
Zopiclone, sold under the brand name Imovane among others, is a nonbenzodiazepine used to treat difficulty sleeping. Zopiclone is molecularly distinct from benzodiazepine drugs and is classed as a cyclopyrrolone. However, zopiclone increases the normal transmission of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the central nervous system, via modulating GABAA receptors similarly to the way benzodiazepine drugs do.

Nitrazepam, sold under the brand name Mogadon among others, is a hypnotic drug of the benzodiazepine class used for short-term relief from severe, disabling anxiety and insomnia. It also has sedative (calming) properties, as well as amnestic, anticonvulsant, and skeletal muscle relaxant effects.

Nonbenzodiazepines, sometimes referred to colloquially as Z-drugs, are a class of psychoactive, depressant, sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic drugs that are benzodiazepine-like in uses, such as for treating insomnia and anxiety.
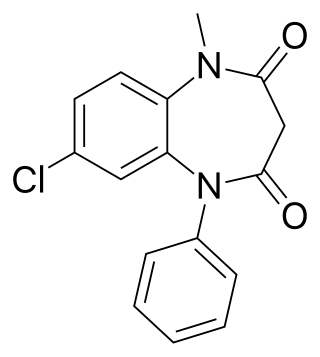
Clobazam, sold under the brand names Frisium, Onfi and others, is a benzodiazepine class medication that was patented in 1968. Clobazam was first synthesized in 1966 and first published in 1969. Clobazam was originally marketed as an anxioselective anxiolytic since 1970, and an anticonvulsant since 1984. The primary drug-development goal was to provide greater anxiolytic, anti-obsessive efficacy with fewer benzodiazepine-related side effects.

Quazepam, sold under brand name Doral among others, is a relatively long-acting benzodiazepine derivative drug developed by the Schering Corporation in the 1970s. Quazepam is used for the treatment of insomnia including sleep induction and sleep maintenance. Quazepam induces impairment of motor function and has relatively selective hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties with considerably less overdose potential than other benzodiazepines. Quazepam is an effective hypnotic which induces and maintains sleep without disruption of the sleep architecture.

Nordazepam is a 1,4-benzodiazepine derivative. Like other benzodiazepine derivatives, it has amnesic, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. However, it is used primarily in the treatment of anxiety disorders. It is an active metabolite of diazepam, chlordiazepoxide, clorazepate, prazepam, pinazepam, and medazepam.

Alpidem, sold under the brand name Ananxyl, is a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic medication which was briefly used to treat anxiety disorders but is no longer marketed. It was previously marketed in France, but was discontinued due to liver toxicity. Alpidem is taken by mouth.
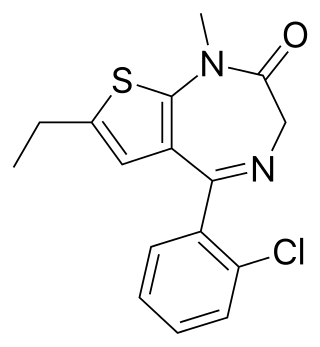
Clotiazepam is a thienodiazepine drug which is a benzodiazepine analog. The clotiazepam molecule differs from benzodiazepines in that the benzene ring has been replaced by a thiophene ring. It possesses anxiolytic, skeletal muscle relaxant, anticonvulsant, sedative properties. Stage 2 NREM sleep is significantly increased by clotiazepam.
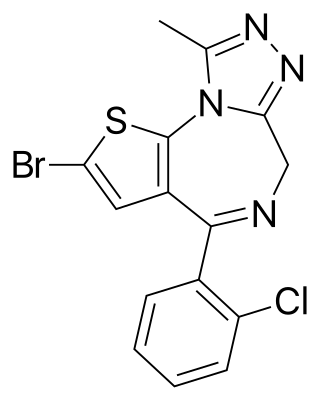
Brotizolam is a sedative-hypnotic thienotriazolodiazepine drug which is a benzodiazepine analog. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties, and is considered to be similar in effect to other short-acting hypnotic benzodiazepines such as triazolam or midazolam. It is used in the short-term treatment of severe insomnia. Brotizolam is a highly potent and short-acting hypnotic, with a typical dose ranging from 0.125 to 0.25 milligrams, which is rapidly eliminated with an average half-life of 4.4 hours.

Bretazenil (Ro16-6028) is an imidazopyrrolobenzodiazepine anxiolytic drug which is derived from the benzodiazepine family, and was invented in 1988. It is most closely related in structure to the GABA antagonist flumazenil, although its effects are somewhat different. It is classified as a high-potency benzodiazepine due to its high affinity binding to benzodiazepine binding sites where it acts as a partial agonist. Its profile as a partial agonist and preclinical trial data suggests that it may have a reduced adverse effect profile. In particular bretazenil has been proposed to cause a less strong development of tolerance and withdrawal syndrome. Bretazenil differs from traditional 1,4-benzodiazepines by being a partial agonist and because it binds to α1, α2, α3, α4, α5 and α6 subunit containing GABAA receptor benzodiazepine receptor complexes. 1,4-benzodiazepines bind only to α1, α2, α3 and α5GABAA benzodiazepine receptor complexes.

Benzoctamine is a drug that possesses sedative and anxiolytic properties. Marketed as Tacitin by Ciba-Geigy, it is different from most sedative drugs because in most clinical trials it does not produce respiratory depression, but actually stimulates the respiratory system. As a result, when compared to other sedative and anxiolytic drugs such as benzodiazepines like diazepam, it is a safer form of tranquilizing. However, when co-administered with other drugs that cause respiratory depression, like morphine, it can cause increased respiratory depression.

Pazinaclone (DN-2327) is a sedative and anxiolytic drug in the cyclopyrrolone family of drugs. Some other cyclopyrrolone drugs include zopiclone and eszopiclone.

QH-II-66 (QH-ii-066) is a sedative drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It produces some of the same effects as other benzodiazepines, but is much more selective than most other drugs of this class and so produces somewhat less sedation and ataxia than other related drugs such as diazepam and triazolam, although it still retains anticonvulsant effects.

Fosazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative; it is a water soluble derivative of diazepam. It has sedative and anxiolytic effects, and is a derivative of diazepam which has been substituted with a dimethylphosphoryl group to improve solubility in water.

Abecarnil (ZK-112,119) is an anxiolytic drug from the β-Carboline family. It is one of a relatively recently developed class of medicines known as the nonbenzodiazepines, which have similar effects to the older benzodiazepine group, but with quite different chemical structures. It is a partial agonist acting selectively at the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor.
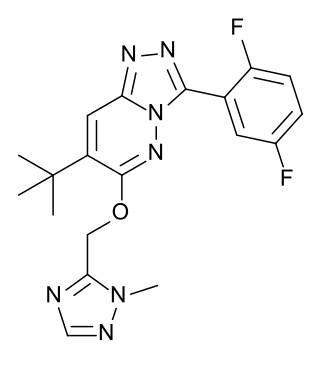
L-838,417 is an anxiolytic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic. The compound was developed by Merck, Sharp and Dohme.

Y-23684 is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic.

Premazepam is a Pyrrolodiazepine class of drug. It is a partial agonist of benzodiazepine receptors and was shown in 1984 to possess both anxiolytic and sedative properties in humans but was never marketed.

ELB-139 (LS-191,811) is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic.

TPA-023 (MK-0777) is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic. It is a mixed, subtype-selective ligand of the benzodiazepine site of α1, α2, α3, and α5-containing GABAA receptors, where it acts as a partial agonist at benzodiazepine sites of the α2 and α3-containing subtypes, but as a silent antagonist at α1 and α5-containing subtypes. It has primarily anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects in animal tests, but with no sedative effects even at 50 times the effective anxiolytic dose.




















