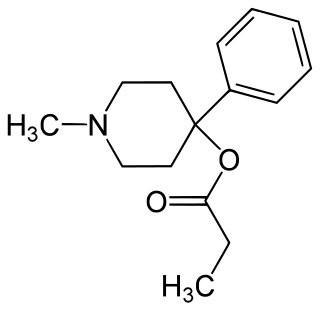
Desmethylprodine or 1-methyl-4-phenyl-4-propionoxypiperidine is an opioid analgesic drug developed in the 1940s by researchers at Hoffmann-La Roche. Desmethylprodine has been labeled by the DEA as a Schedule I drug in the United States. It is an analog of pethidine (meperidine) a Schedule II drug. Chemically, it is a reversed ester of pethidine which has about 70% of the potency of morphine. Unlike its derivative prodine, it does not exhibit optical isomerism. It was reported to have 30 times the activity of pethidine and a greater analgesic effect than morphine in rats, and it was demonstrated to cause central nervous system stimulation in mice.

Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a fully synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisleb, its analgesic properties were first recognized by Otto Schaumann while working for IG Farben, in Germany. Pethidine is the prototype of a large family of analgesics including the pethidine 4-phenylpiperidines, the prodines, bemidones, and others more distant, including diphenoxylate and analogues.
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) is a class of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter (DAT). Reuptake inhibition is achieved when extracellular dopamine not absorbed by the postsynaptic neuron is blocked from re-entering the presynaptic neuron. This results in increased extracellular concentrations of dopamine and increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission.

Phenoperidine, is an opioid analgesic which is structurally related to pethidine and is used clinically as a general anesthetic.
(+)-CPCA is a stimulant drug similar in structure to pethidine and to RTI-31, but nocaine lacks the two-carbon bridge of RTI-31's tropane skeleton. This compound was first developed as a substitute agent for cocaine.

Hydroxypethidine (Bemidone) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of the more commonly used pethidine (meperidine). Hydroxypethidine is slightly more potent than meperidine as an analgesic, 1.5x meperidine in potency, and it also has NMDA antagonist properties like its close relative ketobemidone.

(–)-Benzofuranylpropylaminopentane is an experimental drug related to selegiline which acts as a monoaminergic activity enhancer (MAE). It is orally active in animals.

Allylprodine is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of prodine. It was discovered by Hoffman-La Roche in 1957 during research into the related drug pethidine. Derivatives were tested to prove the theory that phenolic and non-phenolic opioids bind at different sites of the opiate receptor.
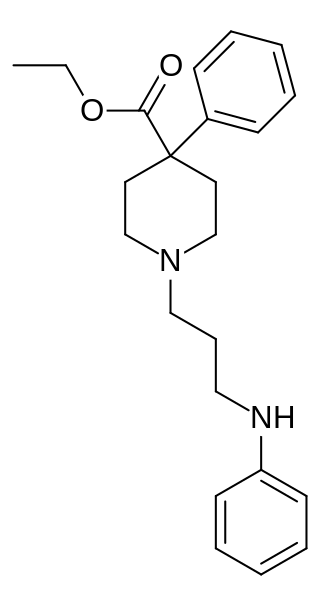
Piminodine (Alvodine) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of pethidine (meperidine). It was used in medicine briefly during the 1960s and 70s, but has largely fallen out of clinical use. It was used particularly for obstetric analgesia and in dental procedures and, like pethidine, could be combined with hydroxyzine to intensify the effects. The duration of action is 2–4 hours; 7.5–10 mg via the subcutaneous route is the most common starting dose, being equal to 80–100 mg of pethidine, 40–60 mg of alphaprodine and 10 mg of morphine. Oral formulations were also available.
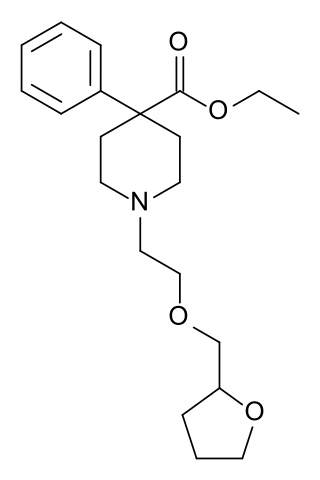
Furethidine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the clinically used opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine), but with around 25x higher potency. According to another source, Furethidine is 500/30 = 16.7 x the potency of pethidine.

Morpheridine (Morpholinoethylnorpethidine) is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the clinically used opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine). It is a strong analgesic with around 4 times the potency of pethidine, and unlike pethidine, does not cause convulsions, although it produces the standard opioid side effects such as sedation and respiratory depression.

Pheneridine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine).

Oxpheneridine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine).

Pethidine intermediate A is a four-phenylpiperidine derivative that is a precursor to the opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine). It is not known to have any analgesic activity in its own right, however other derivatives of pethidine with a 4-cyano group in place of the carboxylate ethyl ester have been found to be active, so pethidine intermediate A might also show opioid effects. It is scheduled by UN Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. It is a Schedule II Narcotic controlled substance in the United States and has an ACSCN of 9232. The 2014 annual manufacturing quota was 6 grammes.

2-Benzylpiperidine is a stimulant drug of the arylpiperidine family. It is similar in structure to certain other stimulants such as methylphenidate and desoxypipradrol. However, it is far less potent as a monoamine reuptake inhibitor in comparison. The drug is little used as a stimulant, with its main use being as a synthetic intermediate in the manufacture of other drugs.

RTI(-4229)-150, is a phenyltropane derivative which acts as a potent dopamine reuptake inhibitor and stimulant drug. It is around 5x more potent than cocaine, but is more selective for the dopamine transporter relative to the other monoamine transporters. RTI-150 has a fast onset of effects and short duration of action, and its abuse potential in animal studies is similar to that of cocaine itself; its main application in scientific research has been in studies investigating the influence of pharmacokinetics on the abuse potential of stimulant drugs, with the rapid entry of RTI-150 into the brain thought to be a key factor in producing its high propensity for development of dependence in animals. RTI-150 is not explicitly illegal anywhere in the world, but its similar structure and pharmacological activity to cocaine makes it possible that it would be considered a controlled substance analogue in countries such as the US, Canada, Australia and New Zealand which have controlled substance analogue legislation.

RTI-126 is a phenyltropane derivative which acts as a potent monoamine reuptake inhibitor and stimulant drug, and has been sold as a designer drug. It is around 5 times more potent than cocaine at inhibiting monoamine reuptake in vitro, but is relatively unselective. It binds to all three monoamine transporters, although still with some selectivity for the dopamine transporter. RTI-126 has a fast onset of effects and short duration of action, and its pharmacological profile in animals is among the closest to cocaine itself out of all the drugs in the RTI series. Its main application in scientific research has been in studies investigating the influence of pharmacokinetics on the abuse potential of stimulant drugs, with its rapid entry into the brain thought to be a key factor in producing its high propensity for development of dependence in animals.

3-Fluoroamphetamine is a stimulant drug from the amphetamine family which acts as a monoamine releaser with similar potency to methamphetamine but more selectivity for dopamine and norepinephrine release over serotonin. It is self-administered by mice to a similar extent to related drugs such as 4-fluoroamphetamine and 3-methylamphetamine.

1-(3-Chlorophenyl)-4-(2-phenylethyl)piperazine (3C-PEP) is a designer drug of the piperazine class of chemical substances. 3C-PEP is related to meta-cholorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) and phenethylamine that can be thought of as mCPP having a phenylethyl group attached to the nitrogen atom at its 4-position. It was first described in 1994 in a patent disclosing a series of piperazine compounds as sigma receptor ligands. Later, it was discovered to be a highly potent dopamine reuptake inhibitor.
3-Methyl-PCPy (3-Me-PCPy) is an arylcyclohexylamine derivative with an unusual spectrum of pharmacological effects, acting as both a potent NMDA antagonist and also a triple reuptake inhibitor which inhibits reuptake of all three monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine and noradrenaline. It also acts as a high affinity sigma receptor ligand, selective for the σ2 subtype. It produces both stimulant and dissociative effects in animal behavioural studies.



















