The N-methyl-D-aspartatereceptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other two being AMPA and kainate receptors. Depending on its subunit composition, its ligands are glutamate and glycine (or D-serine). However, the binding of the ligands is typically not sufficient to open the channel as it may be blocked by Mg2+ ions which are only removed when the neuron is sufficiently depolarized. Thus, the channel acts as a “coincidence detector” and only once both of these conditions are met, the channel opens and it allows positively charged ions (cations) to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is thought to be very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and mediating learning and memory functions.

Ligand-gated ion channels (LICs, LGIC), also commonly referred to as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, and/or Cl− to pass through the membrane in response to the binding of a chemical messenger (i.e. a ligand), such as a neurotransmitter.

Desmoteplase is a novel, highly fibrin-specific "clot-busting" (thrombolytic) drug in development that reached phase III clinical trials. The Danish pharmaceutical company, Lundbeck, owns the worldwide rights to Desmoteplase. In 2009, two large trials were started to test it as a safe and effective treatment for patients with acute ischaemic stroke. After disappointing results in DIAS-3, DIAS-4 was terminated, and in December 2014 Lundbeck announced that they would stop the development of desmoteplase.

NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for animals and humans; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia.

Ifenprodil is an inhibitor of the NMDA receptor, specifically of GluN1 and GluN2B subunits. Additionally, ifenprodil inhibits GIRK channels, and interacts with alpha1 adrenergic, serotonin, and sigma receptors.

Midafotel is a potent, competitive antagonist at the NMDA receptor. It was originally designed as a potential therapy for excitotoxicity, epilepsy or neuropathic pain. It looked very promising in in vitro trials proving to be a potent competitive antagonist at the NMDA without affecting other receptors. Research continued through to in vivo cat studies where it proved to limit damage after occluding the middle cerebral artery, leading to ischaemia. It also blocked photosensitive epilepsies in baboons.

Aptiganel is an unsuccessful drug candidate which acts as a noncompetitive NMDA antagonist, and that was under development by Cambridge Neuroscience, Inc as a treatment for stroke. It has neuroprotective effects and was researched for potential use in the treatment of stroke, but despite positive results in animal studies, human trials showed limited efficacy, as well as undesirable side effects such as sedation and hallucinations, and clinical development was ultimately not continued.

Selfotel (CGS-19755) is a drug which acts as a competitive NMDA antagonist, directly competing with glutamate for binding to the receptor. Initial studies showed it to have anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, analgesic and neuroprotective effects, and it was originally researched for the treatment of stroke, but subsequent animal and human studies showed phencyclidine-like effects, as well as limited efficacy and evidence for possible neurotoxicity under some conditions, and so clinical development was ultimately discontinued.

Lubeluzole (Prosynap) is a drug which acts as an indirect NMDA antagonist. It inhibits the release of glutamate, inhibits nitric oxide synthesis, and blocks calcium and sodium gated ion channels. It has neuroprotective effects particularly in hypoxic conditions, and was developed for the treatment of stroke. Trials showed it to be safe, effective and well tolerated at low doses, but unfortunately higher doses produced the dangerous cardiac side effect of lengthening the QTc interval, which could potentially lead to heart failure, and so this meant that subsequent trials were limited to using only the low dose range. Animal studies had shown lubeluzole to produce neuroprotective effects when administered for prolonged periods, but the aim of its developers was to produce a drug that would be effective for preventing damage from acute stroke, and so ultimately it failed to show sufficient efficacy in trials and development for medical use was halted.
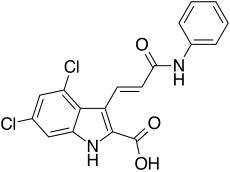
Eliprodil is an NMDA antagonist drug candidate which selectively inhibits the NR2B (GLUN2B) subtype NMDA receptor at submicromolar concentrations. Eliprodil failed a Phase III clinical trial for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke in 1996, sponsored by Synthélabo Recherche.

Remacemide is a drug which acts as a low-affinity NMDA antagonist with sodium channel blocking properties. It has been studied for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke, epilepsy, Huntington's disease, and Parkinson's disease.

Neramexane is a drug related to memantine, which acts as an NMDA antagonist and has neuroprotective effects. It is being developed for various possible applications, including treatment of tinnitus, Alzheimer's disease, drug addiction and as an analgesic. Animal studies have also suggested antidepressant and nootropic actions, so there are a wide range of potential applications this drug may be used for. It also acts as a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist.
NMDA receptor modulators are a new form of antipsychotic that are in Phase II FDA studies. The first compound studied was glycine which was hypothesized by Daniel Javitt after observation that people with phencyclidine(PCP)-induced psychosis were lacking in glutamate transmission. In giving glycine to people with PCP-induced psychosis a recovery rate was noted. From there, it was hypothesized that people with psychosis from schizophrenia would benefit from increased glutamate transmission and glycine was added with strong recovery rates noted especially in the area of negative and cognitive symptoms. Glycine, however, sporadic results aside remains an adjunct antipsychotic and an unworkable compound. However, the Eli Lilly and Company study drug LY-2140023 is being studied as a primary antipsychotic and is showing strong recovery rates, especially in the area of negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Tardive dyskinesia, diabetes and other standard complications have not been noted:
Treatment with LY2140023, like treatment with olanzapine, was safe and well-tolerated; treated patients showed statistically significant improvements in both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia compared to placebo. Notably, patients treated with LY-2140023 did not differ from placebo-treated patients with respect to prolactin elevation, extrapyramidal symptoms or weight gain. These data suggest that mGlu2/3 receptor agonists have antipsychotic properties and may provide a new alternative for the treatment of schizophrenia.

Repinotan (BAYx3702), an aminomethylchroman derivative, is a selective 5-HT1A receptor full agonist with high potency and efficacy. It has neuroprotective effects in animal studies, and was trialed in humans for reducing brain injury following head trauma. It was subsequently trialed up to phase II for treatment of stroke, but while side effects were mild and consisted mainly of nausea, repinotan failed to demonstrate sufficient efficacy to justify further clinical trials. However, repinotan continues to be investigated for other applications, and was found to be effective at counteracting the respiratory depression produced by morphine, though with slight reduction in analgesic effects.

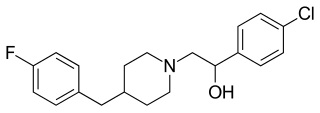
Traxoprodil is a drug developed by Pfizer which acts as an NMDA antagonist, selective for the NR2B subunit. It has neuroprotective, analgesic, and anti-Parkinsonian effects in animal studies. Traxoprodil has been researched in humans as a potential treatment to lessen the damage to the brain after stroke, but results from clinical trials showed only modest benefit. The drug was found to cause EKG abnormalities and its clinical development was stopped. More recent animal studies have suggested traxoprodil may exhibit rapid-acting antidepressant effects similar to those of ketamine, although there is some evidence for similar psychoactive side effects and abuse potential at higher doses, which might limit clinical acceptance of traxoprodil for this application.

Bitopertin is a glycine reuptake inhibitor which was under development by Roche as an adjunct to antipsychotics for the treatment of persistent negative symptoms or suboptimally controlled positive symptoms associated with schizophrenia. Research into this indication has been largely halted as a result of disappointing trial results.

Licostinel (INN) is a competitive, silent antagonist of the glycine site of the NMDA receptor. It was under investigation by Acea Pharmaceuticals as a neuroprotective agent for the treatment of cerebral ischemia associated with stroke and head injuries but was ultimately never marketed. In clinical trials, licostinel did not produce phencyclidine-like psychotomimetic effects at the doses tested, though transient sedation, dizziness, and nausea were observed. In addition to its actions at the NMDA receptor, licostinel also acts as an antagonist of the AMPA and kainate receptors at high concentrations.

L-4-Chlorokynurenine is an orally active small molecule prodrug of 7-chlorokynurenic acid, a NMDA receptor antagonist. It was investigated as a potential rapid-acting antidepressant.

Svetlana Dambinova is a Russian neuroscientist, Doctor of Biological Sciences, Distinguished Professor at Laboratory of biomarkers at Medical Center "DeKalb", Atlanta, USA. Dambinova was awarded as Honored Worker of Science of the Republic of Buryatia (1996) and Russian Federation (1998). Known in the world for research of glutamate receptors. The Head of the project of the International Department of Neurology SPBGMU them. Acad. Pavlov's.
A cerebroprotectant is a drug that is intended to protect the brain after the onset of acute ischemic stroke. As stroke is the second largest cause of death worldwide and a leading cause of adult disability, over 150 drugs tested in clinical trials to provide cerebroprotection.