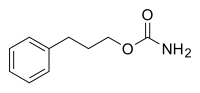
Carisoprodol, sold under the brand name Soma among others, is a medication used for musculoskeletal pain. Effects generally begin within half an hour and last for up to six hours. It is taken orally.
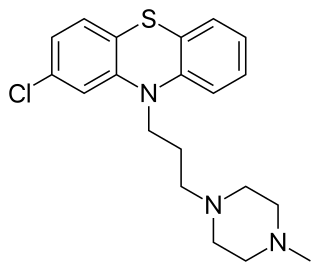
Prochlorperazine, formerly sold under the brand name Compazine among others, is a medication used to treat nausea, migraines, schizophrenia, psychosis and anxiety. It is a less preferred medication for anxiety. It may be taken by mouth, rectally, injection into a vein, or injection into a muscle.
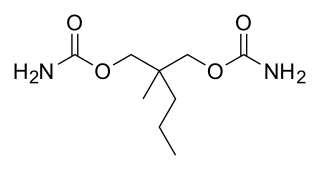
Meprobamate—marketed as Miltown by Wallace Laboratories and Equanil by Wyeth, among others—is a carbamate derivative used as an anxiolytic drug. It was the best-selling minor tranquilizer for a time, but has largely been replaced by the benzodiazepines due to their wider therapeutic index and lower incidence of serious side effects.

Ergometrine, also known as ergonovine and sold under the brand names Ergotrate, Ergostat, and Syntometrine among others, is a medication used to cause contractions of the uterus to treat heavy vaginal bleeding after childbirth. It can be used either by mouth, by injection into a muscle, or injection into a vein. It begins working within 15 minutes when taken by mouth and is faster in onset when used by injection. Effects last between 45 and 180 minutes.

Nordazepam is a 1,4-benzodiazepine derivative. Like other benzodiazepine derivatives, it has amnesic, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. However, it is used primarily in the treatment of anxiety disorders. It is an active metabolite of diazepam, chlordiazepoxide, clorazepate, prazepam, pinazepam, and medazepam.

Emylcamate is an anxiolytic and muscle relaxant. It was patented in the US in 1961 and advertised for the treatment of anxiety and tension. It was claimed to be superior to meprobamate, which would eventually replace emylcamate.

Droperidol is an antidopaminergic drug used as an antiemetic and as an antipsychotic. Droperidol is also often used as a rapid sedative in intensive-care treatment, and where "agitation aggression or violent behavior" are present.

Biperiden, sold under the brand name Akineton among others, is a medication used to treat Parkinson disease, certain drug-induced movement disorders and Tourette Syndrome. It is not recommended for tardive dyskinesias. It is taken by mouth, injection into a vein, or muscle.

Loprazolam (triazulenone) marketed under many brand names is a benzodiazepine medication. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is licensed and marketed for the short-term treatment of moderately-severe insomnia.

Camazepam is a benzodiazepine psychoactive drug, marketed under the brand names Albego, Limpidon and Paxor. It is the dimethyl carbamate ester of temazepam, a metabolite of diazepam. While it possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, skeletal muscle relaxant and hypnotic properties it differs from other benzodiazepines in that its anxiolytic properties are particularly prominent but has comparatively limited anticonvulsant, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.

Ethyl loflazepate is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. In animal studies it was found to have low toxicity, although in rats evidence of pulmonary phospholipidosis occurred with pulmonary foam cells developing with long-term use of very high doses. Its elimination half-life is 51–103 hours. Its mechanism of action is similar to other benzodiazepines. Ethyl loflazepate also produces an active metabolite which is stronger than the parent compound. Ethyl loflazepate was designed to be a prodrug for descarboxyloflazepate, its active metabolite. It is the active metabolite which is responsible for most of the pharmacological effects rather than ethyl loflazepate. The main metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are descarbethoxyloflazepate, loflazepate and 3-hydroxydescarbethoxyloflazepate. Accumulation of the active metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are not affected by those with kidney failure or impairment. The symptoms of an overdose of ethyl loflazepate include sleepiness, agitation and ataxia. Hypotonia may also occur in severe cases. These symptoms occur much more frequently and severely in children. Death from therapeutic maintenance doses of ethyl loflazepate taken for 2 – 3 weeks has been reported in 3 elderly patients. The cause of death was asphyxia due to benzodiazepine toxicity. High doses of the antidepressant fluvoxamine may potentiate the adverse effects of ethyl loflazepate.
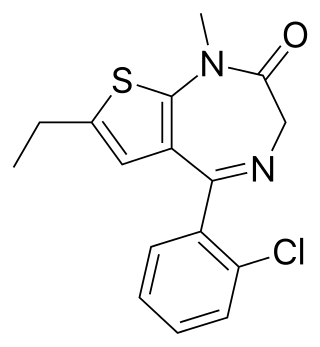
Clotiazepam is a thienodiazepine drug which is a benzodiazepine analog. The clotiazepam molecule differs from benzodiazepines in that the benzene ring has been replaced by a thiophene ring. It possesses anxiolytic, skeletal muscle relaxant, anticonvulsant, sedative properties. Stage 2 NREM sleep is significantly increased by clotiazepam.

Chlordiazepoxide, trade name Librium among others, is a sedative and hypnotic medication of the benzodiazepine class; it is used to treat anxiety, insomnia and symptoms of withdrawal from alcohol, benzodiazepines, and other drugs.

Norethandrolone, sold under the brand names Nilevar and Pronabol among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which has been used to promote muscle growth and to treat severe burns, physical trauma, and aplastic anemia but has mostly been discontinued. It is still available for use in France however. It is taken by mouth.

Zuclopenthixol, also known as zuclopentixol, is a medication used to treat schizophrenia and other psychoses. It is classed, pharmacologically, as a typical antipsychotic. Chemically it is a thioxanthene. It is the cis-isomer of clopenthixol. Clopenthixol was introduced in 1961, while zuclopenthixol was introduced in 1978.

Delorazepam, also known by the synonyms chlordesmethyldiazepam and nordiclazepam, is a drug which is a benzodiazepine and a derivative of desmethyldiazepam. It is marketed in Italy, where it is available under the trade name EN and Dadumir. Delorazepam (chlordesmethyldiazepam) is also an active metabolite of the benzodiazepine drugs diclazepam and cloxazolam. Adverse effects may include hangover type effects, drowsiness, behavioural impairments and short-term memory impairments. Similar to other benzodiazepines delorazepam has anxiolytic, skeletal muscle relaxant, hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties.

Benactyzine is an anticholinergic drug that was used in the treatment of clinical depression and anxiety disorders before it was pulled from the U.S. market by the FDA due to serious side effects.
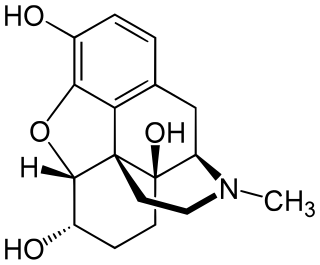
Hydromorphinol, is an opiate analogue that is a derivative of morphine, where the 14-position has been hydroxylated and the 7,8- double bond saturated. It has similar effects to morphine such as sedation, analgesia and respiratory depression, but is twice as potent as morphine and has a steeper dose-response curve and longer half-life. It is used in medicine as the bitartrate salt and hydrochloride

Clonazolam is a drug of the triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) class, which are benzodiazepines (BZDs) fused with a triazole ring. Although little research has been done about its effects and metabolism, it is sold online as a designer drug.
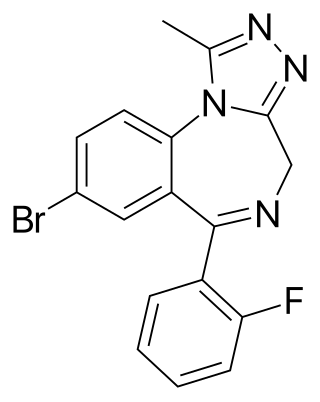
Flubromazolam (JYI-73) is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD), which are benzodiazepine (BZD) derivatives. Flubromazolam is reputed to be highly potent, and concerns have been raised that clonazolam and flubromazolam in particular may pose comparatively higher risks than other designer benzodiazepines, due to their ability to produce strong sedation and amnesia at oral doses of as little as 0.5 mg. Life-threatening adverse reactions have been observed at doses of only 3 mg of flubromazolam.