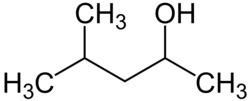
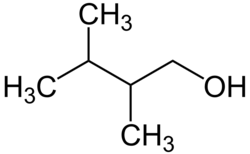
Hexanol may refer to any of the following isomeric organic compounds with the formula C6H13OH:
Structure Type IUPAC name Boiling point (°C) 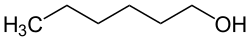
Primary Hexan-1-ol 158 
Secondary Hexan-2-ol 140 Secondary Hexan-3-ol 135 Primary 2-Methylpentan-1-ol 147 Primary 3-Methylpentan-1-ol 152 Primary 4-Methylpentan-1-ol 151 Tertiary 2-Methylpentan-2-ol 121 Secondary 3-Methylpentan-2-ol 134 Secondary 4-Methylpentan-2-ol 131 Secondary 2-Methylpentan-3-ol 126 Tertiary 3-Methylpentan-3-ol 122 
Primary 2,2-Dimethylbutan-1-ol 137 Primary 2,3-Dimethylbutan-1-ol 145 Primary 3,3-Dimethylbutan-1-ol 143 Tertiary 2,3-Dimethylbutan-2-ol 119 Secondary 3,3-Dimethylbutan-2-ol 120 Primary 2-Ethylbutan-1-ol 146