Related Research Articles
A bronchodilator or broncholytic is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lungs. Bronchodilators may be originating naturally within the body, or they may be medications administered for the treatment of breathing difficulties, usually in the form of inhalers. They are most useful in obstructive lung diseases, of which asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are the most common conditions. Although this remains somewhat controversial, they might be useful in bronchiolitis and bronchiectasis. They are often prescribed but of unproven significance in restrictive lung diseases.
ATC code A03Drugs for functional gastrointestinal disorders is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup A03 is part of the anatomical group A Alimentary tract and metabolism.
ATC code D07Corticosteroids, dermatological preparations is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup D07 is part of the anatomical group D Dermatologicals.
ATC code D11Other dermatological preparations is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup D11 is part of the anatomical group D Dermatologicals.
ATC code M03Muscle relaxants is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup M03 is part of the anatomical group M Musculo-skeletal system.
ATC code R01Nasal preparations is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup R01 is part of the anatomical group R Respiratory system.
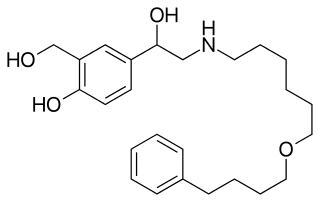
Salmeterol is a long-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist (LABA) used in the maintenance and prevention of asthma symptoms and maintenance of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) symptoms. Symptoms of bronchospasm include shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing and chest tightness. It is also used to prevent breathing difficulties during exercise.

Formoterol, also known as eformoterol, is a long-acting β2 agonist (LABA) used as a bronchodilator in the management of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Formoterol has an extended duration of action compared to short-acting β2 agonists such as salbutamol (albuterol), which are effective for 4 h to 6 h. Formoterol has a relatively rapid onset of action compared to other LABAs, and is effective within 2-3 minutes. The 2022 Global Initiative for Asthma report recommends a combination formoterol/inhaled corticosteroid inhaler as both a preventer and reliever treatment for asthma in adults. In children, a short-actingβ2 agonist is still recommended.
An adrenergic agonist is a drug that stimulates a response from the adrenergic receptors. The five main categories of adrenergic receptors are: α1, α2, β1, β2, and β3, although there are more subtypes, and agonists vary in specificity between these receptors, and may be classified respectively. However, there are also other mechanisms of adrenergic agonism. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are endogenous and broad-spectrum. More selective agonists are more useful in pharmacology.
Beta2-adrenergic agonists, also known as adrenergic β2 receptor agonists, are a class of drugs that act on the β2 adrenergic receptor. Like other β adrenergic agonists, they cause smooth muscle relaxation. β2 adrenergic agonists' effects on smooth muscle cause dilation of bronchial passages, vasodilation in muscle and liver, relaxation of uterine muscle, and release of insulin. They are primarily used to treat asthma and other pulmonary disorders. Bronchodilators are considered an important treatment regime for Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and are usually used in combination with short acting medications and long acting medications in a combined inhaler.

Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.

Long-acting β adrenoceptor agonists (LABAs) are beta-adrenergic agonists usually prescribed for moderate-to-severe persistent asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). They are designed to reduce the need for shorter-acting β2 agonists such as salbutamol (albuterol), as they have a duration of action of approximately 12 hours in comparison with the 4-to-6-hour duration of salbutamol, making them candidates for sparing high doses of corticosteroids or treating nocturnal asthma and providing symptomatic improvement in patients with COPD. With the exception of formoterol, long-acting β2 agonists are not recommended for the treatment of acute asthma exacerbations because of their slower onset of action compared to salbutamol. Their long duration of action is due to the addition of a long, lipophilic side-chain that binds to an exosite on adrenergic receptors. This allows the active portion of the molecule to continuously bind and unbind at β2 receptors in the smooth muscle in the lungs.

Beta adrenergic agonists or beta agonists are medications that relax muscles of the airways, causing widening of the airways and resulting in easier breathing. They are a class of sympathomimetic agents, each acting upon the beta adrenoceptors. In general, pure beta-adrenergic agonists have the opposite function of beta blockers: beta-adrenoreceptor agonist ligands mimic the actions of both epinephrine- and norepinephrine- signaling, in the heart and lungs, and in smooth muscle tissue; epinephrine expresses the higher affinity. The activation of β1, β2 and β3 activates the enzyme, adenylate cyclase. This, in turn, leads to the activation of the secondary messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP); cAMP then activates protein kinase A (PKA) which phosphorylates target proteins, ultimately inducing smooth muscle relaxation and contraction of the cardiac tissue.
There are several categories of respiratory drugs, each specific to a drug's purpose and mode of action. The following is a list of key pharmaceuticals in the prevention and treatment of respiratory-related ailments.

Vilanterol is an ultra-long-acting β2 adrenoreceptor agonist (ultra-LABA), which was approved in May 2013 in combination with fluticasone furoate for sale as Breo Ellipta by GlaxoSmithKline for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).. The combination is also approved for the treatment of asthma in Canada, Europe, Japan and New Zealand.
β2-adrenoceptor agonists are a group of drugs that act selectively on β2-receptors in the lungs causing bronchodilation. β2-agonists are used to treat asthma and COPD, diseases that cause obstruction in the airways. Prior to their discovery, the non-selective beta-agonist isoprenaline was used. The aim of the drug development through the years has been to minimise side effects, achieve selectivity and longer duration of action. The mechanism of action is well understood and has facilitated the development. The structure of the binding site and the nature of the binding is also well known, as is the structure activity relationship.
Beclometasone/formoterol/glycopyrronium, sold under the brand name Trimbow among others, is an inhalable fixed-dose combination medication for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. It contains beclometasone dipropionate, formoterol fumarate dihydrate, and glycopyrronium bromide.
References
- ↑ "ATC (Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System) – Synopsis". National Institutes of Health . Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ↑ World Health Organization. "Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification". World Health Organization. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ "Structure and principles". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. 15 February 2018. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ "ATC/DDD Index 2022: code R03". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology.
- ↑ "ATCvet Index 2022: code QR03". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology.