An international nonproprietary name (INN) is an official generic and non-proprietary name given to a pharmaceutical drug or an active ingredient. INNs are intended to make communication more precise by providing a unique standard name for each active ingredient, to avoid prescribing errors. The INN system has been coordinated by the World Health Organization (WHO) since 1953.

Cysticercosis is a tissue infection caused by the young form of the pork tapeworm. People may have few or no symptoms for years. In some cases, particularly in Asia, solid lumps of between one and two centimetres may develop under the skin. After months or years these lumps can become painful and swollen and then resolve. A specific form called neurocysticercosis, which affects the brain, can cause neurological symptoms. In developing countries this is one of the most common causes of seizures.
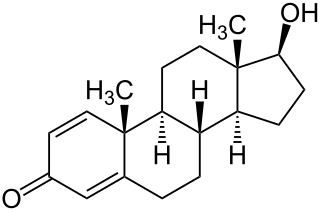
Boldenone, is a naturally occurring anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and the 1(2)-dehydrogenated analogue of testosterone. Boldenone itself has never been marketed; as a pharmaceutical drug, it is used as boldenone undecylenate, the undecylenate ester.

Fluorometholone, also known as 6α-methyl-9α-fluoro-11β,17α-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, is a synthetic glucocorticoid which is used in the treatment of inflammatory eye diseases. The C17α acetate ester, fluorometholone acetate, is also a glucocorticoid and is used for similar indications. Specifically, it is indicated for use in the treatment of steroid-responsive inflammatory conditions of the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea, and anterior segment of the eye.

Thiotepa (INN,, sold under the brand name Tepadina, is an alkylating agent medication used to treat cancer.

Heptabarb, also known as heptabarbitone (BAN) or heptabarbital, is a sedative and hypnotic drug of the barbiturate family. It was used in Europe for the treatment of insomnia from the 1950s onwards, but has since been discontinued.

Etynodiol, or ethynodiol, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which was never marketed. A diacylated derivative, etynodiol diacetate, is used as a hormonal contraceptive. Etynodiol is sometimes used as a synonym for etynodiol diacetate.

Mepitiostane, sold under the brand name Thioderon, is an orally active antiestrogen and anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) of the dihydrotestosterone (DHT) group which is marketed in Japan as an antineoplastic agent for the treatment of breast cancer. It is a prodrug of epitiostanol. The drug was patented and described in 1968.

Stenbolone is an anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) of the dihydrotestosterone (DHT) group which was never marketed. A C17β ester prodrug of stenbolone, stenbolone acetate, is used as an AAS for depot intramuscular injection under the brand names Anatrofin and Stenobolone.

Delmadinone (INN) is a steroidal progestin which was never marketed. An acylated derivative, delmadinone acetate, is used in veterinary medicine.

Promestriene (INN), also known as estradiol 3-propyl 17β-methyl diether, is a synthetic estrogen which is used topically in a 1% cream formulation for the treatment of vaginal atrophy in women. It is the 3-propyl and 17β-methyl diether of estradiol and does not appear to convert into estradiol in the body. Promestriene is minimally absorbed and appears to have negligible systemic estrogenic effect. The drug has been described as a tropic agent and antiseborrheic. It has not been found to be effective in the treatment of pattern hair loss or other conditions of cutaneous androgenization. Promestriene was first introduced in France in 1974 and has been marketed in 34 countries worldwide. It has been used in millions of women.
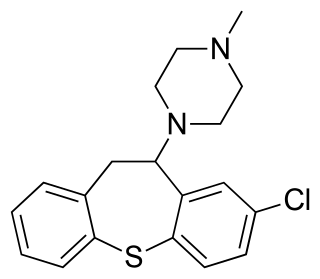
Clorotepine, also known as octoclothepin or octoclothepine, is an antipsychotic of the tricyclic group which was derived from perathiepin in 1965 and marketed in the Czech Republic by Spofa in or around 1971 for the treatment of schizophrenic psychosis.
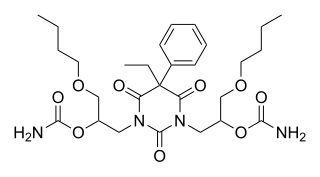
Difebarbamate (INN) is a tranquilizer of the barbiturate and carbamate families which is used in Europe as a component of a combination drug formulation referred to as tetrabamate.
Tetrabamate is a combination drug formulation of febarbamate, difebarbamate, and phenobarbital which was marketed in France and Spain and was used to treat anxiety and alcohol withdrawal-associated muscle tremors, agitation, and depression. It was largely, but not completely discontinued on April 4, 1997 after over 30 years of use due to reports of hepatitis and acute liver failure. The decision to restrict the use of the drug had been long-awaited.

Levomethadone, sold under the brand name L-Polamidon among others, is a synthetic opioid analgesic and antitussive which is marketed in Europe and is used for pain management and in opioid maintenance therapy. In addition to being used as a pharmaceutical drug itself, levomethadone is the main therapeutic component of methadone.

Megestrol is a progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group which was never marketed and is not currently used clinically. Its acylated derivative megestrol acetate is also a progestogen, which, in contrast to megestrol itself, has been extensively used as a pharmaceutical drug.
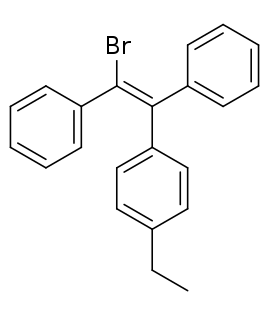
Broparestrol (INN), also known as α-bromo-α,β-diphenyl-β-p-ethylphenylethylene (BDPE), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that has been used in Europe as a dermatological agent and for the treatment of breast cancer. The drug is described as slightly estrogenic and potently antiestrogenic, and inhibits mammary gland development and suppresses prolactin levels in animals. It is structurally related to clomifene and diethylstilbestrol. Broparestrol is a mixture of E- and Z- isomers, both of which are active and are similarly antiestrogenic but, unlike broparestrol, were never marketed.

Flugestone acetate (FGA), sold under the brand name Cronolone among others, is a progestin medication which is used in veterinary medicine.

Estramustine is an estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was never marketed. It is an estrogen ester – specifically, the C3 normustine ester of estradiol – and acts in part as a prodrug of estradiol in the body. Estramustine phosphate, the C17β phosphate ester of estramustine and a prodrug of estramustine, estromustine, estradiol, and estrone, is marketed and used in the treatment of prostate cancer.

Endrisone (INN), or endrysone (USAN), is a synthetic, steroidal glucocorticoid which is or has been marketed in Italy by SIFI. It is used as a topical and ophthalmic anti-inflammatory drug in the treatment of skin and eye conditions, respectively.


















