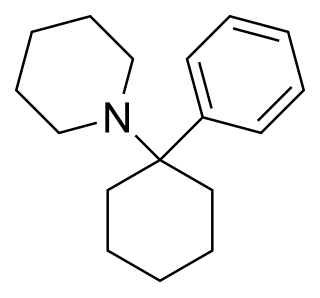
Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP), also known in its use as a street drug as angel dust among other names, is a dissociative anesthetic mainly used recreationally for its significant mind-altering effects. PCP may cause hallucinations, distorted perceptions of sounds, and violent behavior. As a recreational drug, it is typically smoked, but may be taken by mouth, snorted, or injected. It may also be mixed with cannabis or tobacco.
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) is a class of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter (DAT). Reuptake inhibition is achieved when extracellular dopamine not absorbed by the postsynaptic neuron is blocked from re-entering the presynaptic neuron. This results in increased extracellular concentrations of dopamine and increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission.

Dizocilpine (INN), also known as MK-801, is a pore blocker of the NMDA receptor, a glutamate receptor, discovered by a team at Merck in 1982. Glutamate is the brain's primary excitatory neurotransmitter. The channel is normally blocked with a magnesium ion and requires depolarization of the neuron to remove the magnesium and allow the glutamate to open the channel, causing an influx of calcium, which then leads to subsequent depolarization. Dizocilpine binds inside the ion channel of the receptor at several of PCP's binding sites thus preventing the flow of ions, including calcium (Ca2+), through the channel. Dizocilpine blocks NMDA receptors in a use- and voltage-dependent manner, since the channel must open for the drug to bind inside it. The drug acts as a potent anti-convulsant and probably has dissociative anesthetic properties, but it is not used clinically for this purpose because of the discovery of brain lesions, called Olney's lesions (see below), in laboratory rats. Dizocilpine is also associated with a number of negative side effects, including cognitive disruption and psychotic-spectrum reactions. It inhibits the induction of long term potentiation and has been found to impair the acquisition of difficult, but not easy, learning tasks in rats and primates. Because of these effects of dizocilpine, the NMDA receptor pore blocker ketamine is used instead as a dissociative anesthetic in human medical procedures. While ketamine may also trigger temporary psychosis in certain individuals, its short half-life and lower potency make it a much safer clinical option. However, dizocilpine is the most frequently used uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist in animal models to mimic psychosis for experimental purposes.

Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine" (literally, "working on dopamine"), dopamine being a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain. Dopaminergic brain pathways facilitate dopamine-related activity. For example, certain proteins such as the dopamine transporter (DAT), vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2), and dopamine receptors can be classified as dopaminergic, and neurons that synthesize or contain dopamine and synapses with dopamine receptors in them may also be labeled as dopaminergic. Enzymes that regulate the biosynthesis or metabolism of dopamine such as aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase or DOPA decarboxylase, monoamine oxidase (MAO), and catechol O-methyl transferase (COMT) may be referred to as dopaminergic as well. Also, any endogenous or exogenous chemical substance that acts to affect dopamine receptors or dopamine release through indirect actions (for example, on neurons that synapse onto neurons that release dopamine or express dopamine receptors) can also be said to have dopaminergic effects, two prominent examples being opioids, which enhance dopamine release indirectly in the reward pathways, and some substituted amphetamines, which enhance dopamine release directly by binding to and inhibiting VMAT2.

NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for humans and non-human animals; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia.
Rimcazole is an antagonist of the sigma receptor as well as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor. Sigma receptors are thought to be involved in the drug psychosis that can be induced by some drugs such as phencyclidine and cocaine, and rimcazole was originally researched as a potential antipsychotic with a different mechanism of action to traditional antipsychotic drugs. Trials proved inconclusive and rimcazole was not pursued for this application, but other sigma antagonists continue to be researched for a variety of potential applications. Rimcazole has been shown to reduce the effects of cocaine, and analogues of rimcazole have been shown to be highly effective at blocking the convulsions caused by cocaine overdose in animal models.
Etoxadrol (CL-1848C) is a dissociative anaesthetic drug that has been found to be an NMDA antagonist and produce similar effects to PCP in animals. Etoxadrol, along with another related drug dexoxadrol, were developed as analgesics for use in humans, but development was discontinued in the late 1970s after patients reported side effects such as nightmares and hallucinations.
Reuptake inhibitors (RIs) are a type of reuptake modulators. It is a drug that inhibits the plasmalemmal transporter-mediated reuptake of a neurotransmitter from the synapse into the pre-synaptic neuron. This leads to an increase in extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter and an increase in neurotransmission. Various drugs exert their psychological and physiological effects through reuptake inhibition, including many antidepressants and psychostimulants.

GBR-12935 is a piperazine derivative which is a potent and selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor. It was originally developed in its 3H radiolabelled form for the purpose of mapping the distribution of dopaminergic neurons in the brain by selective labelling of dopamine transporter proteins. This has led to potential clinical uses in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease, although selective radioligands such as Ioflupane (123I) are now available for this application. GBR-12935 is now widely used in animal research into Parkinson's disease and the dopamine pathways in the brain.

Benocyclidine, also known as benzothiophenylcyclohexylpiperidine (BTCP), is a psychoactive recreational drug of the arylcyclohexylamine class which is related to phencyclidine (PCP). It was first described in a patent application naming Marc Caron and colleagues at Duke University in 1997.

LY-379,268 is a drug that is used in neuroscience research, which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3).
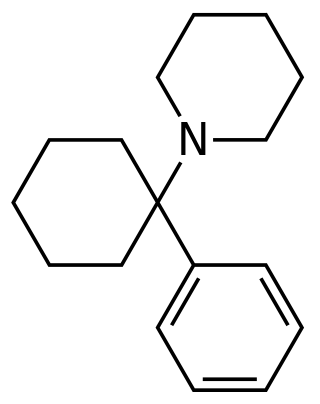
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs.

Sunifiram is an experimental drug which has antiamnesic effects in animal studies and with significantly higher potency than piracetam. Sunifiram is a molecular simplification of unifiram (DM-232). Another analogue is sapunifiram (MN-19). As of 2016, sunifiram had not been subjected to toxicology testing, nor to any human clinical trials, and is not approved for use anywhere in the world.

3-Methoxyphencyclidine (3-MeO-PCP) is a dissociative hallucinogen of the arylcyclohexylamine class related to phencyclidine (PCP) which has been sold online as a designer drug. It acts mainly as an NMDA receptor antagonist, though it has also been found to interact with the sigma σ1 receptor and the serotonin transporter. The drug does not possess any opioid activity nor does it act as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor.
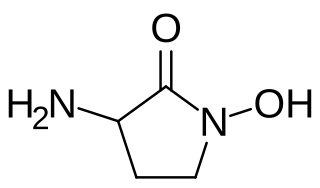
HA-966 or (±)-3-amino-1-hydroxy-pyrrolidin-2-one is a molecule used in scientific research as a glycine receptor and NMDA receptor antagonist / low efficacy partial agonist. It has neuroprotective and anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, antinociceptive and sedative / hypnotic effects in animal models. Pilot human clinical trials in the early 1960s showed that HA-966 appeared to benefit patients with tremors of extrapyramidal origin.

Ephenidine is a dissociative anesthetic that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is illegal in some countries as a structural isomer of the banned opioid drug lefetamine, but has been sold in countries where it is not yet banned.
3-Hydroxyphencyclidine (3-HO-PCP) is a dissociative of the arylcyclohexylamine class related to phencyclidine (PCP) that has been sold online as a designer drug.
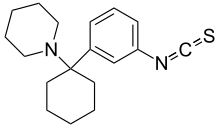
Fourphit (4-isothiocyanato-1-[1-phenylcyclohexyl]piperidine) is a covalent binding NMDA antagonist, dopaminergic and sigma receptor agonist.

PD-137889 (N-methylhexahydrofluorenamine) is a chemical compound that is active as an NMDA receptor antagonist in the central nervous system at roughly 30 times the potency of the "flagship" of its class, ketamine, and substitutes for phencyclidine in animal studies. Ki [3H]TCP binding = 27 nM versus ketamine's Ki = 860 nM.

PCP site 2 is a binding site that was identified as a high-affinity target for phencyclidine (PCP), an anesthetic and dissociative hallucinogen that acts primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist. The site is distinct from the PCP binding site on the NMDA receptor and the common/main sites on the monoamine transporters. It is associated with monoamine reuptake inhibition, and it has been suggested that the site may be an allosteric/regulatory site of the monoamine transporters.