 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
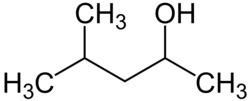
| Preferred IUPAC name 4-Methylpentan-2-ol | |
| Other names 4-Methyl-2-pentanol Methyl isobutyl carbinol MIBC Isobutyl methyl carbinol 2-Methyl-4-pentanol 4-Methylpentane-2-ol 1,3-Dimethylbutanol Methyl amyl alcohol Isobutyl methyl methanol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.229 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2053 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14O | |
| Molar mass | 102.174 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Odor | mild |
| Density | 0.8075 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | −90 °C (−130 °F; 183 K) |
| Boiling point | 131.6 °C (268.9 °F; 404.8 K) |
| 15 g/L | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether |
| Vapor pressure | 0.698 kPa |
| −80.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Viscosity | 4.07 mPa·s |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) | 273.0 J·mol−1·K−1 (liquid) |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | −394.7 kJ·mol−1 (liquid) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H226, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P271, P280, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P312, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 41 °C (106 °F; 314 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1-5.5% [2] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) | 2590 mg/kg (rat, oral) [3] |
LDLo (lowest published) | 1000 mg/kg (mouse, oral) [3] |
LC50 (median concentration) | 2000 ppm (rat, 4 hr) [3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) | TWA 25 ppm (100 mg/m3) [skin] [2] |
REL (Recommended) | TWA 25 ppm (100 mg/m3) ST 40 ppm (165 mg/m3) [skin] [2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) | 400 ppm [2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds | Hexanol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
4-Methyl-2-pentanol (IUPAC name: 4-methylpentan-2-ol) or methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC) is an organic chemical compound used primarily as a frother in mineral flotation and in the production of lubricant oil additives such as Zinc dithiophosphate. [4] It is also used as a solvent, in organic synthesis, and in the manufacture of brake fluid [5] and as a precursor to some plasticizers. It is an acetone derivative in liquid state, with limited solubility in water but generally miscible with most organic solvents. [4]
