A United States Adopted Name (USAN) is a unique nonproprietary name assigned to a medication marketed in the United States. Each name is assigned by the USAN Council, which is co-sponsored by the American Medical Association (AMA), the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA).
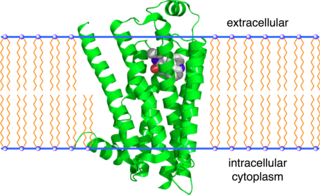
The beta-2 adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRB2, is a cell membrane-spanning beta-adrenergic receptor that binds epinephrine (adrenaline), a hormone and neurotransmitter whose signaling, via adenylate cyclase stimulation through trimeric Gs proteins, increases cAMP, and, via downstream L-type calcium channel interaction, mediates physiologic responses such as smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation.
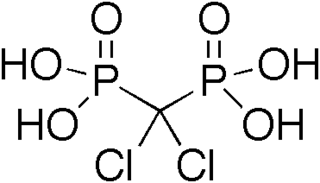
Clodronic acid (INN) or clodronate disodium (Na2CH2Cl2O6P2) (USAN) is a first generation (non-nitrogenous) bisphosphonate. It is an anti-osteoporotic drug approved for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in post-menopausal women and men to reduce vertebral fractures, hyperparathyroidism, hypercalcemia in malignancy, multiple myeloma and fracture related pain because of its anti-inflammatory effects shown as a reduction in inflammatory markers like IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α.

Dimethyltubocurarinium chloride is a non-depolarizing nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist used as a muscle relaxant.

Minaprine is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressant drug that was used in France for the treatment of depression until it was withdrawn from the market in 1996 because it caused convulsions.

Procaterol is an intermediate-acting β2 adrenoreceptor agonist used for the treatment of asthma. It has never been filed for FDA evaluation in the United States, where it is not marketed. The drug is readily oxidized in the presence of moisture and air, making it unsuitable for therapeutic use by inhalation. Pharmaceutical company Parke-Davis/Warner-Lambert researched a stabilizer to prevent oxidation, but an effective one was never developed.

Tigilanol tiglate, sold under the brand name Stelfonta is a medication used to treat dogs with non-metastatic, skin-based (cutaneous) mast cell tumors (MCTs). The FDA is also approving Stelfonta to treat non-metastatic MCTs located under the dog's skin (subcutaneous), in particular areas of a dog's leg. Stelfonta is injected directly into the MCT. Stelfonta works by activating a protein that spreads throughout the treated tumor, which disintegrates tumor cells.
Intetumumab is a human monoclonal antibody targeting integrins that was being studied for the treatment of solid tumors.

Nalmexone is a semisynthetic, opioid partial agonist or mixed agonist-antagonist with both analgesic and narcotic antagonist properties that was never marketed. In clinical studies it was found to have comparable analgesic efficacy to morphine, though with several-fold reduced potency. In addition, nalmexone's side effects, the most common of which were sleepiness and sweating, were reported to be similar to those of morphine, albeit with a noticeably higher degree of incidence.
Drug nomenclature is the systematic naming of drugs, especially pharmaceutical drugs. In the majority of circumstances, drugs have 3 types of names: chemical names, the most important of which is the IUPAC name; generic or nonproprietary names, the most important of which are international nonproprietary names (INNs); and trade names, which are brand names. Under the INN system, generic names for drugs are constructed out of affixes and stems that classify the drugs into useful categories while keeping related names distinguishable. A marketed drug might also have a company code or compound code.

Tofogliflozin is an experimental drug for the treatment of diabetes mellitus and is being developed by Chugai Pharma in collaboration with Kowa and Sanofi. It is an inhibitor of subtype 2 sodium-glucose transport protein (SGLT2), which is responsible for at least 90% of the glucose reabsorption in the kidney. As of September 2012, the drug is in Phase III clinical trials.
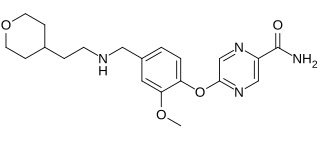
Bevenopran is a peripherally acting μ-opioid receptor antagonist that also acts on δ-opioid receptors and was under development by Cubist Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of chronic opioid-induced constipation. It reached phase III clinical trials for this indication before being discontinued.

Tigestol, also known as 17α-ethynylestr-5(10)-en-17β-ol, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group that was developed by Organon in the 1960s but was never marketed. It is an isomer of the related 19-nortestosterone derivative progestins lynestrenol and cingestol.

Segesterone, also known as 17α-hydroxy-16-methylene-19-norprogesterone or as 17α-deacetylnestorone, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-norprogesterone group that was never marketed. An acetate ester, segesterone acetate, better known as nestorone or elcometrine, is marketed for clinical use. Segesterone acetate produces segesterone as a metabolite.

Taleranol, or teranol, also known as β-zearalanol, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the resorcylic acid lactone group related to mycoestrogens found in Fusarium spp which was never marketed. It is the β epimer of zeranol (α-zearalanol) and is a major metabolite of zeranol but with less biological activity.

Stercuronium iodide is an aminosteroid neuromuscular blocking agent which was never marketed. It acts as a competitive antagonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), and is also reported to be an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.













