Related Research Articles

In medicine, dialysis is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. This is referred to as renal replacement therapy.

Peritonitis is inflammation of the peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part or the entire abdomen may be tender. Complications may include shock and acute respiratory distress syndrome.

Rhabdomyolysis is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle breaks down rapidly. Symptoms may include muscle pains, weakness, vomiting, and confusion. There may be tea-colored urine or an irregular heartbeat. Some of the muscle breakdown products, such as the protein myoglobin, are harmful to the kidneys and may lead to kidney failure.

Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys are functioning at less than 15% of normal. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, high blood potassium, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anemia.

Uremia is the condition of having high levels of urea in the blood. Urea is one of the primary components of urine. It can be defined as an excess of amino acid and protein metabolism end products, such as urea and creatinine, in the blood that would be normally excreted in the urine. Uremic syndrome can be defined as the terminal clinical manifestation of kidney failure. It is the signs, symptoms and results from laboratory tests which result from inadequate excretory, regulatory and endocrine function of the kidneys. Both uremia and uremic syndrome have been used interchangeably to denote a very high plasma urea concentration that is the result of renal failure. The former denotation will be used for the rest of the article.

Hemodialysis, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply dialysis, is a process of purifying the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatinine and urea and free water from the blood when the kidneys are in a state of kidney failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapies. An alternative method for extracorporeal separation of blood components such as plasma or cells is apheresis.
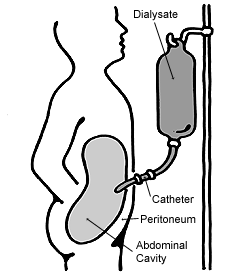
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis which uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte problems, and remove toxins in those with kidney failure. Peritoneal dialysis has better outcomes than hemodialysis during the first couple of years. Other benefits include greater flexibility and better tolerability in those with significant heart disease.

Home hemodialysis (HHD), is the provision of hemodialysis to purify the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally, in their own home.
In medicine, Kt/V is a number used to quantify hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis treatment adequacy.
The urea reduction ratio (URR), is a dimensionless number used to quantify dialysis treatment adequacy.
Standardized Kt/V, also std Kt/V, is a way of measuring (renal) dialysis adequacy. It was developed by Frank Gotch and is used in the United States to measure dialysis. Despite the name, it is quite different from Kt/V. In theory, both peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis can be quantified with std Kt/V.

Frank A. Gotch was an American physician known for his work in renal dialysis adequacy, specifically the development of Kt/V and standardized Kt/V. He was an Associate Professor of Medicine at the University of California, San Francisco.

Temocillin is a β-lactamase-resistant penicillin introduced by Beecham, marketed by Eumedica Pharmaceuticals as Negaban. It is used primarily for the treatment of multiple drug-resistant, Gram-negative bacteria.
It is a 6-methoxy penicillin; it is also a carboxypenicillin.
In nephrology, dialysis adequacy is the measurement of renal dialysis for the purpose of determining dialysis treatment regime and to better understand the pathophysiology of renal dialysis. It is an area of considerable controversy in nephrology.
Hemoperfusion or hæmoperfusion is a method of filtering the blood extracorporeally to remove a toxin. As with other extracorporeal methods, such as hemodialysis (HD), hemofiltration (HF), and hemodiafiltration (HDF), the blood travels from the patient into a machine, gets filtered, and then travels back into the patient, typically by venovenous access.

Northwest Kidney Centers is a regional, not-for-profit community-based provider of kidney dialysis, public health education, and research into the causes and treatments of chronic kidney disease. Established in Seattle in 1962, it was the world's first out-of-hospital dialysis provider. It offers dialysis throughout the greater Seattle area in 18 free-standing clinics, eight hospitals and its home dialysis program. It plans to open its first clinic in Everett in 2020.
In 1972 the United States Congress passed legislation authorizing the End Stage Renal Disease Program (ESRD) under Medicare. Section 299I of Public Law 92-603, passed on October 30, 1972, extended Medicare coverage to Americans if they had stage five chronic kidney disease (CKD) and were otherwise qualified under Medicare's work history requirements. The program's launch was July 1, 1973. Previously only those over 65 could qualify for Medicare benefits. This entitlement is nearly universal, covering over 90% of all U.S. citizens with severe CKD.
The Rogosin Institute is an independent, not-for-profit treatment and research center with facilities throughout New York City that treat patients with kidney disease, including dialysis and kidney transplantation; lipid disorders; and hypertension. It is affiliated with NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Cornell Medical College and is a leader in research programs for cancer and diabetes.
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide is a non-calcium, iron-based phosphate binder used for the control of serum phosphorus levels in adult patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on haemodialysis (HD) or peritoneal dialysis (PD). It is used in form of chewable tablets.
Qian Jiaqi, also romanized as Jia-Qi Qian, was a Chinese nephrologist and professor at Renji Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine. He was the first clinical physician to perform hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in China, and established a Kt/V value of at least 1.7 as the target for peritoneal dialysis.
References
- ^ Scribner BH, Oreopoulos DG, The Hemodialysis Product (HDP): A Better Index of Dialysis Adequacy than Kt/V, Dialysis & Transplantation, 2002 Jan;31(1):13-15. Full Text Full Text (Mirror)
- ^ Eltayeb M, Elshinawy H, Ramadan A, Abouellal H, Hemodialysis Product: A Reliable New Index for Dialysis Adequacy, Sci. Med. J., Jan. 2011; 23 (1): 73–93, ISSN 1110-5607. Full text