Related Research Articles
Radionuclide therapy uses radioactive substances called radiopharmaceuticals to treat medical conditions, particularly cancer. These are introduced into the body by various means and localise to specific locations, organs or tissues depending on their properties and administration routes. This includes anything from a simple compound such as sodium iodide that locates to the thyroid via trapping the iodide ion, to complex biopharmaceuticals such as recombinant antibodies which are attached to radionuclides and seek out specific antigens on cell surfaces.
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a synthetic derivative of a natural compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide. By virtue of its radioactive decay, it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tracing the path that the radioisotope follows from reactants to products. Radiolabeling or radiotracing is thus the radioactive form of isotopic labeling. In biological contexts, experiments that use radioisotope tracers are sometimes called radioisotope feeding experiments.
ATC code A01Stomatological preparations is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup A01 is part of the anatomical group A Alimentary tract and metabolism.
ATC code B01Antithrombotic agents is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup B01 is part of the anatomical group B Blood and blood forming organs.
ATC code B05Blood substitutes and perfusion solutions is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup B05 is part of the anatomical group B Blood and blood forming organs.
ATC code D08Antiseptics and disinfectants is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup D08 is part of the anatomical group D Dermatologicals.
ATC code N01Anesthetics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup N01 is part of the anatomical group N Nervous system.
ATC code R05Cough and cold preparations is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup R05 is part of the anatomical group R Respiratory system.
ATC code S01Ophthalmologicals is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup S01 is part of the anatomical group S Sensory organs.
ATC code V10Therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup V10 is part of the anatomical group V Various.

Scintigraphy, also known as a gamma scan, is a diagnostic test in nuclear medicine, where radioisotopes attached to drugs that travel to a specific organ or tissue (radiopharmaceuticals) are taken internally and the emitted gamma radiation is captured by gamma cameras, which are external detectors that form two-dimensional images in a process similar to the capture of x-ray images. In contrast, SPECT and positron emission tomography (PET) form 3-dimensional images and are therefore classified as separate techniques from scintigraphy, although they also use gamma cameras to detect internal radiation. Scintigraphy is unlike a diagnostic X-ray where external radiation is passed through the body to form an image.
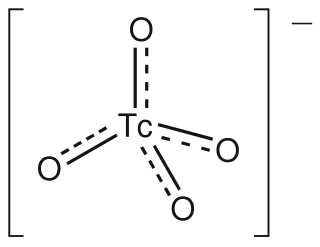
The pertechnetate ion is an oxyanion with the chemical formula TcO−
4. It is often used as a convenient water-soluble source of isotopes of the radioactive element technetium (Tc). In particular it is used to carry the 99mTc isotope which is commonly used in nuclear medicine in several nuclear scanning procedures.

There are 37 known isotopes of iodine (53I) from 108I to 144I; all undergo radioactive decay except 127I, which is stable. Iodine is thus a monoisotopic element.
Iodine-125 (125I) is a radioisotope of iodine which has uses in biological assays, nuclear medicine imaging and in radiation therapy as brachytherapy to treat a number of conditions, including prostate cancer, uveal melanomas, and brain tumors. It is the second longest-lived radioisotope of iodine, after iodine-129.
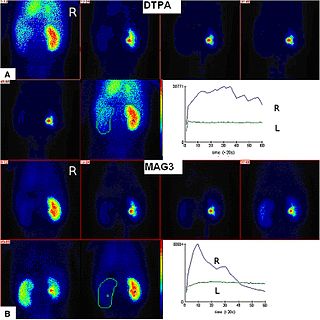
Radioisotope renography is a form of medical imaging of the kidneys that uses radiolabelling. A renogram, which may also be known as a MAG3 scan, allows a nuclear medicine physician or a radiologist to visualize the kidneys and learn more about how they are functioning. MAG3 is an acronym for mercapto acetyl tri glycine, a compound that is chelated with a radioactive element – technetium-99m.
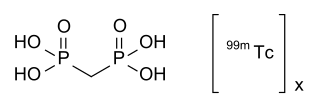
Technetium (99mTc) medronic acid is a pharmaceutical product used in nuclear medicine to localize bone metastases as well as other diseases that can alter the natural turn-over in the bone by bone scintigraphy.
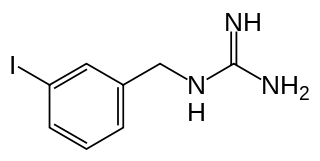
Iobenguane, or MIBG, is an aralkylguanidine analog of the adrenergic neurotransmitter norepinephrine (noradrenaline), typically used as a radiopharmaceutical. It acts as a blocking agent for adrenergic neurons. When radiolabeled, it can be used in nuclear medicinal diagnostic and therapy techniques as well as in neuroendocrine chemotherapy treatments.

An octreotide scan is a type of SPECT scintigraphy used to find carcinoid, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, and to localize sarcoidosis. It is also called somatostatin receptor scintigraphy (SRS). Octreotide, a drug similar to somatostatin, is radiolabeled with indium-111, and is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. The radioactive octreotide attaches to tumor cells that have receptors for somatostatin. A gamma camera detects the radioactive octreotide, and makes pictures showing where the tumor cells are in the body, typically by a SPECT technique. A technetium-99m based radiopharmaceutical kit is also available.

Radiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is different from contrast media which absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound. Radiopharmacology is the branch of pharmacology that specializes in these agents.
A PSMA scan is a nuclear medicine imaging technique used in the diagnosis and staging of prostate cancer. It is carried out by injection of a radiopharmaceutical with a positron or gamma emitting radionuclide and a prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) targeting ligand. After injection, imaging of positron emitters such as gallium-68 (68Ga), copper-64 (64Cu), and fluorine-18 (18F) is carried out with a positron emission tomography (PET) scanner. For gamma emitters such as technetium-99m (99mTc) and indium-111 (111In) single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging is performed with a gamma camera.
References
- ↑ "ATC (Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System) – Synopsis". National Institutes of Health . Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ↑ World Health Organization. "Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification". World Health Organization. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ "Structure and principles". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. 15 February 2018. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ "ATC/DDD Index 2022: code V09". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology.
- ↑ "ATCvet Index 2022: code QV09". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology.