
Benzodiazepines, colloquially known as "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955, and was made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, which followed with the development of diazepam (Valium) three years later, in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide.

Hypnotic, or soporific drugs, commonly known as sleeping pills, are a class of psychoactive drugs whose primary function is to induce sleep and to treat insomnia (sleeplessness).

Diazepam, sold under the brand name Valium among others, is a medicine of the benzodiazepine family that acts as an anxiolytic. It is used to treat a range of conditions, including anxiety, seizures, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, muscle spasms, insomnia, and restless legs syndrome. It may also be used to cause memory loss during certain medical procedures. It can be taken orally, as a suppository inserted into the rectum, intramuscularly, intravenously or used as a nasal spray. When injected intravenously, effects begin in one to five minutes and last up to an hour. When taken by mouth, effects begin after 15 to 60 minutes.

Zopiclone, sold under the brand name Imovane among others, is a nonbenzodiazepine, specifically a cyclopyrrolone, used to treat difficulty sleeping. Zopiclone is molecularly distinct from benzodiazepine drugs and is classed as a cyclopyrrolone. However, zopiclone increases the normal transmission of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the central nervous system, via modulating GABAA receptors similarly to the way benzodiazepine drugs do inducing sedation but not with the anti-anxiety properties of the benzodiazepines.

Nitrazepam, sold under the brand name Mogadon among others, is a hypnotic drug of the benzodiazepine class used for short-term relief from severe, disabling anxiety and insomnia. It also has sedative (calming) properties, as well as amnestic, anticonvulsant, and skeletal muscle relaxant effects.

Bromazepam, sold under many brand names, is a benzodiazepine. It is mainly an anti-anxiety agent with similar side effects to diazepam. In addition to being used to treat anxiety or panic states, bromazepam may be used as a premedicant prior to minor surgery. Bromazepam typically comes in doses of 3 mg and 6 mg tablets.

Zaleplon, sold under the brand name Sonata among others, is a sedative and hypnotic which is used to treat insomnia. It is a nonbenzodiazepine or Z-drug of the pyrazolopyrimidine class. It was developed by King Pharmaceuticals and approved for medical use in the United States in 1999.

Quazepam, sold under the brand name Doral among others, is a relatively long-acting benzodiazepine derivative drug developed by the Schering Corporation in the 1970s. Quazepam is used for the treatment of insomnia, including sleep induction and sleep maintenance. Quazepam induces impairment of motor function and has relatively selective hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties with considerably less overdose potential than other benzodiazepines. Quazepam is an effective hypnotic which induces and maintains sleep without disruption of the sleep architecture.
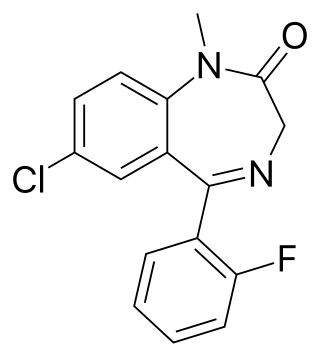
Fludiazepam, marketed under the brand name Erispan (エリスパン) is a potent benzodiazepine and 2ʹ-fluoro derivative of diazepam, originally developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1960s. It is marketed in Japan and Taiwan. It exerts its pharmacological properties via enhancement of GABAergic inhibition. Fludiazepam has 4 times more binding affinity for benzodiazepine receptors than diazepam. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Fludiazepam has been used recreationally.

Etizolam is a thienodiazepine derivative which is a benzodiazepine analog. The etizolam molecule differs from a benzodiazepine in that the benzene ring has been replaced by a thiophene ring and triazole ring has been fused, making the drug a thienotriazolodiazepine.

Bretazenil (Ro16-6028) is an imidazopyrrolobenzodiazepine anxiolytic drug which is derived from the benzodiazepine family, and was invented in 1988. It is most closely related in structure to the GABA antagonist flumazenil, although its effects are somewhat different. It is classified as a high-potency benzodiazepine due to its high affinity binding to benzodiazepine binding sites where it acts as a partial agonist. Its profile as a partial agonist and preclinical trial data suggests that it may have a reduced adverse effect profile. In particular bretazenil has been proposed to cause a less strong development of tolerance and withdrawal syndrome. Bretazenil differs from traditional 1,4-benzodiazepines by being a partial agonist and because it binds to α1, α2, α3, α4, α5 and α6 subunit containing GABAA receptor benzodiazepine receptor complexes. 1,4-benzodiazepines bind only to α1, α2, α3 and α5GABAA benzodiazepine receptor complexes.

Imidazenil is an experimental anxiolytic drug which is derived from the benzodiazepine family, and is most closely related to other imidazobenzodiazepines such as midazolam, flumazenil, and bretazenil.

Abecarnil (ZK-112,119) is an anxiolytic drug from the β-Carboline family. It is one of a relatively recently developed class of medicines known as the nonbenzodiazepines, which have similar effects to the older benzodiazepine group, but with quite different chemical structures. It is a partial agonist acting selectively at the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor.
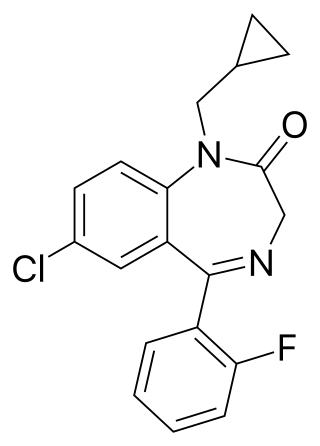
Flutoprazepam (Restas) is a drug which is a benzodiazepine. It was patented in Japan by Sumitomo in 1972 and its medical use remains mostly confined to that country. Its muscle relaxant properties are approximately equivalent to those of diazepam - however, it has more powerful sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects and is around four times more potent by weight compared to diazepam. It is longer acting than diazepam due to its long-acting active metabolites, which contribute significantly to its effects. Its principal active metabolite is n-desalkylflurazepam, also known as norflurazepam, which is also a principal metabolite of flurazepam.

Rilmazafone is a water-soluble prodrug developed in Japan. Inside the human body, rilmazafone is converted into several benzodiazepine metabolites that have sedative and hypnotic effects.

Y-23684 is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic.

ELB-139 (LS-191,811) is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic.

ZK-93426 (ethyl-5-isopropoxy-4-methyl-beta-carboline-3-carboxylate) is a drug from the beta-carboline family. It acts as a weak partial inverse agonist of benzodiazepine receptors, meaning that it causes the opposite effects to the benzodiazepine class of drugs and has anxiogenic properties, although unlike most benzodiazepine antagonists it is not a convulsant and actually has weak anticonvulsant effects. In human tests it produced alertness, restlessness and feelings of apprehension, and reversed the effect of the benzodiazepine lormetazepam. It was also shown to produce nootropic effects and increased release of acetylcholine.

JM-1232 is a sedative and hypnotic drug being researched as a potential anesthetic. It has similar effects to sedative-hypnotic benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic. It was developed by a team at Maruishi Pharmaceutica.

In pharmacology, GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators, also known as GABAkines or GABAA receptor potentiators, are positive allosteric modulator (PAM) molecules that increase the activity of the GABAA receptor protein in the vertebrate central nervous system.




















