 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | PAH, PAHA, Aminohippurate, 4-Aminohippuric acid, N-(4-Aminobenzoyl)glycine, para-Aminohippurate |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.472 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
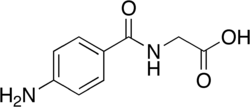
| Formula | C9H10N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 194.190 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Aminohippuric acid or para-aminohippuric acid (PAH), a derivative of hippuric acid, is a diagnostic agent useful in medical tests involving the kidney used in the measurement of renal plasma flow. It is an amide derivative of the amino acid glycine and para-aminobenzoic acid that is not naturally found in humans; it needs to be IV infused before diagnostic use.