Related Research Articles

Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) is a precursor polypeptide with 241 amino acid residues. POMC is synthesized in corticotrophs of the anterior pituitary from the 267-amino-acid-long polypeptide precursor pre-pro-opiomelanocortin (pre-POMC), by the removal of a 26-amino-acid-long signal peptide sequence during translation. POMC is part of the central melanocortin system.

In structural biology, a protein subunit is a polypeptide chain or single protein molecule that assembles with others to form a protein complex. Large assemblies of proteins such as viruses often use a small number of types of protein subunits as building blocks.
Dynorphins (Dyn) are a class of opioid peptides that arise from the precursor protein prodynorphin. When prodynorphin is cleaved during processing by proprotein convertase 2 (PC2), multiple active peptides are released: dynorphin A, dynorphin B, and α/β-neo-endorphin. Depolarization of a neuron containing prodynorphin stimulates PC2 processing, which occurs within synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic terminal. Occasionally, prodynorphin is not fully processed, leading to the release of “big dynorphin.” “Big Dynorphin” is a 32-amino acid molecule consisting of both dynorphin A and dynorphin B.
Opioid receptors are a group of inhibitory G protein-coupled receptors with opioids as ligands. The endogenous opioids are dynorphins, enkephalins, endorphins, endomorphins and nociceptin. The opioid receptors are ~40% identical to somatostatin receptors (SSTRs). Opioid receptors are distributed widely in the brain, in the spinal cord, on peripheral neurons, and digestive tract.

An enkephalin is a pentapeptide involved in regulating nociception in the body. The enkephalins are termed endogenous ligands, as they are internally derived and bind to the body's opioid receptors. Discovered in 1975, two forms of enkephalin have been found, one containing leucine ("leu"), and the other containing methionine ("met"). Both are products of the proenkephalin gene.

beta-Endorphin (β-endorphin) is an endogenous opioid neuropeptide and peptide hormone that is produced in certain neurons within the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. It is one of three endorphins that are produced in humans, the others of which include α-endorphin and γ-endorphin.

Opioid peptides or opiate peptides are peptides that bind to opioid receptors in the brain; opiates and opioids mimic the effect of these peptides. Such peptides may be produced by the body itself, for example endorphins. The effects of these peptides vary, but they all resemble those of opiates. Brain opioid peptide systems are known to play an important role in motivation, emotion, attachment behaviour, the response to stress and pain, control of food intake, and the rewarding effects of alcohol and nicotine.

The Chimpanzee Genome Project was an effort to determine the DNA sequence of the chimpanzee genome. Sequencing began in 2005 and by 2013 twenty-four individual chimpanzees had been sequenced. This project was folded into the Great Ape Genome Project.
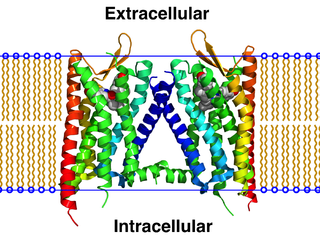
The κ-opioid receptor or kappa opioid receptor, abbreviated KOR or KOP for its ligand ketazocine, is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the OPRK1 gene. The KOR is coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and is one of four related receptors that bind opioid-like compounds in the brain and are responsible for mediating the effects of these compounds. These effects include altering nociception, consciousness, motor control, and mood. Dysregulation of this receptor system has been implicated in alcohol and drug addiction.
Lipotropin is the name for two hormones produced by the cleavage of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC). The anterior pituitary gland produces the pro-hormone POMC, which is then cleaved again to form adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) and β-lipotropin (β-LPH).

The nociceptin opioid peptide receptor (NOP), also known as the nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) receptor or kappa-type 3 opioid receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OPRL1 gene. The nociceptin receptor is a member of the opioid subfamily of G protein-coupled receptors whose natural ligand is the 17 amino acid neuropeptide known as nociceptin (N/OFQ). This receptor is involved in the regulation of numerous brain activities, particularly instinctive and emotional behaviors. Antagonists targeting NOP are under investigation for their role as treatments for depression and Parkinson's disease, whereas NOP agonists have been shown to act as powerful, non-addictive painkillers in non-human primates.

Toll-like receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLR4 gene. TLR4 is a transmembrane protein, member of the toll-like receptor family, which belongs to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family. Its activation leads to an intracellular signaling pathway NF-κB and inflammatory cytokine production which is responsible for activating the innate immune system.

Opioid-binding protein/cell adhesion molecule is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OPCML gene.

CDK5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDK5RAP2 gene. It has necessary roles in the formation and stability of microtubules from the centrosome and has been found to be linked to human brain size variation in males. Multiple transcript variants exist for this gene, but the full-length nature of only two has been determined.

Opioid growth factor receptor, also known as OGFr or the ζ-opioid receptor, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the OGFR gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for opioid growth factor (OGF), also known as [Met(5)]-enkephalin. The endogenous ligand is thus a known opioid peptide, and OGFr was originally discovered and named as a new opioid receptor zeta (ζ). However it was subsequently found that it shares little sequence similarity with the other opioid receptors, and has quite different function.

There is much to be discovered about the evolution of the brain and the principles that govern it. While much has been discovered, not everything currently known is well understood. The evolution of the brain has appeared to exhibit diverging adaptations within taxonomic classes such as Mammalia and more vastly diverse adaptations across other taxonomic classes. Brain to body size scales allometrically. This means as body size changes, so do other physiological, anatomical, and biochemical constructs connecting the brain to the body. Small bodied mammals have relatively large brains compared to their bodies whereas large mammals have a smaller brain to body ratios. If brain weight is plotted against body weight for primates, the regression line of the sample points can indicate the brain power of a primate species. Lemurs for example fall below this line which means that for a primate of equivalent size, we would expect a larger brain size. Humans lie well above the line indicating that humans are more encephalized than lemurs. In fact, humans are more encephalized compared to all other primates. This means that human brains have exhibited a larger evolutionary increase in its complexity relative to its size. Some of these evolutionary changes have been found to be linked to multiple genetic factors such as, proteins and other organelles.

Adrenorphin, also sometimes referred to as metorphamide, is an endogenous, C-terminally amidated, opioid octapeptide (Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Met-Arg-Arg-Val-NH2, YGGFMRRV-NH2) that is produced from proteolytic cleavage of proenkephalin A and is widely distributed throughout the mammalian brain. It was named based on the fact that it was originally detected in human phaeochromocytoma tumour derived from the adrenal medulla, and was subsequently found in normal human and bovine adrenal medulla as well. Adrenorphin exhibits potent opioid activity, acting as a balanced μ- and κ-opioid receptor agonist while having no effects on δ-opioid receptors. It possesses analgesic and respiratory depressive properties.

α-Neoendorphin is an endogenous opioid peptide with a decapeptide structure and the amino acid sequence Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Lys-Tyr-Pro-Lys.
Neoendorphins are a group of endogenous opioid peptides derived from the proteolytic cleavage of prodynorphin. They include α-neoendorphin and β-neoendorphin. The α-neoendorphin is present in greater amounts in the brain than β-neoendorphin. Both are products of the dynorphin gene, which also expresses dynorphin A, dynorphin A-(1-8), and dynorphin B. These opioid neurotransmitters are especially active in Central Nervous System receptors, whose primary function is pain sensation. These peptides all have the consensus amino acid sequence of Try-Gly-Gly-Phe-Met (met-enkephalin) or Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu ( leu-enkephalin). Binding of neoendorphins to opioid receptors (OPR), in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons results in the reduction of time of calcium-dependent action potential. The α-neoendorphins bind OPRD1(delta), OPRK1(kappa), and OPRM1 (mu) and β-neoendorphin bind OPRK1.
References
- ↑ Charles Chavkin; William J Shoemaker; Jacquiline F. McGinti; Alejandro Bayon; Floyd E. Bloom (March 1985). "Characterization of the Prodynorphin and Proenkephalin Neuropeptide Systems in Rat Hippocampus" (PDF). Journal of Neuroscience. 5 (3): 806–816. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.05-03-00808.1985 . PMC 6565022 . PMID 3838345.
- ↑ Alberto Pérez-Rosado; María Gómez; Jorge Manzanares; José A. Ramos; Javier Fernándezruiz (2002). "Changes in prodynorphin and POMC gene expression in several brain regions of rat fetuses prenatally exposed to Δ-tetrahydrocannabinol". Neurotoxicity Research. 4 (3): 211–218. doi:10.1080/10298420290023936. PMID 12829401. S2CID 25878244.
- ↑ Chang-wang Wang; Min Ma; Wei-guang Lu; Ru-qin Luo (11 September 2019). "Association between prodynorphin gene polymorphisms and opioid dependence susceptibility: a meta-analysis". BMC Psychiatry. 19 (281). doi: 10.1186/s12888-019-2272-7 . PMID 31510971. S2CID 202550535.