
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.

The macrolides are a class of natural products that consist of a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Macrolides are bacteriostatic in that they suppress or inhibit bacterial growth rather than killing bacteria completely.

The Doors of Perception is an autobiographical book written by Aldous Huxley. Published in 1954, it elaborates on his psychedelic experience under the influence of mescaline in May 1953. Huxley recalls the insights he experienced, ranging from the "purely aesthetic" to "sacramental vision", and reflects on their philosophical and psychological implications. In 1956, he published Heaven and Hell, another essay which elaborates these reflections further. The two works have since often been published together as one book; the title of both comes from William Blake's 1793 book The Marriage of Heaven and Hell.

Mescaline (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine) is a naturally occurring psychedelic protoalkaloid of the substituted phenethylamine class, known for its hallucinogenic effects comparable to those of LSD and psilocybin. It occurs naturally in the San Pedro cactus, the Peruvian torch, the Bolivian torch cactus , the peyote cactus, and other species of cacti. It is also found in small amounts in certain members of the bean family, Fabaceae, including Acacia berlandieri. However those claims concerning Acacia species have been challenged and have been unsupported in any additional analysis.

Psychedelics are a class of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary states of consciousness via serotonin 2A receptor agonism. This causes specific psychological, visual and auditory changes, and often a substantially altered state of consciousness. The "classical" psychedelics, the psychedelics with the largest scientific and cultural influence, are mescaline, LSD, psilocybin, and DMT.

Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot, and swollen joint. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intensity in less than 12 hours. The joint at the base of the big toe is affected in about half of cases. It may also result in tophi, kidney stones, or kidney damage.

Colchicine is a medication used to treat gout and Behçet's disease. In gout, it is less preferred to NSAIDs or steroids. Other uses for colchicine include the management of pericarditis and familial Mediterranean fever. Colchicine is taken by mouth.

Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) is a hereditary inflammatory disorder. FMF is an autoinflammatory disease caused by mutations in Mediterranean fever gene, which encodes a 781–amino acid protein called pyrin. While all ethnic groups are susceptible to FMF, it usually occurs in people of Mediterranean origin—including Sephardic Jews, Mizrahi Jews, Ashkenazi Jews, Assyrians, Armenians, Levantines, Turks, Greeks and Italians.

Colchicum autumnale, commonly known as autumn crocus, meadow saffron or naked ladies, is a toxic autumn-blooming flowering plant that resembles the true crocuses, but is a member of the plant family Colchicaceae, unlike the true crocuses which belong to the family Iridaceae. The name "naked ladies" comes from the fact that the flowers emerge from the ground long before the leaves appear. Despite the vernacular name of "meadow saffron", this plant is not the source of saffron, which is obtained from the saffron crocus, Crocus sativus – and that plant too is sometimes called "autumn crocus".

Echinopsis peruviana, the Peruvian torch cactus, is a fast-growing columnar cactus native to the western slope of the Andes in Peru, between about 2,000–3,000 m (6,600–9,800 ft) above sea level.

3C-P is a psychedelic phenethylamine. It has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to the drugs mescaline, proscaline, and amphetamine. Little information exists on the human pharmacology of 3C-P, but a psychedelic dosage appears to be 20–40 mg, and is accompanied by stimulant and psychedelic effects such as visual enhancement and distortion. It can be synthesized from syringaldehyde by reaction with n-propyl iodide followed by condensation with nitroethane and reduction.
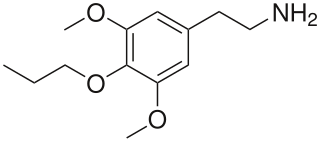
Proscaline (4-propoxy-3,5-DMPEA) is a psychedelic and hallucinogenic drug. It has structural properties similar to the drugs mescaline, isoproscaline, and escaline. In PiHKAL, Alexander Shulgin reports that a dose of 30–60 mg produces effects lasting 8–12 hours.

Lophophine is a putative psychedelic and entactogen drug of the methylenedioxyphenethylamine class. It is the α-demethylated homologue of MMDA, and is also closely related to mescaline.

Acute pericarditis is a type of pericarditis usually lasting less than 6 weeks. It is the most common condition affecting the pericardium.

The peyote is a small, spineless cactus with psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline. Peyote is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl peyōtl, meaning "caterpillar cocoon", from a root peyōni, "to glisten". Peyote is native to Mexico and southwestern Texas. It is found primarily in the Sierra Madre Occidental, the Chihuahuan Desert and in the states of Nayarit, Coahuila, Nuevo León, Tamaulipas, and San Luis Potosí among scrub. It flowers from March to May, and sometimes as late as September. The flowers are pink, with thigmotactic anthers.

Jimscaline is a conformationally-restricted derivative of the cactus-derived hallucinogen mescaline, which was discovered in 2006 by a team at Purdue University led by David E. Nichols. It acts as a potent agonist for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors with the more active (R)-enantiomer having a Ki of 69 nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor, and around three times the potency of mescaline in drug-substitution experiments in animals. This discovery that the side chain of the phenethylamine hallucinogens could be constrained to give chiral ligands with increased activity then led to the later development of the super-potent benzocyclobutene derivative TCB-2.
Postpericardiotomy syndrome (PPS) is a medical syndrome referring to an immune phenomenon that occurs days to months after surgical incision of the pericardium. PPS can also be caused after a trauma, a puncture of the cardiac or pleural structures, after percutaneous coronary intervention, or due to pacemaker or pacemaker wire placement.
Tubulin inhibitors are chemotherapy drugs that interfere directly with the tubulin system, which is in contrast to those chemotherapy drugs acting on DNA. Microtubules play an important role in eukaryotic cells. Alpha- and beta-tubulin, the main components of microtubules, have gained considerable interest because of their function and biophysical properties and has become the subject of intense study. The addition of tubulin ligands can affect microtubule stability and function, including mitosis, cell motion and intracellular organelle transport. Tubulin binding molecules have generated significant interest after the introduction of the taxanes into clinical oncology and the general use of the vinca alkaloids. These compounds inhibit cell mitosis by binding to the protein tubulin in the mitotic spindle and preventing polymerization or depolymerization into the microtubules. This mode of action is also shared with another natural agent called colchicine.

NBOMe-mescaline or mescaline-NBOMe is a synthetic substituted phenethylamine. It is a partial agonist of serotonin receptors with a 5-HT2A pKi originally reported as 7.3, though more modern techniques assayed it as 140nM at 5-HT2A and 640nM at 5-HT2C, making it one of the least potent compounds among the n-benzyl phenethylamines.
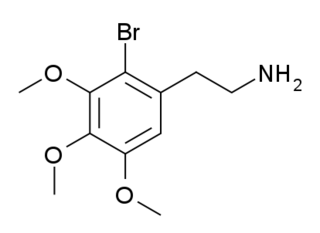
2-Bromomescaline (2-Br-M) is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen mescaline which has an unusual 2-bromo substitution. It is an agonist for serotonin receptors, with a binding affinity of 215 nM at 5-HT1A, 513 nM at 5-HT2A and 379 nM at 5-HT2C, so while it is around ten times more tightly binding than mescaline at 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors, it is over twenty times more potent at 5-HT2C.


















