 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
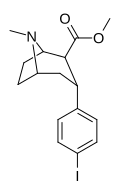
| IUPAC name Methyl 3α-(4-iodophenyl)tropane-2β-carboxylate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name Methyl (1R,2S,3R,5S)-3-(4-iodophenyl)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2-carboxylate | |
| Other names RTI-4229-352 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H20INO2 | |
| Molar mass | 385.245 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
RTI-352 is a phenyltropane that is used as a radiolabeling ligand for the DAT. [1]
RTI-352 is a geometric isomer of RTI-55 (β-CIT). [2]
Based on X-ray crystallography, this compound is in a tautomeric equilibrium residing mostly on the side of the boat-shaped conformer.