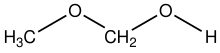
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula CH3OH (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, volatile, colorless and flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odour similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol). Methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced chiefly by the destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide.

In organic chemistry, an aldehyde is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure R−CH=O. The functional group itself can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology.

Formaldehyde is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula CH2O and structure H−CHO. The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde, hence it is stored as an aqueous solution (formalin), which is also used to store animal specimens. It is the simplest of the aldehydes and one of the simplest of the carbohydrates. The common name of this substance comes from its similarity and relation to formic acid.
In chemistry, dehydrogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the removal of hydrogen, usually from an organic molecule. It is the reverse of hydrogenation. Dehydrogenation is important, both as a useful reaction and a serious problem. At its simplest, it is useful way of converting alkanes, which are relatively inert and thus low-valued, to olefins, which are reactive and thus more valuable. Alkenes are precursors to aldehydes, alcohols, polymers, and aromatics. As a problematic reaction, the fouling and inactivation of many catalysts arises via coking, which is the dehydrogenative polymerization of organic substrates.
Methylamine is an organic compound with a formula of CH3NH2. This colorless gas is a derivative of ammonia, but with one hydrogen atom being replaced by a methyl group. It is the simplest primary amine.
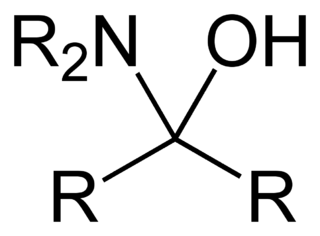
In organic chemistry, a hemiaminal is a functional group or type of chemical compound that has a hydroxyl group and an amine attached to the same carbon atom: −C(OH)(NR2)−. R can be hydrogen or an alkyl group. Hemiaminals are intermediates in imine formation from an amine and a carbonyl by alkylimino-de-oxo-bisubstitution. Hemiaminals can be viewed as a blend of aminals and geminal diol. They are a special case of amino alcohols.

Dimethyl sulfite is a sulfite ester with the chemical formula (CH3O)2SO.

In organic chemistry, a carbonate ester is an ester of carbonic acid. This functional group consists of a carbonyl group flanked by two alkoxy groups. The general structure of these carbonates is R−O−C(=O)−O−R' and they are related to esters, ethers and also to the inorganic carbonates.
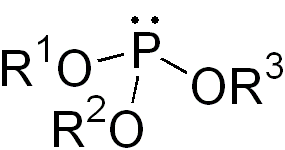
In organic chemistry, a phosphite ester or organophosphite usually refers to an organophosphorous compound with the formula P(OR)3. They can be considered as esters of an unobserved tautomer phosphorous acid, H3PO3, with the simplest example being trimethylphosphite, P(OCH3)3. Some phosphites can be considered esters of the dominant tautomer of phosphorous acid (HP(O)(OH)2). The simplest representative is dimethylphosphite with the formula HP(O)(OCH3)2. Both classes of phosphites are usually colorless liquids.

In organic chemistry, an ortho ester is a functional group containing three alkoxy groups attached to one carbon atom, i.e. with the general formula RC(OR′)3. Orthoesters may be considered as products of exhaustive alkylation of unstable orthocarboxylic acids and it is from these that the name 'ortho ester' is derived. An example is ethyl orthoacetate, CH3C(OCH2CH3)3, more correctly known as 1,1,1-triethoxyethane.

Atomic carbon, systematically named carbon and λ0-methane, is a colourless gaseous inorganic chemical with the chemical formula C. It is kinetically unstable at ambient temperature and pressure, being removed through autopolymerisation.
Methanediol, also known as formaldehyde monohydrate or methylene glycol, is an organic compound with chemical formula CH2(OH)2. It is the simplest geminal diol. In aqueous solutions it coexists with oligomers. The compound is closely related and convertible to the industrially significant derivatives paraformaldehyde, formaldehyde, and 1,3,5-trioxane.

Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH. Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements.

Roy A. Periana is a Guyanese-American organometallic chemist.

1,2-Dimethyldiborane is an organoboron compound with the formula [(CH3)BH2]2. Structurally, it is related to diborane, but with methyl groups replacing terminal hydrides on each boron. It is the dimer of methylborane, CH3BH2, the simplest alkylborane. 1,2-Dimethyldiborane can exist in a cis- and a trans arrangement. 1,2-Dimethyldiborane is an easily condensed, colorless gas that ignites spontaneously in air.

Trimethyldiborane, (CH3)3B2H3 is a molecule containing boron carbon and hydrogen. It is an alkylborane, consisting of three methyl group substituted for a hydrogen in diborane. It can be considered a mixed dimer: (CH3)2BH2BH(CH3) or dimethylborane and methylborane. called 1,2-dimethyldiborane. Other combinations of methylation occur on diborane, including monomethyldiborane, 1,2-dimethyldiborane, tetramethyldiborane, 1,1-dimethylborane and trimethylborane. At room temperature the substance is at equilibrium between these forms, so it is difficult to keep it pure. The methylboranes were first prepared by H. I. Schlesinger and A. O. Walker in the 1930s.
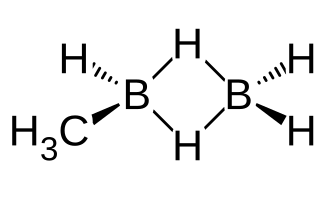
Methyldiborane, CH3B2H5, or monomethyldiborane is the simplest of alkyldiboranes, consisting of a methyl group substituted for a hydrogen in diborane. As with other boranes it exists in the form of a dimer with a twin hydrogen bridge that uses three-center two-electron bonding between the two boron atoms, and can be imagined as methyl borane (CH3BH2) bound to borane (BH3). Other combinations of methylation occur on diborane, including 1,1-dimethylborane, 1,2-dimethyldiborane, trimethyldiborane, tetramethyldiborane, and trimethylborane (which is not a dimer). At room temperature the substance is at equilibrium between these molecules.
1,2-Difluoroethane is a saturated hydrofluorocarbon containing an atom of fluorine attached to each of two carbons atoms. The formula can be written CH2FCH2F. It is an isomer of 1,1-difluoroethane. It has a HFC name of HFC-152 with no letter suffix. When cooled to cryogenic temperatures it can have different conformers, gauche and trans. In the liquid form these are about equally abundant and easily interconvert. As a gas it is mostly the gauche form.

Sulfoxylic acid (H2SO2) (also known as hyposulfurous acid or sulfur dihydroxide) is an unstable oxoacid of sulfur in an intermediate oxidation state between hydrogen sulfide and dithionous acid. It consists of two hydroxy groups attached to a sulfur atom. Sulfoxylic acid contains sulfur in an oxidation state of +2. Sulfur monoxide (SO) can be considered as a theoretical anhydride for sulfoxylic acid, but it is not actually known to react with water.

Formyl cyanide is a simple organic compound with the formula HCOCN and structure HC(=O)−C≡N. It is simultaneously a nitrile and an aldehyde. Formyl cyanide is the simplest member of the acyl cyanide family. It is known to occur in space in the Sgr B2 molecular cloud.