
Temazepam, sold under the brand name Restoril among others, is a medication of the benzodiazepine class which is generally used to treat severe or debilitating insomnia. It is taken by mouth. Temazepam is rapidly absorbed, and significant hypnotic and anxiolytic effects begin in less than 30 minutes and can last for up to eight hours. Prescriptions for hypnotics such as temazepam have seen a dramatic decrease since 2010, while anxiolytics such as alprazolam, clonazepam, and lorazepam have increased or remained stable. Temazepam and similar hypnotics, such as triazolam (Halcion) are generally reserved for severe and debilitating insomnia. They have largely been replaced by z-drugs and atypical antidepressants as first line treatment for insomnia.
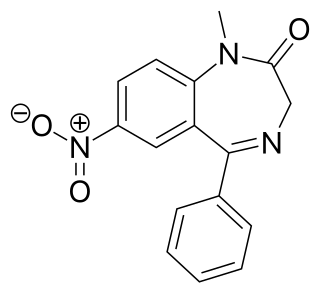
Nimetazepam is an intermediate-acting hypnotic drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It was first synthesized by a team at Hoffmann-La Roche in 1964. It possesses powerful hypnotic, anxiolytic, sedative, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Nimetazepam is also a particularly potent anticonvulsant. It is marketed in 5 mg tablets known as Erimin, which is the brand name manufactured and marketed by the large Japanese corporation Sumitomo. Japan is the sole manufacturer of nimetazepam in the world. Outside of Japan, Erimin is available in much of East and Southeast Asia and was widely prescribed for the short-term treatment of severe insomnia in patients who have difficulty falling asleep or maintaining sleep. Sumitomo has ceased manufacturing Erimin since November 2015. It is still available as a generic drug or as Lavol.

Camazepam is a benzodiazepine psychoactive drug, marketed under the brand names Albego, Limpidon and Paxor. It is the dimethyl carbamate ester of temazepam, a metabolite of diazepam. While it possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, skeletal muscle relaxant and hypnotic properties it differs from other benzodiazepines in that its anxiolytic properties are particularly prominent but has comparatively limited anticonvulsant, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.

Etizolam is a thienodiazepine derivative which is a benzodiazepine analog. The etizolam molecule differs from a benzodiazepine in that the benzene ring has been replaced by a thiophene ring and triazole ring has been fused, making the drug a thienotriazolodiazepine.
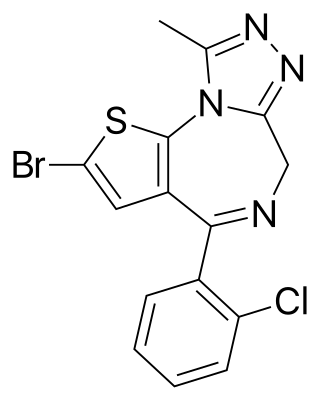
Brotizolam is a sedative-hypnotic thienotriazolodiazepine drug which is a benzodiazepine analog. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties, and is considered to be similar in effect to other short-acting hypnotic benzodiazepines such as triazolam or midazolam. It is used in the short-term treatment of severe insomnia. Brotizolam is a highly potent and short-acting hypnotic, with a typical dose ranging from 0.125 to 0.25 milligrams, which is rapidly eliminated with an average half-life of 4.4 hours.

Zapizolam is a pyridodiazepine drug, which is a benzodiazepine analog of pyridotriazolodiazepine group. It has sedative and anxiolytic effects similar to those produced by benzodiazepine derivatives, and has been sold illicitly as a designer drug.

Menitrazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It is similar in structure to tetrazepam and nimetazepam, with the 7-chloro group of tetrazepam replaced by nitro. It is a hypnotic agent used in the treatment of insomnia, and therefore has strong sedative, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, and anxiolytic actions like those of other hypnotic benzodiazepines. Menitrazepam is a good oral hypnotic agent, however, delay in the time for peak plasma levels to reach their maximum brings into question the benefit of menitrazepam for the treatment of insomnia when compared to other hypnotics. Typically, the sleep inducing properties of hypnotics occur within 0.5 hours. In some cases, as with temazepam and nitrazepam, strong hypnotic effects can be felt 15 to 20 minutes after oral ingestion.

Meclonazepam ((S)-3-methylclonazepam) was discovered by a team at Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1970s and is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative similar in structure to clonazepam. It has sedative and anxiolytic actions like those of other benzodiazepines, and also has anti-parasitic effects against the parasitic worm Schistosoma mansoni.
Benzodiazepine use disorder (BUD), also called misuse or abuse, is the use of benzodiazepines without a prescription and/or for recreational purposes, which poses risks of dependence, withdrawal and other long-term effects. Benzodiazepines are one of the more common prescription drugs used recreationally. When used recreationally benzodiazepines are usually administered orally but sometimes they are taken intranasally or intravenously. Recreational use produces effects similar to alcohol intoxication.

Pyrazolam (SH-I-04) is a benzodiazepine derivative originally developed by a team led by Leo Sternbach at Hoffman-La Roche in the 1970s. It has since been "rediscovered" and sold as a designer drug since 2012.

Diclazepam (Ro5-3448), also known as chlorodiazepam and 2'-chloro-diazepam, is a benzodiazepine and functional analog of diazepam. It was first synthesized by Leo Sternbach and his team at Hoffman-La Roche in 1960. It is not currently approved for use as a medication, but rather sold as an unscheduled substance. Efficacy and safety have not been tested in humans.

Flubromazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative which was first synthesized in 1960, but was never marketed and did not receive any further attention or study until late 2012 when it appeared on the grey market as a novel designer drug.

3-Hydroxyphenazepam is a benzodiazepine with hypnotic, sedative, anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant properties. It is an active metabolite of phenazepam, as well as the active metabolite of the benzodiazepine prodrug cinazepam. Relative to phenazepam, 3-hydroxyphenazepam has diminished myorelaxant properties, but is about equivalent in most other regards. Like other benzodiazepines, 3-hydroxyphenazepam behaves as a positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor with an EC50 value of 10.3 nM. It has been sold as a designer drug.
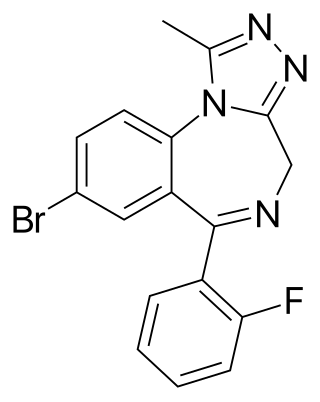
Flubromazolam (JYI-73) is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD), which are benzodiazepine (BZD) derivatives. Flubromazolam is reputed to be highly potent, and concerns have been raised that clonazolam and flubromazolam in particular may pose comparatively higher risks than other designer benzodiazepines, due to their ability to produce strong sedation and amnesia at oral doses of as little as 0.5 mg. Life-threatening adverse reactions have been observed at doses of only 3 mg of flubromazolam.
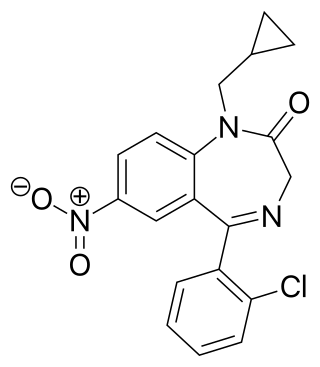
Cloniprazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative and a prodrug of clonazepam, 7-aminoclonazepam, and other metabolites.

Flualprazolam is a tranquilizer of the triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) class, which are benzodiazepines (BZDs) fused with a triazole ring. It was first synthesised in 1976, but was never marketed. It can be seen as the triazolo version of fludiazepam. It has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, first being definitively identified as such in Sweden in 2018. It can be described as the 2'-fluoro derivative of alprazolam or the fluoro instead of chloro analogue of triazolam, and has similar sedative and anxiolytic effects.

Difludiazepam (Ro07-4065) is a benzodiazepine derivative which is the 2',6'-difluoro derivative of fludiazepam. It was invented in the 1970s but was never marketed, and has been used as a research tool to help determine the shape and function of the GABAA receptors, at which it has an IC50 of 4.1nM. Difludiazepam has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, and was first notified to the EMCDDA by Swedish authorities in 2017.

Fluclotizolam is a thienotriazolodiazepine derivative which was first synthesised in 1979, but was never marketed. It has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, first being definitively identified in 2017.

Phenazolam, is a benzodiazepine derivative which acts as a potent sedative and hypnotic drug. It was first invented in the early 1980s, but was never developed for medical use. It has been sold over the internet as a designer drug, first being identified in seized samples by a laboratory in Sweden in March 2016.



















