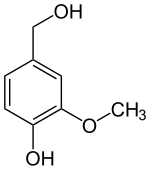
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 4-(Hydroxymethyl)-2-methoxyphenol | |
| Other names 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzenemethanol 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl alcohol Vanillic alcohol Vanillin alcohol | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.140 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 154.165 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Crystalline white to off-white powder |
| Melting point | 113 °C (235 °F; 386 K) [1] |
| Boiling point | 293 °C (559 °F; 566 K) [1] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.75 [1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related phenols | vanillic acid, vanillin |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Vanillyl alcohol is derived from vanillin. [2] It is used to flavor food [1] and scent fragrances, and is described to have a mild, sweet, balsamic vanilla-like scent. Recent studies have shown that vanillyl alcohol has some neuro-protective effects by suppressing the oxidative stress and anti-apoptotic activity in toxin-induced dopaminergic MN9D cells. This could make it a potential candidate for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's disease. [3]