In biochemistry, a kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. This transesterification produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group. These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis.
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions.

Thymidine, also known as deoxythymidine, deoxyribosylthymine, or thymine deoxyriboside, is a pyrimidine deoxynucleoside. Deoxythymidine is the DNA nucleoside T, which pairs with deoxyadenosine (A) in double-stranded DNA. In cell biology it is used to synchronize the cells in G1/early S phase. The prefix deoxy- is often left out since there are no precursors of thymine nucleotides involved in RNA synthesis.

Thymidine kinase is an enzyme, a phosphotransferase : 2'-deoxythymidine kinase, ATP-thymidine 5'-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.21. It can be found in most living cells. It is present in two forms in mammalian cells, TK1 and TK2. Certain viruses also have genetic information for expression of viral thymidine kinases. Thymidine kinase catalyzes the reaction:
An antimetabolite is a chemical that inhibits the use of a metabolite, which is another chemical that is part of normal metabolism. Such substances are often similar in structure to the metabolite that they interfere with, such as the antifolates that interfere with the use of folic acid; thus, competitive inhibition can occur, and the presence of antimetabolites can have toxic effects on cells, such as halting cell growth and cell division, so these compounds are used as chemotherapy for cancer.
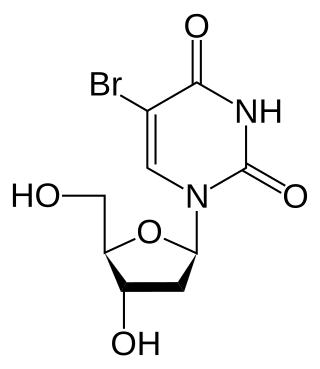
Bromodeoxyuridine is a synthetic nucleoside analogue with a chemical structure similar to thymidine. BrdU is commonly used to study cell proliferation in living tissues and has been studied as a radiosensitizer and diagnostic tool in people with cancer.

Thymidylate synthase (TS) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). Thymidine is one of the nucleotides in DNA. With inhibition of TS, an imbalance of deoxynucleotides and increased levels of dUMP arise. Both cause DNA damage.

Acute myeloblastic leukemia with maturation (M2) is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).

ETV6 protein is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the ETV6 gene. The ETV6 protein regulates the development and growth of diverse cell types, particularly those of hematological tissues. However, its gene, ETV6 frequently suffers various mutations that lead to an array of potentially lethal cancers, i.e., ETV6 is a clinically significant proto-oncogene in that it can fuse with other genes to drive the development and/or progression of certain cancers. However, ETV6 is also an anti-oncogene or tumor suppressor gene in that mutations in it that encode for a truncated and therefore inactive protein are also associated with certain types of cancers.
Cell synchronization is a process by which cells in a culture at different stages of the cell cycle are brought to the same phase. Cell synchrony is a vital process in the study of cells progressing through the cell cycle as it allows population-wide data to be collected rather than relying solely on single-cell experiments. The types of synchronization are broadly categorized into two groups; physical fractionization and chemical blockade.
Transcription factor E2F1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the E2F1 gene.
Thymidine kinase 1, soluble, is a human thymidine kinase.

TYMP is a gene that encodes for the enzyme thymidine phosphorylase. The TYMP gene is also known as ECGF1 and MNGIE due to its role in MNGIE syndrome.

Thymidine phosphorylase is an enzyme that is encoded by the TYMP gene and catalyzes the reaction:
Proliferation, as one of the hallmarks and most fundamental biological processes in tumors, is associated with tumor progression, response to therapy, and cancer patient survival. Consequently, the evaluation of a tumor proliferative index has clinical significance in characterizing many solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. This has led investigators to develop different technologies to evaluate the proliferation index in tumor samples. The most commonly used methods in evaluating a proliferative index include mitotic indexing, thymidine-labeling index, bromodeoxyuridine assay, the determination of fraction of cells in various phases of cell cycle, and the immunohistochemical evaluation of cell cycle-associated proteins.

5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) is a thymidine analogue which is incorporated into the DNA of dividing cells. EdU is used to assay DNA synthesis in cell culture and detect cells in embryonic, neonatal and adult animals which have undergone DNA synthesis. Whilst at high doses it can be cytotoxic, this molecule is now widely used to track proliferating cells in multiple biological systems.
Thymidylate kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of thymidine 5'-monophosphate (dTMP) to form thymidine 5'-diphosphate (dTDP) in the presence of ATP and magnesium:

Trifluridine/tipiracil, sold under the brand name Lonsurf, is a fixed-dose combination medication that is used as a third- or fourth-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer or gastric cancer, after chemotherapy and targeted therapeutics have failed. It is a combination of two active pharmaceutical ingredients: trifluridine, a nucleoside analog, and tipiracil, a thymidine phosphorylase inhibitor. Tipiracil prevents rapid metabolism of trifluridine, increasing the bioavailability of trifluridine.
Thymidine kinase is an enzyme, a phosphotransferase : 2'-deoxythymidine kinase, ATP-thymidine 5'-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.21 that catalyzes the reaction:

Fluorodeoxyuridylate, also known as FdUMP, 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridylate, and 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine 5'-monophosphate, is a molecule formed in vivo from 5-fluorouracil and 5-fluorodeoxyuridine.