In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist.
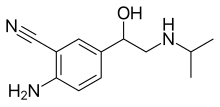
Salmeterol is a long-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist (LABA) used in the maintenance and prevention of asthma symptoms and maintenance of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) symptoms. Symptoms of bronchospasm include shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing and chest tightness. It is also used to prevent breathing difficulties during exercise.
Beta2-adrenergic agonists, also known as adrenergic β2 receptor agonists, are a class of drugs that act on the β2 adrenergic receptor. Like other β adrenergic agonists, they cause smooth muscle relaxation. β2 adrenergic agonists' effects on smooth muscle cause dilation of bronchial passages, vasodilation in muscle and liver, relaxation of uterine muscle, and release of insulin. They are primarily used to treat asthma and other pulmonary disorders, such as Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).

An adrenergic antagonist is a drug that inhibits the function of adrenergic receptors. There are five adrenergic receptors, which are divided into two groups. The first group of receptors are the beta (β) adrenergic receptors. There are β1, β2, and β3 receptors. The second group contains the alpha (α) adrenoreceptors. There are only α1 and α2 receptors. Adrenergic receptors are located near the heart, kidneys, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. There are also α-adreno receptors that are located on vascular smooth muscle.
Befunolol (INN) is a beta blocker with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity used in the management of open-angle glaucoma. It also acts as a β adrenoreceptor partial agonist. Befunolol was introduced in Japan in 1983 by Kakenyaku Kako Co. under the trade name Bentos.

The beta-3 adrenergic receptor (β3-adrenoceptor), also known as ADRB3, is a beta-adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it.
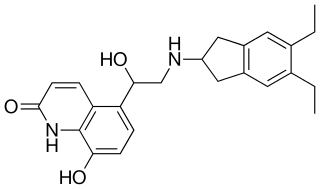
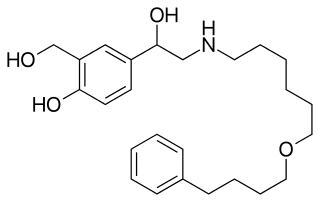
Indacaterol is an ultra-long-acting beta-adrenoceptor agonist developed by Novartis. It needs to be taken only once a day, unlike the related drugs formoterol and salmeterol. It is licensed only for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is delivered as an aerosol formulation through a dry powder inhaler.

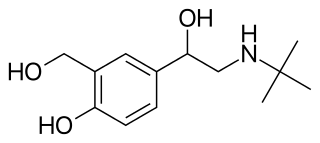
Tulobuterol (INN) is a long-acting beta2-adrenergic receptor agonist, marketed in Japan as a transdermal patch under the name Hokunalin tape (ホクナリンテープ).
Solabegron is a drug which acts as a selective agonist for the β3 adrenergic receptor. It is being developed for the treatment of overactive bladder and irritable bowel syndrome. It has been shown to produce visceral analgesia by releasing somatostatin from adipocytes.
Amibegron (SR-58,611A) was a drug developed by Sanofi-Aventis which acts as a selective agonist for the β3 adrenergic receptor. It is the first orally active β3 agonist developed that is capable of entering the central nervous system, and has antidepressant and anxiolytic effects.

Denopamine (INN) is a cardiotonic drug which acts as a β1 adrenergic receptor agonist. It is used in the treatment of angina and may also have potential uses in the treatment of congestive heart failure and for clearing pulmonary oedema. It is marketed in Japan under the brand name Kalgut (カルグート) and available as tablets of 5 and 10 mg, and 5% fine granules.

Beta adrenergic agonists or beta agonists are medications that relax muscles of the airways, causing widening of the airways and resulting in easier breathing. They are a class of sympathomimetic agents, each acting upon the beta adrenoceptors. In general, pure beta-adrenergic agonists have the opposite function of beta blockers: beta-adrenoreceptor agonist ligands mimic the actions of both epinephrine- and norepinephrine- signaling, in the heart and lungs, and in smooth muscle tissue; epinephrine expresses the higher affinity. The activation of β1, β2 and β3 activates the enzyme, adenylate cyclase. This, in turn, leads to the activation of the secondary messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP); cAMP then activates protein kinase A (PKA) which phosphorylates target proteins, ultimately inducing smooth muscle relaxation and contraction of the cardiac tissue.
Beta1-adrenergic agonists, also known as Beta1-adrenergic receptor agonists, are a class of drugs that bind selectively to the beta-1 adrenergic receptor. As a result, they act more selectively upon the heart. Beta-adrenoceptors typically bind to norepinephrine release by sympathetic adrenergic nerves and to circulating epinephrine. The effect of B-adrenoceptors is cardiac stimulation, such as increased heart rate, heart contractility, heart conduction velocity and heart relaxation.

Mabuterol is a selective β2 adrenoreceptor agonist.
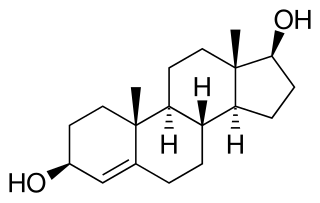
4-Androstenediol, also known as androst-4-ene-3β,17β-diol, is an androstenediol that is converted to testosterone. The conversion rate is about 15.76%, almost triple that of 4-androstenedione, due to utilization of a different enzymatic pathway. There is also some conversion into estrogen, since testosterone is the metabolic precursor of the estrogens.

Prinaberel is a synthetic, nonsteroidal, and highly selective agonist of the ERβ subtype of the estrogen receptor. It is used in scientific research to elucidate the role of the ERβ receptor. Studies have indicated that selective ERβ agonists like prinaberel could be useful in the clinical treatment of a variety of medical conditions including inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, endometriosis, and sepsis. Accordingly, prinaberel either was or still is under investigation by Wyeth for the treatment of some of these conditions.

Alifedrine is a partial beta-adrenergic agonist.
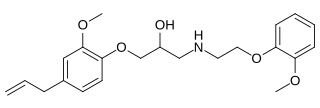
Eugenodilol is an alpha-1 blocker and beta blocker with weak β2-adrenergic receptor agonist activity derived from eugenol.

Erteberel is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen which acts as a selective ERβ agonist and is under development by Eli Lilly for the treatment of schizophrenia. It is specifically under investigation for the treatment of negative symptoms and cognitive impairment associated with the condition. As of 2015, it is in phase II clinical trials for this indication in the United States. Erteberel was also under investigation for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and reached phase II clinical studies for this use but failed to improve symptoms in men with the condition and development for this indication was discontinued. The drug has also been proposed as a potential novel treatment for glioblastoma.
Beclometasone/formoterol/glycopyrronium, sold under the brand name Trimbow among others, is an inhalable fixed-dose combination medication for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It contains beclometasone dipropionate, formoterol fumarate dihydrate, and glycopyrronium bromide.