
Diazepam, sold under the brand name Valium among others, is a medicine of the benzodiazepine family that acts as an anxiolytic. It is used to treat a range of conditions, including anxiety, seizures, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, muscle spasms, insomnia, and restless legs syndrome. It may also be used to cause memory loss during certain medical procedures. It can be taken orally, as a suppository inserted into the rectum, intramuscularly, intravenously or used as a nasal spray. When injected intravenously, effects begin in one to five minutes and last up to an hour. When taken by mouth, effects begin after 15 to 60 minutes.

Bromazepam, sold under many brand names, is a benzodiazepine. It is mainly an anti-anxiety agent with similar side effects to diazepam. In addition to being used to treat anxiety or panic states, bromazepam may be used as a premedicant prior to minor surgery. Bromazepam typically comes in doses of 3 mg and 6 mg tablets.

Quazepam, sold under the brand name Doral among others, is a relatively long-acting benzodiazepine derivative drug developed by the Schering Corporation in the 1970s. Quazepam is used for the treatment of insomnia, including sleep induction and sleep maintenance. Quazepam induces impairment of motor function and has relatively selective hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties with considerably less overdose potential than other benzodiazepines. Quazepam is an effective hypnotic which induces and maintains sleep without disruption of the sleep architecture.
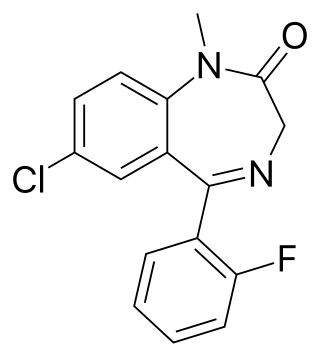
Fludiazepam, marketed under the brand name Erispan (エリスパン) is a potent benzodiazepine and 2ʹ-fluoro derivative of diazepam, originally developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1960s. It is marketed in Japan and Taiwan. It exerts its pharmacological properties via enhancement of GABAergic inhibition. Fludiazepam has 4 times more binding affinity for benzodiazepine receptors than diazepam. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Fludiazepam has been used recreationally.

Imidazenil is an experimental anxiolytic drug which is derived from the benzodiazepine family, and is most closely related to other imidazobenzodiazepines such as midazolam, flumazenil, and bretazenil.

QH-II-66 (QH-ii-066) is a sedative drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It produces some of the same effects as other benzodiazepines, but is much more selective than most other drugs of this class and so produces somewhat less sedation and ataxia than other related drugs such as diazepam and triazolam, although it still retains anticonvulsant effects.

CL-218,872 is a sedative and hypnotic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to sedative-hypnotic benzodiazepine drugs such as triazolam, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic.
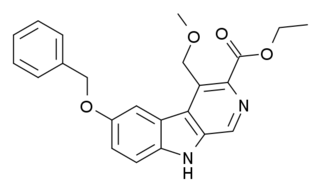
ZK-93423 is an anxiolytic drug from the β-Carboline family, closely related to abecarnil. It is a nonbenzodiazepine GABAA agonist which is not subtype selective and stimulates α1, α2, α3, and α5-subunit containing GABAA receptors equally. It has anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant and appetite stimulating properties comparable to benzodiazepine drugs. ZK-93423 has also been used as a base to develop new and improved beta-carboline derivatives and help map the binding site of the GABAA receptor.

JM-1232 is a sedative and hypnotic drug being researched as a potential anesthetic. It has similar effects to sedative-hypnotic benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic. It was developed by a team at Maruishi Pharmaceutica.

In pharmacology, GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators, also known as GABAkines or GABAA receptor potentiators, are positive allosteric modulator (PAM) molecules that increase the activity of the GABAA receptor protein in the vertebrate central nervous system.
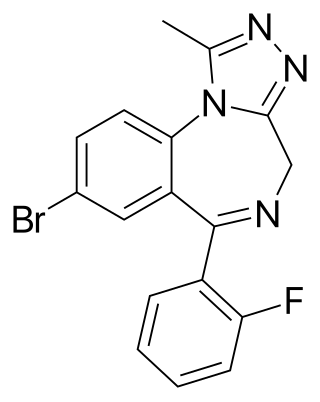
Flubromazolam (JYI-73) is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD), which are benzodiazepine (BZD) derivatives. Flubromazolam is reputed to be highly potent, and concerns have been raised that clonazolam and flubromazolam in particular may pose comparatively higher risks than other designer benzodiazepines, due to their ability to produce strong sedation and amnesia at oral doses of as little as 0.5 mg. Life-threatening adverse reactions have been observed at doses of only 3 mg of flubromazolam.

GL-II-73 (GL-ii-073) is a benzodiazepine derivative related in chemical structure to compounds such as midazolam and adinazolam. It is described as an α5 preferring positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors, with weaker activity at α2 and α3 and no significant affinity for the α1 subtype. In animal tests it was found to produce effects consistent with antidepressant, anxiolytic and nootropic actions.

Fluclotizolam is a thienotriazolodiazepine derivative which was first synthesised in 1979, but was never marketed. It has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, first being definitively identified in 2017.

Ro20-8552 is a benzodiazepine derivative with sedative and anxiolytic effects, which has been sold as a designer drug.

Ro09-9212 is a thienodiazepine derivative with sedative and anxiolytic effects, which has been sold as a designer drug.

Ro07-9749 is a benzodiazepine derivative with sedative and anxiolytic effects, which has been used as an internal standard in the analysis of other benzodiazepines, and also sold as a designer drug.

Fluadinazolam is a benzodiazepine derivative developed in 1973, with sedative and anxiolytic effects. It is a derivative of the never commercially marketed benzodiazepine adinazolam and has similarly been sold as a designer drug.
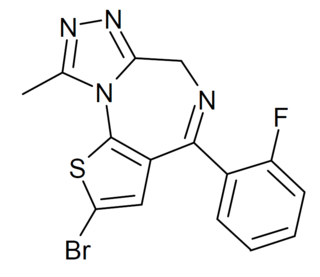
Flubrotizolam is a thienotriazolodiazepine derivative with potent sedative and anxiolytic effects, which has been sold as a designer drug.

Ro07-5220 (6'-Chlorodiclazepam) is a benzodiazepine derivative with sedative, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects, which has been sold as a designer drug.



















