroidal progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group that was never marketed. An acetate ester, clomegestone acetate, also exists, and similarly was never marketed.
| This antihypertensive-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |