A bronchodilator or broncholytic is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lungs. Bronchodilators may be originating naturally within the body, or they may be medications administered for the treatment of breathing difficulties, usually in the form of inhalers. They are most useful in obstructive lung diseases, of which asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are the most common conditions. They may be useful in bronchiolitis and bronchiectasis, although this remains somewhat controversial. They are often prescribed but of unproven significance in restrictive lung diseases.

Salbutamol, also known as albuterol and sold under the brand name Ventolin among others, is a medication that opens up the medium and large airways in the lungs. It is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist that causes relaxation of airway smooth muscle. It is used to treat asthma, including asthma attacks and exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, as well as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It may also be used to treat high blood potassium levels. Salbutamol is usually used with an inhaler or nebulizer, but it is also available in a pill, liquid, and intravenous solution. Onset of action of the inhaled version is typically within 15 minutes and lasts for two to six hours.

Fluticasone/salmeterol, sold under the brand name Advair among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication containing fluticasone propionate, an inhaled corticosteroid; and salmeterol, a long-acting beta2‑adrenergic agonist. It is used in the management of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is used by inhaling the medication into the lungs.
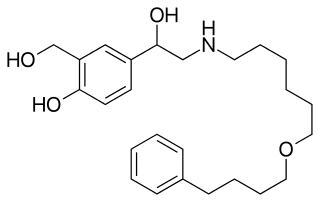
Salmeterol is a long-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist (LABA) used in the maintenance and prevention of asthma symptoms and maintenance of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) symptoms. Symptoms of bronchospasm include shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing and chest tightness. It is also used to prevent breathing difficulties during exercise.

Budesonide/formoterol, sold under the brand name Symbicort among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication used in the management of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It contains budesonide, a steroid; and formoterol, a long-acting β2-agonist (LABA). The product monograph does not support its use for sudden worsening or treatment of active bronchospasm. However, a 2020 review of the literature does support such use. It is used by breathing in the medication.

An inhaler is a medical device used for delivering medicines into the lungs through the work of a person's breathing. This allows medicines to be delivered to and absorbed in the lungs, which provides the ability for targeted medical treatment to this specific region of the body, as well as a reduction in the side effects of oral medications. There are a wide variety of inhalers, and they are commonly used to treat numerous medical conditions with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) being among the most notable.
Beta2-adrenergic agonists, also known as adrenergic β2 receptor agonists, are a class of drugs that act on the β2 adrenergic receptor. Like other β adrenergic agonists, they cause smooth muscle relaxation. β2 adrenergic agonists' effects on smooth muscle cause dilation of bronchial passages, vasodilation in muscle and liver, relaxation of uterine muscle, and release of insulin. They are primarily used to treat asthma and other pulmonary disorders. Bronchodilators are considered an important treatment regime for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and are usually used in combination with short acting medications and long acting medications in a combined inhaler.

Long-acting β adrenoceptor agonists (LABAs) are beta-adrenergic agonists usually prescribed for moderate-to-severe persistent asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).

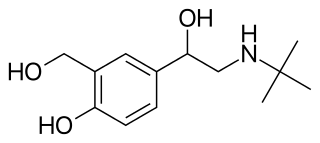
Levosalbutamol, also known as levalbuterol, is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist used in the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Evidence is inconclusive regarding the efficacy of levosalbutamol versus salbutamol or salbutamol-levosalbutamol combinations, though levosalbutamol is believed to have a better safety profile due to its more selective binding to β2 receptors versus β1.
Indacaterol is an ultra-long-acting beta-adrenoceptor agonist developed by Novartis. It needs to be taken only once a day, unlike the related drugs formoterol and salmeterol. It is licensed only for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is delivered as an aerosol formulation through a dry powder inhaler.

Mometasone/formoterol, sold under the brand name Dulera among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication used in the long-term treatment of asthma. It contains mometasone a steroid and formoterol a long-acting beta agonist. It is only recommended in those for whom an inhaled steroid is not sufficient. It is used by inhalation.

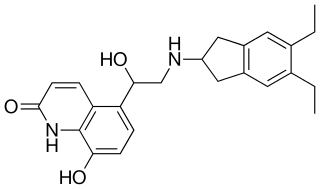
Olodaterol is an ultra-long-acting β adrenoreceptor agonist (ultra-LABA) used as an inhalation for treating people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is manufactured by Boehringer Ingelheim.
β2-adrenoceptor agonists are a group of drugs that act selectively on β2-receptors in the lungs causing bronchodilation. β2-agonists are used to treat asthma and COPD, diseases that cause obstruction in the airways. Prior to their discovery, the non-selective beta-agonist isoprenaline was used. The aim of the drug development through the years has been to minimise side effects, achieve selectivity and longer duration of action. The mechanism of action is well understood and has facilitated the development. The structure of the binding site and the nature of the binding is also well known, as is the structure activity relationship.

Indacaterol/glycopyrronium bromide, sold under the brand name Ultibro Breezhaler among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication for inhalation consisting of the following two active ingredients:

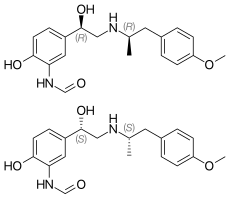
Carmoterol is a non-catechol experimental ultra-long-acting β adrenoreceptor agonist (ultra-LABA) that was in clinical trials before 2010 when it has been withdrawn from further development based on evidence that the compound does not possess a competitive profile.
Viatris Inc. is an American global pharmaceutical and healthcare corporation headquartered in Canonsburg, Pennsylvania. The corporation was formed through the merger of Mylan and Upjohn, a legacy division of Pfizer, on November 16, 2020.
Glycopyrronium bromide/formoterol, sold under the brand name Bevespi Aerosphere, is a combination medication used for the maintenance treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is a combination of glycopyrronium bromide and formoterol. It is inhaled.
Salbutamol/budesonide, sold under the brand name Airsupra, is a fixed-dose combination medication for the treatment of bronchoconstriction and asthma. It is a combination of salbutamol sulfate, a short-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist, and budesonide, an inhaled corticosteroid. It is inhaled using a pressurized metered-dose inhaler.
An anti-asthmatic agent, also known as an anti-asthma drug, refers to a drug that can aid in airway smooth muscle dilation to allow normal breathing during an asthma attack or reduce inflammation on the airway to decrease airway resistance for asthmatic patients, or both. The goal of asthmatic agents is to reduce asthma exacerbation frequencies and related hospital visits.