
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat whereas the latter is defined as the emotional response to a real threat. It is often accompanied by nervous behavior such as pacing back and forth, somatic complaints, and rumination.

Carnivora is an order of placental mammals that have specialized in primarily eating flesh, whose members are formally referred to as carnivorans. The order Carnivora is the fifth largest order of mammals, comprising at least 279 species.

Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introduced by a group of US clinicians in the mid-1970s, the term was adopted by the American Psychiatric Association for this symptom cluster under mood disorders in the 1980 version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-III), and has become widely used since.
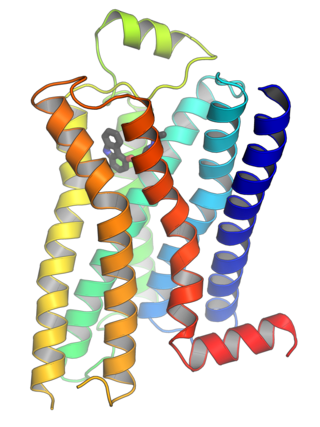
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. Since they are coupled with G proteins, they pass through the cell membrane seven times in form of six loops of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops or to the binding site within transmembrane helices. They are all activated by agonists, although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor has also been observed.

The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of Lentivirus that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype.

A mitochondrion is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term mitochondrion was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name.
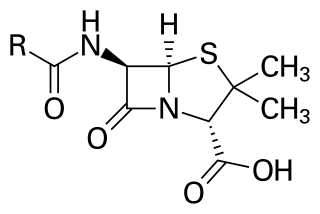
Penicillins are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from Penicillium moulds, principally P. chrysogenum and P. rubens. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G and penicillin V. Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use.
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides which have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.

Vertebrates comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata, including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following:

Escherichia coli, also known as E. coli, is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes (EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of E. coli benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between E. coli and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship — where both the humans and the E. coli are benefitting each other. E. coli is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massively in fresh faecal matter under aerobic conditions for three days, but its numbers decline slowly afterwards.

In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable changes in cell function that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix epi- in epigenetics implies features that are "on top of" or "in addition to" the traditional genetic basis for inheritance. Epigenetics most often involves changes that affect the regulation of gene expression, and that persist through cellular division. Such effects on cellular and physiological phenotypic traits may result from external or environmental factors, or be part of normal development. It can also lead to diseases such as cancer.
Multiplesclerosis (MS) is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks or building up over time. In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances.
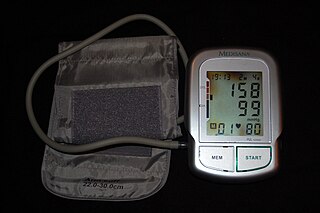
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. High blood pressure, however, is a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide.

Itchy butt syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain and or abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may occur over a long time, sometimes for years. IBS can negatively affect quality of life and may result in missed school or work or reduced productivity at work. Disorders such as anxiety, major depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome are common among people with IBS.

The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called Human gammaherpesvirus 4, is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus.

A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 9,000 of the millions of virus species have been described in detail. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology.

Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera. With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is 29–34 millimetres in length, 150 mm (6 in) across the wings and 2–2.6 g in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox, reaching a weight of 1.6 kg and having a wingspan of 1.7 m.

Eukaryota or Eukarya, whose members are known as eukaryotes, is a diverse domain of organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of living things, along with the two groups of prokaryotes, the Bacteria and the Archaea.

Neanderthals, also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. The reasons for Neanderthal extinction are disputed. Theories for their extinction include demographic factors such as small population size and inbreeding; competitive replacement; interbreeding and assimilation with modern humans; climate change; disease; or a combination of these factors.

The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism, autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or sometimes autism spectrum condition (ASC), identifies a loosely defined cluster of neurodevelopmental disorders characterized by challenges in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and often repetitive behaviors and restricted interests. Other common features include unusual responses to sensory stimuli and a preference for sameness or unusual adherence to routines.



















