 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H33NO2 |
| Molar mass | 355.51 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
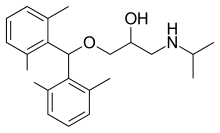
Xipranolol is a beta blocker. [1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H33NO2 |
| Molar mass | 355.51 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Xipranolol is a beta blocker. [1]

Beta blockers are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack. They are also widely used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension), although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most patients.
The international nonproprietary name (INN) is an official generic and non-proprietary name given to a pharmaceutical drug or an active ingredient. INNs make communication more precise by providing a unique standard name for each active ingredient, to avoid prescribing errors. The INN system has been coordinated by the World Health Organization (WHO) since 1953.
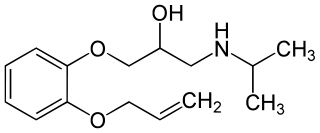
Oxprenolol is a non-selective beta blocker with some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. It is used for the treatment of angina pectoris, abnormal heart rhythms and high blood pressure.
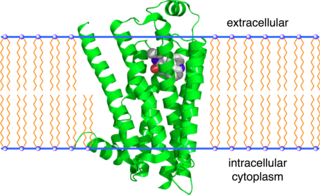
The beta-2 adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRB2, is a cell membrane-spanning beta-adrenergic receptor that interacts with (binds) epinephrine, a hormone and neurotransmitter whose signaling, via adenylate cyclase stimulation through trimeric Gs proteins, increased cAMP, and downstream L-type calcium channel interaction, mediates physiologic responses such as smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation.

Enoximone is an imidazole phosphodiesterase inhibitor. It is used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and is selective for phosphodiesterase 3.

Butaxamine is a β2-selective beta blocker. Its primary use is in experimental situations in which blockade of β2 receptors is necessary to determine the activity of the drug. It has no clinical use. An alternative name is α-(1-[tert-butylamino]ethyl)-2,5-dimethoxybenzyl alcohol.
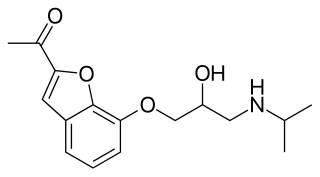
Befunolol (INN) is a beta blocker with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity used in the management of open-angle glaucoma. It also acts as a β adrenoreceptor partial agonist. Befunolol was introduced in Japan in 1983 by Kakenyaku Kako Co. under the trade name Bentos.
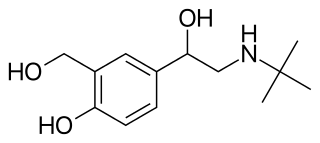
Beta adrenergic agonists or beta agonists are medications that relax muscles of the airways, which widen the airways and result in easier breathing. They are a class of sympathomimetic agents which act upon the beta adrenoceptors. In general, pure beta-adrenergic agonists have the opposite function of beta blockers. Beta adrenoreceptor agonist ligands mimic the action of epinephrine and norepinephrine signaling in the heart, lungs, and smooth muscle tissue, with epinephrine expressing the highest affinity. The activation of β1, β2 and β3 activates the enzyme, adenylate cyclase. This, in turn, leads to the activation of the secondary messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), cAMP then activates protein kinase A (PKA) which phosphorylates target proteins, ultimately inducing smooth muscle relaxation and contraction of the cardiac tissue.

Tilisolol is a beta blocker.
Arotinolol is a medication in the class of mixed alpha/beta blockers. It also acts as a β3 receptor agonist. A 1979 publication suggests arotinolol as having first been described in the scientific literature by Sumitomo Chemical as "β-adrenergic blocking, antiarrhythmic compound S-596".
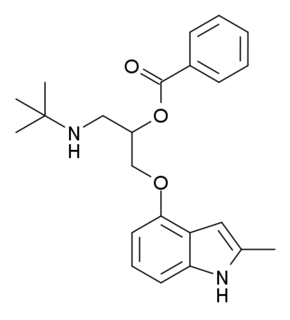
Bopindolol (INN) is a beta blocker. It is an ester which acts as a prodrug for its active metabolite 4-(3-t-butylamino-2-hydroxypropoxy)-2-methylindole.
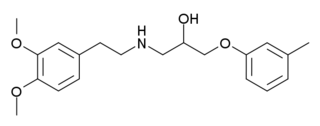
Bevantolol (INN) was a drug candidate for angina and hypertension that acted as both a beta blocker and a calcium channel blocker. It was discovered and developed by Warner-Lambert but in January 1989 the company announced that it had withdrawn the New Drug Application; the company's chairman said: "Who needs the 30th beta blocker?" As of 2016 it wasn't marketed in the US, UK, or Europe and the authors of a Cochrane review could find no product monograph for it.
Adaprolol is a beta blocker.

Alfurolol is a beta blocker.

Ancarolol is a beta blocker.
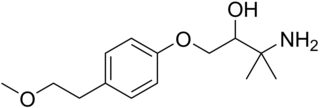
Arnolol is a beta blocker.

Xibenolol is a beta blocker.

Butidrine (INN), or butedrine or butydrine, also known as hydrobutamine or idrobutamine, is a beta blocker related to pronethalol and propranolol that was developed in the 1960s. Similarly to certain other beta blockers, butidrine also possesses local anesthetic properties.
Eptinezumab is an experimental drug being developed by Alder Biopharmaceuticals for the treatment of migraine. It is a monoclonal antibody that targets calcitonin gene-related peptides (CGRP) alpha and beta. It is in Phase III clinical trials as of August 2017.
Galcanezumab, marketed under the trade name Emgality, is a humanized monoclonal antibody used for the prevention of migraine. It is directed against calcitonin-related polypeptides alpha and beta.
| This antihypertensive-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |