
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body.

Single-photon emission computed tomography is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera, but is able to provide true 3D information. This information is typically presented as cross-sectional slices through the patient, but can be freely reformatted or manipulated as required.

The GABA receptors are a class of receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the chief inhibitory compound in the mature vertebrate central nervous system. There are two classes of GABA receptors: GABAA and GABAB. GABAA receptors are ligand-gated ion channels ; whereas GABAB receptors are G protein-coupled receptors, also called metabotropic receptors.

The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Accurate regulation of GABAergic transmission through appropriate developmental processes, specificity to neural cell types, and responsiveness to activity is crucial for the proper functioning of nearly all aspects of the central nervous system (CNS). Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to chloride ions (Cl−) and, to a lesser extent, bicarbonate ions (HCO3−).

Alpidem, sold under the brand name Ananxyl, is a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic medication which was briefly used to treat anxiety disorders but is no longer marketed. It was previously marketed in France, but was discontinued due to liver toxicity. Alpidem is taken by mouth.

Bretazenil (Ro16-6028) is an imidazopyrrolobenzodiazepine anxiolytic drug which is derived from the benzodiazepine family, and was invented in 1988. It is most closely related in structure to the GABA antagonist flumazenil, although its effects are somewhat different. It is classified as a high-potency benzodiazepine due to its high affinity binding to benzodiazepine binding sites where it acts as a partial agonist. Its profile as a partial agonist and preclinical trial data suggests that it may have a reduced adverse effect profile. In particular bretazenil has been proposed to cause a less strong development of tolerance and withdrawal syndrome. Bretazenil differs from traditional 1,4-benzodiazepines by being a partial agonist and because it binds to α1, α2, α3, α4, α5 and α6 subunit containing GABAA receptor benzodiazepine receptor complexes. 1,4-benzodiazepines bind only to α1, α2, α3 and α5GABAA benzodiazepine receptor complexes.

Pagoclone is an anxiolytic agent from the cyclopyrrolone family, related to better-known drugs such as the sleeping medication zopiclone. It was synthesized by a French team working for Rhone-Poulenc & Rorer S.A. Pagoclone belongs to the class of nonbenzodiazepines, which have similar effects to the older benzodiazepine group, but with quite different chemical structures. It was never commercialised.

Gaboxadol, also known as 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo(5,4-c)pyridin-3-ol (THIP), is a conformationally constrained derivative of the alkaloid muscimol that was first synthesized in 1977 by the Danish chemist Poul Krogsgaard-Larsen. In the early 1980s gaboxadol was the subject of a series of pilot studies that tested its efficacy as an analgesic and anxiolytic, as well as a treatment for tardive dyskinesia, Huntington's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and spasticity. It was not until 1996 that researchers attempted to harness gaboxadol's frequently reported sedative "adverse effect" for the treatment of insomnia, resulting in a series of clinical trials sponsored by Lundbeck and Merck. In March, 2007, Merck and Lundbeck cancelled work on the drug, citing safety concerns and the failure of an efficacy trial. It acts on the GABA system, but in a different way from benzodiazepines, Z-Drugs, and barbiturates. Lundbeck states that gaboxadol also increases deep sleep. Unlike benzodiazepines, gaboxadol does not demonstrate reinforcement in mice or baboons despite activation of dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area.
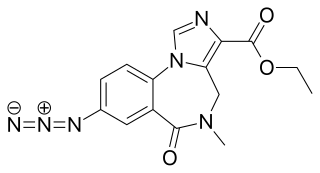
Ro15-4513(IUPAC: Ethyl-8-azido-5,6-dihydro-5-methyl-6-oxo-4H-imidazo-1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylate) is a weak partial inverse agonist of the benzodiazepine class of drugs, developed by Hoffmann–La Roche in the 1980s. It acts as an inverse agonist, and can therefore be an antidote to the acute impairment caused by alcohols, including ethanol, isopropanol, tert-butyl alcohol, tert-amyl alcohol, 3-methyl-3-pentanol, methylpentynol and ethchlorvynol.

RTI(-4229)-55, also called RTI-55 or iometopane, is a phenyltropane-based psychostimulant used in scientific research and in some medical applications. This drug was first cited in 1991. RTI-55 is a non-selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor derived from methylecgonidine. However, more selective analogs are derived by conversion to "pyrrolidinoamido" RTI-229, for instance. Due to the large bulbous nature of the weakly electron withdrawing iodo halogen atom, RTI-55 is the most strongly serotonergic of the simple para-substituted troparil based analogs. In rodents RTI-55 actually caused death at a dosage of 100 mg/kg, whereas RTI-51 and RTI-31 did not. Another notable observation is the strong propensity of RTI-55 to cause locomotor activity enhancements, although in an earlier study, RTI-51 was actually even stronger than RTI-55 in shifting baseline LMA. This observation serves to highlight the disparities that can arise between studies.

Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5, also known as GABRA5, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the GABRA5 gene.

Altanserin is a compound that binds to the 5-HT2A receptor. Labeled with the isotope fluorine-18 it is used as a radioligand in positron emission tomography (PET) studies of the brain, i.e., studies of the 5-HT2A neuroreceptors. Besides human neuroimaging studies altanserin has also been used in the study of rats.

DASB, also known as 3-amino-4-(2-dimethylaminomethylphenylsulfanyl)-benzonitrile, is a compound that binds to the serotonin transporter. Labeled with carbon-11 — a radioactive isotope — it has been used as a radioligand in neuroimaging with positron emission tomography (PET) since around year 2000. In this context it is regarded as one of the superior radioligands for PET study of the serotonin transporter in the brain, since it has high selectivity for the serotonin transporter.

5-I-R91150 is a compound that acts as a potent and selective antagonist of 5-HT2A receptors. Its main application is as its iodine-123 radiolabeled form, in which it can be used in SPECT scanning in human neuroimaging studies, to examine the distribution of the 5-HT2A receptor subtype in the brain, e.g. with respect to sex and age and in adults with Asperger syndrome or Alzheimer's disease.

L-655,708 (FG-8094) is a nootropic drug invented in 1996 by a team working for Merck, Sharp and Dohme, that was the first compound developed which acts as a subtype-selective inverse agonist at the α5 subtype of the benzodiazepine binding site on the GABAA receptor. It acts as an inverse agonist at the α1, α2, α3 and α5 subtypes, but with much higher affinity for α5, and unlike newer α5 inverse agonists such as α5IA, L-655,708 exerts its subtype selectivity purely via higher binding affinity for this receptor subtype, with its efficacy as an inverse agonist being around the same at all the subtypes it binds to.
Anissa Abi-Dargham is an American psychiatrist and researcher. She is a psychiatry professor and vice-chair of research at Stony Brook University and professor emerita at the Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons.

Iofetamine, brand names Perfusamine, SPECTamine), or N-isopropyl-(123I)-p-iodoamphetamine (IMP), is a lipid-soluble amine and radiopharmaceutical drug used in cerebral blood perfusion imaging with single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). Labeled with the radioactive isotope iodine-123, it is approved for use in the United States as a diagnostic aid in determining the localization of and in the evaluation of non-lacunar stroke and complex partial seizures, as well as in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.

In pharmacology, GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators, also known as GABAkines or GABAA receptor potentiators, are positive allosteric modulator (PAM) molecules that increase the activity of the GABAA receptor protein in the vertebrate central nervous system.

Basmisanil is a highly selective inverse agonist/negative allosteric modulator of α5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors which is under development by Roche for the treatment of cognitive impairment associated with Down syndrome. As of June 2016, it is no longer studied. It is studied with schizophrenia patients.
A GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulator is a negative allosteric modulator (NAM), or inhibitor, of the GABAA receptor, a ligand-gated ion channel of the major inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). They are closely related and similar to GABAA receptor antagonists. The effects of GABAA receptor NAMs are functionally the opposite of those of GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) like the benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and ethanol (alcohol). Non-selective GABAA receptor NAMs can produce a variety of effects including convulsions, neurotoxicity, and anxiety, among others.


















