
Orexin, also known as hypocretin, is a neuropeptide that regulates arousal, wakefulness, and appetite. It exists in the forms of orexin-A and orexin-B. The most common form of narcolepsy, type 1, in which the individual experiences brief losses of muscle tone, is caused by a lack of orexin in the brain due to destruction of the cells that produce it.

Zolpidem, sold under the brand name Ambien among others, is a medication primarily used for the short-term treatment of sleeping problems. Guidelines recommend that it be used only after cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia and behavioral changes, such as sleep hygiene, have been tried. It decreases the time to sleep onset by about fifteen minutes and at larger doses helps people stay asleep longer. It is taken by mouth and is available in conventional tablets, sublingual tablets, or oral spray.

Eszopiclone, sold under the brand name Lunesta among others, is a medication used in the treatment of insomnia. Evidence supports slight to moderate benefit up to six months. It is taken by mouth.
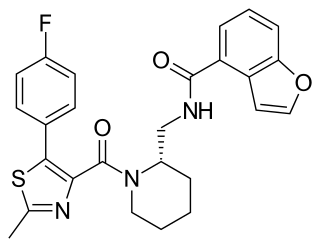
SB-649868 is a dual orexin receptor antagonist that was being developed by GlaxoSmithKline as a treatment for insomnia.
The orexin receptor (also referred to as the hypocretin receptor) is a G-protein-coupled receptor that binds the neuropeptide orexin. There are two variants, OX1 and OX2, each encoded by a different gene (HCRTR1, HCRTR2).

Orexin receptor type 1 (Ox1R or OX1), also known as hypocretin receptor type 1 (HcrtR1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCRTR1 gene.

Orexin receptor type 2 (Ox2R or OX2), also known as hypocretin receptor type 2 (HcrtR2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCRTR2 gene.

TCS-OX2-29 is an orexin antagonist. It was the first non-peptide antagonist developed that is selective for the orexin receptor subtype OX2, with an IC50 of 40nM and selectivity of around 250x for OX2 over OX1 receptors. Orexin antagonists are expected to be useful for the treatment of insomnia, with subtype-selective antagonists such as TCS-OX2-29 potentially offering more specificity of action compared to non-selective orexin antagonists like almorexant.

Suvorexant, sold under the brand name Belsomra, is an orexin antagonist medication which is used in the treatment of insomnia. It is indicated specifically for the treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulties with sleep onset and/or maintenance in adults. Suvorexant helps with falling asleep faster, sleeping longer, being awake less in the middle of the night, and having better quality of sleep. Its effectiveness is modest, and is similar to that of other orexin antagonists, but is lower than that of benzodiazepines and Z-drugs. Suvorexant is taken by mouth.
An orexin receptor antagonist, or orexin antagonist, is a drug that inhibits the effect of orexin by acting as a receptor antagonist of one (selective orexin receptor antagonist or SORA) or both (dual orexin receptor antagonis or DORA) of the orexin receptors, OX1 and OX2. Medical applications include treatment of sleep disorders such as insomnia.
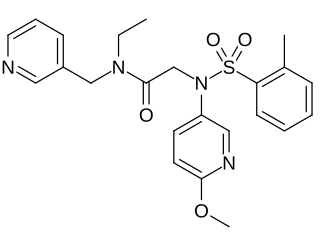
EMPA is a selective antagonist of the OX2 receptor, with 900-fold selectivity in binding for OX2 over OX1.

Filorexant (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name, USANTooltip United States Approved Name; developmental code name MK-6096) is an orexin antagonist which was under development by Merck for the treatment of insomnia, depression, diabetic neuropathy, and migraine. It is a dual antagonist of the orexin OX1 and OX2 receptors. It has a relatively short elimination half-life of 3 to 6 hours. However, it dissociates slowly from the orexin receptors and may thereby have a longer duration. Possibly in relation to this, filorexant shows next-day somnolence similarly to suvorexant. In phase 2 clinical trials, filorexant was found to be effective in the treatment of insomnia, but was not effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder, painful diabetic neuropathy, or migraine. As of May 2015, filorexant was no longer listed on Merck's online development pipeline and hence development of the drug appears to have been discontinued. Development of filorexant may have been discontinued due to lack of differentiation from suvorexant (which was also developed by Merck).

Seltorexant, also known by its developmental code names MIN-202 and JNJ-42847922, is an orexin antagonist medication which is under development for the treatment of depression and insomnia. It is a selective antagonist of the orexin OX2 receptor (2-SORA). The medication is taken by mouth. As of February 2022, seltorexant is in phase 3 clinical trials for treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) and phase 2 trials for treatment of insomnia. It was also under investigation for the treatment of sleep apnea, but no recent development has been reported for this indication. Seltorexant is under development by Minerva Neurosciences and Johnson & Johnson's Janssen Pharmaceuticals.

Lemborexant, sold under the brand name Dayvigo, is an orexin antagonist medication which is used in the treatment of insomnia. It is indicated specifically for the treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulties with sleep onset and/or maintenance in adults. The medication is taken by mouth.

Daridorexant, sold under the brand name Quviviq, is an orexin antagonist medication which is used for the treatment of insomnia. Daridorexant is taken by mouth.

Vornorexant, also known by its developmental code names ORN-0829 and TS-142, is an orexin antagonist medication which is under development for the treatment of insomnia and sleep apnea. It is a dual orexin OX1 and OX2 receptor antagonist (DORA). The medication is taken by mouth. As of June 2021, vornorexant is in phase 2 clinical trials for insomnia and phase 1 trials for sleep apnea. It is under development by Taisho Pharmaceutical.

Firazorexton (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name; development code TAK-994) is an experimental orexin 2 (OX2) receptor agonist first described in a 2019 patent filed by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company.

ACT-462206 is a dual orexin receptor antagonist (IC50 for OX1 = 60nM, OX2 = 11nM) which has been investigated for the treatment of insomnia. In human trials, ACT-462206 produced dose-dependent sedative effects and was generally well tolerated, with residual sleepiness and headache being the most common adverse events.

ACT-539313 is an orexin antagonist medication which is under development for the treatment of binge eating disorder and was previously under development for the treatment of anxiety disorders. It is an orally active small-molecule compound with an elimination half-life of 3.3 to 6.5 hours and acts as a selective orexin OX1 receptor antagonist (1-SORA). As of May 2022, the drug is in phase 2 clinical trials for binge eating disorder. Following negative efficacy results of a phase 2 trial of ACT-539313 for binge eating disorder, Idorsia (the developer of ACT-539313) signaled in May 2022 that it would not pursue further development of the drug for this indication.

Somnifacient, also known as sedatives or sleeping pills, is a class of medications that induces sleep. It is mainly used for treatment of insomnia. Examples of somnifacients include benzodiazepines, barbiturates and antihistamines.


















