 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
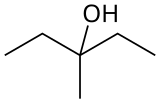
| Preferred IUPAC name 3-Methylpentan-3-ol | |
| Other names 3-Methyl-3-pentanol Diethyl carbinol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.959 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14O | |
| Molar mass | 102.174 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Odor | fruity |
| Density | 0.8286 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | −23.6 °C (−10.5 °F; 249.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 122.4 °C (252.3 °F; 395.5 K) |
| 45 g/L | |
| Solubility | miscible with ethanol, diethyl ether |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) | 293.4 J·mol−1·K−1 (liquid) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H226, H302 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P264, P270, P280, P301+P312, P303+P361+P353, P330, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) | 710 mg/kg rat |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | http://www.sciencelab.com/msds.php?msdsId=9926087 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds | Hexanol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
3-Methyl-3-pentanol (IUPAC name: 3-methylpentan-3-ol) is an organic chemical compound and a tertiary hexanol. It is used in the synthesis of the tranquilizer emylcamate, [2] and has similar sedative and anticonvulsant actions itself. [3]
