
Atomoxetine, sold under the brand name Strattera, is a medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and, to a lesser extent, cognitive disengagement syndrome. It may be used alone or along with psychostimulants. It is also used as a cognitive and executive functioning enhancer to improve self-motivation, persistence, attention, inhibition, and working memory. Use of atomoxetine is only recommended for those who are at least six years old. It is taken orally. Atomoxetine is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor and is believed to work by increasing norepinephrine and dopamine levels in the brain. The effectiveness of atomoxetine is comparable to the commonly prescribed stimulant medication methylphenidate.
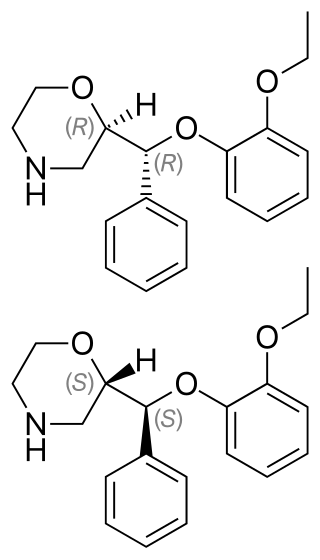
Reboxetine, sold under the brand name Edronax among others, is a drug of the norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI) class, marketed as an antidepressant by Pfizer for use in the treatment of major depression, although it has also been used off-label for panic disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). It is approved for use in many countries worldwide, but has not been approved for use in the United States. Although its effectiveness as an antidepressant has been challenged in multiple published reports, its popularity has continued to increase.

Viloxazine, sold under the brand name Qelbree and formerly as Vivalan among others, is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor medication which is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adults. It was marketed for almost 30 years as an antidepressant for the treatment of depression before being discontinued and subsequently repurposed as a treatment for ADHD. Viloxazine is taken orally. It was used as an antidepressant in an immediate-release form and is used in ADHD in an extended-release form.
A serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI), also known as a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI), is a type of drug that acts as a combined reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. It does this by concomitantly inhibiting the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. Inhibition of the reuptake of these neurotransmitters increases their extracellular concentrations and, therefore, results in an increase in serotonergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic neurotransmission. The naturally-occurring and potent SNDRI cocaine is widely used recreationally and often illegally for the euphoric effects it produces.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder management options are evidence-based practices with established treatment efficacy for ADHD.

Tesofensine (NS2330) is a serotonin–noradrenaline–dopamine reuptake inhibitor from the phenyltropane family of drugs, which is being developed for the treatment of obesity. Tesofensine was originally developed by a Danish biotechnology company, NeuroSearch, who transferred the rights to Saniona in 2014.

Remogliflozin etabonate (INN/USAN) is a drug of the gliflozin class for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis ("NASH") and type 2 diabetes. Remogliflozin was discovered by the Japanese company Kissei Pharmaceutical and is currently being developed by BHV Pharma, a wholly owned subsidiary of North Carolina, US-based Avolynt, and Glenmark Pharmaceuticals through a collaboration with BHV. In 2002, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) received a license to use it. From 2002 to 2009, GSK carried out a significant clinical development program for the treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus in various nations across the world and obesity in the UK. Remogliflozin etabonate's pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and clinical dose regimens were characterized in 18 Phase I and 2 Phase II investigations. Due to financial concerns, GSK stopped working on remogliflozin and sergliflozin, two further SGLT2 inhibitors that were licensed to the company, in 2009. Remogliflozin was commercially launched first in India by Glenmark in May 2019.
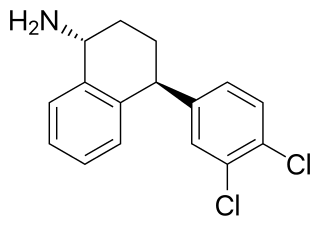
Dasotraline is a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) that was under development by Sunovion for the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and binge eating disorder (BED). Structurally, dasotraline is a stereoisomer of desmethylsertraline (DMS), which is an active metabolite of the marketed selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant sertraline (Zoloft).

Losmapimod (GW856553X) is an investigational drug being developed by Fulcrum Therapeutics for the treatment of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD); a phase III clinical trial is pending approval. Losmapimod selectively inhibits enzymes p38α/β mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), which are modulators of DUX4 expression and mediators of inflammation.

Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors are a class of medical drugs that are mainly used to treat advanced cancers. They function by inhibiting one or more of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) enzymes, which are part of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. This signal pathway regulates cellular functions such as growth and survival. It is strictly regulated in healthy cells, but is always active in many cancer cells, allowing the cancer cells to better survive and multiply. PI3K inhibitors block the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and thus slow down cancer growth. They are examples of a targeted therapy. While PI3K inhibitors are an effective treatment, they can have very severe side effects and are therefore only used if other treatments have failed or are not suitable.

Esmirtazapine (ORG-50,081) is a tetracyclic antidepressant drug that was under development by Organon for the treatment of insomnia and vasomotor symptoms (e.g., hot flashes) associated with menopause. Esmirtazapine is the (S)-(+)-enantiomer of mirtazapine and possesses similar overall pharmacology, including inverse agonist actions at H1 and 5-HT2 receptors and antagonist actions at α2-adrenergic receptors.
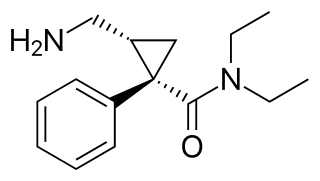
Levomilnacipran is an antidepressant which was approved in the United States in 2013 for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults. It is the levorotatory enantiomer of milnacipran, and has similar effects and pharmacology, acting as a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI).

Amitifadine is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) or so-called triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI) which is or was being developed by Euthymics Bioscience It was under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder, but in May 2013, it was reported that the drug failed to show superior efficacy to placebo in a phase IIb/IIIa clinical trial. It was suggested that this may have been due to the drug being underdosed. In September 2017, development of amitifadine for the treatment of major depressive disorder was finally officially discontinued. As of September 2017, it is still listed as being under development for the treatment of alcoholism and smoking withdrawal.

Brexpiprazole, sold under the brand name Rexulti among others, is a medication used for the treatment of major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, and agitation associated with dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. It is an atypical antipsychotic.

Metadoxine, also known as pyridoxine-pyrrolidone carboxylate, is a drug used to treat chronic and acute alcohol intoxication. Metadoxine accelerates alcohol clearance from the blood.

Centanafadine (INN) is a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) that began its development with Euthymics Bioscience after they acquired DOV Pharmaceutical. It was developed as a treatment for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin with a ratio of 1:6:14, respectively. In 2011, Euthymics Bioscience spun off its development of centanafadine to a new company called Neurovance. In March 2017, Otsuka Pharmaceutical acquired Neurovance and the rights to centanafadine. As of January 2018, Otsuka's pipeline indicates it is in Phase II and III clinical trials for a number of different applications to medical conditions.

Dextromethorphan/bupropion (DXM/BUP), sold under the brand name Auvelity, is a combination medication for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). Its active components are dextromethorphan (DXM) and bupropion. Patients who stayed on the medication had an average of 11% greater reduction in depressive symptoms than placebo in an FDA approval trial. It is taken as a tablet by mouth.

Solriamfetol, sold under the brand name Sunosi, is a wakefulness-promoting medication used in the treatment of excessive sleepiness related to narcolepsy and sleep apnea. It is taken by mouth.
Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (sNRIs) are a class of drugs that have been marketed as antidepressants and are used for various mental disorders, mainly depression and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The norepinephrine transporter (NET) serves as the fundamental mechanism for the inactivation of noradrenergic signaling because of the NET termination in the reuptake of norepinephrine (NE). The selectivity and mechanism of action for the NRI drugs remain mostly unresolved and, to date, only a limited number of NRI-selective inhibitors are available. The first commercially available selective NRI was the drug reboxetine (Edronax), developed as a first-line therapy for major depressive disorder. Atomoxetine (Strattera) is another potent and selective NRI which is also effective and well tolerated for the treatment of ADHD in adults; it may also be a new treatment option for adults with ADHD, particularly for those patients at risk of substance abuse.
















