Ampakines or AMPAkines are a subgroup of AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulators with a benzamide or closely related chemical structure. They are also known as "CX compounds". Ampakines take their name from the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), a type of ionotropic glutamate receptor with which the ampakines interact and act as positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) of. Although all ampakines are AMPAR PAMs, not all AMPAR PAMs are ampakines.

CX717 is an ampakine compound created by Christopher Marrs and Gary Rogers in 1996 at Cortex Pharmaceuticals. It affects the neurotransmitter glutamate, with trials showing the drug improves cognitive functioning and memory.

Farampator is an ampakine drug. It was developed by Cortex Pharmaceuticals, and licensed to Organon BioSciences for commercial development. Following the purchase of Organon by Schering-Plough in 2007, the development license to farampator was transferred. The development of farampator was eventually terminated, reportedly due to concerns about cardiac toxicity.
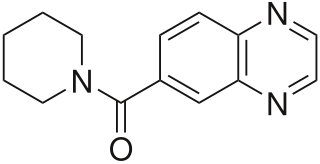
CX-614 is an ampakine drug developed by Cortex Pharmaceuticals. It has been investigated for its effect on AMPA receptors.

IDRA-21 is a positive allosteric modulator of the AMPA receptor and a benzothiadiazine derivative. It is a chiral molecule, with (+)-IDRA-21 being the active form.

LY-503430 is an AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulator developed by Eli Lilly.
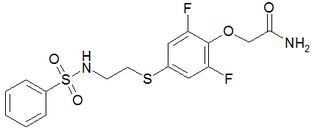
PEPA is a sulfonamide AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulator, which is up to 100 times more potent than aniracetam in vitro. It produces memory-enhancing effects in rats when administered intravenously.

LY-404187 is an AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulator which was developed by Eli Lilly and Company. It is a member of the biarylpropylsulfonamide class of AMPA receptor potentiators.

Pregnenolone sulfate is an endogenous excitatory neurosteroid that is synthesized from pregnenolone. It is known to have cognitive and memory-enhancing, antidepressant, anxiogenic, and proconvulsant effects.
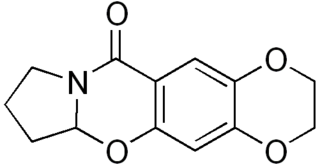
S-18986 is a positive allosteric modulator of the AMPA receptor related to cyclothiazide. It has nootropic and neuroprotective effects in animal studies, and induces both production of BDNF and AMPA-mediated release of noradrenaline and acetylcholine in the hippocampus and frontal cortex of the brain.

ORG-26576 is an ampakine originally developed by Cortex Pharmaceuticals and then licensed to Organon International for development. In animal studies it has been shown to effectively potentiate AMPA receptor function, leading to increased BDNF release and enhanced neuronal differentiation and survival, as well as producing nootropic effects in standardised assays. Development as an antidepressant has been halted due to a failed Phase II trial for major depressive disorder.

ALTO-100, previously known as NSI-189, is a drug described as a hippocampal neurogenesis stimulant and indirect brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) modulator which is under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD), bipolar depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). There has also been interest in ALTO-100 for possible treatment of cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. It is taken by mouth.
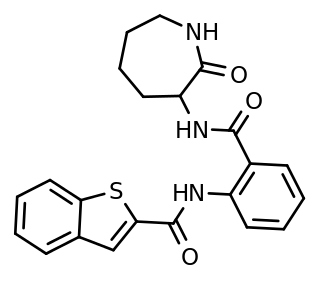
ANA-12 is a selective, small-molecule non-competitive antagonist of TrkB, the main receptor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). ANA-12 was originally discovered and developed by Cazorla M. and colleagues at Université Paris and Inserm in 2011. The compound crosses the blood-brain-barrier and exerts central TrkB blockade, producing effects as early as 30 minutes and as long as 6 hours following intraperitoneal injection in mice. It blocks the neurotrophic actions of BDNF without compromising neuron survival.

Pesampator is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), an ionotropic glutamate receptor, which was under development by Pfizer for the treatment of cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia. In March 2018, the development of the drug was transferred over from Pfizer to Biogen. It was also under development for the treatment of age-related sensorineural hearing loss, but development for this indication was terminated due to insufficient effectiveness. In July 2022, Biogen discontinued the development of pesampator for cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia due to ineffectiveness.

Mibampator is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), an ionotropic glutamate receptor, which was under development by Eli Lilly for the treatment of agitation/aggression in Alzheimer's disease but was never marketed. It reached phase II clinical trials prior to the discontinuation of its development.

AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulators are positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) of the AMPA receptor (AMPR), a type of ionotropic glutamate receptor which mediates most fast synaptic neurotransmission in the central nervous system.
A GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulator is a negative allosteric modulator (NAM), or inhibitor, of the GABAA receptor, a ligand-gated ion channel of the major inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). They are closely related and similar to GABAA receptor antagonists. The effects of GABAA receptor NAMs are functionally the opposite of those of GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) like the benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and ethanol (alcohol). Non-selective GABAA receptor NAMs can produce a variety of effects including convulsions, neurotoxicity, and anxiety, among others.

GL-II-73 (GL-ii-073) is a benzodiazepine derivative related in chemical structure to compounds such as midazolam and adinazolam. It is described as an α5 preferring positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors, with weaker activity at α2 and α3 and no significant affinity for the α1 subtype. In animal tests it was found to produce effects consistent with antidepressant, anxiolytic and nootropic actions.
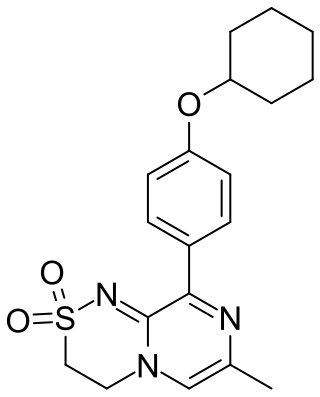
Osavampator is an experimental drug being investigated as a treatment for treatment-resistant depression. It is being developed by Takeda Pharmaceuticals.

















