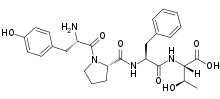
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid agonist used for chronic pain and also for opioid dependence. It is used to treat chronic pain, and it is also used to treat addiction to heroin or other opioids. Prescribed for daily use, the medicine relieves cravings and removes withdrawal symptoms. Detoxification using methadone can be accomplished in less than a month, or it may be done gradually over as long as six months. While a single dose has a rapid effect, maximum effect can take up to five days of use. The pain-relieving effects last about six hours after a single dose. After long-term use, in people with normal liver function, effects last 8 to 36 hours. Methadone is usually taken by mouth and rarely by injection into a muscle or vein.

The term narcotic originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates and opioids, commonly morphine and heroin, as well as derivatives of many of the compounds found within raw opium latex. The primary three are morphine, codeine, and thebaine.

Naloxone, sold under the brand name Narcan among others, is a medication used to reverse the effects of opioids. It is commonly used to counter decreased breathing in opioid overdose. Naloxone may also be combined with an opioid, to decrease the risk of misuse through injection. Effects begin within two minutes when given intravenously, and within five minutes when injected into a muscle. The medicine can also be administered by spraying it into a person's nose. Naloxone commonly blocks the effects of opioids for 30 to 90 minutes. Multiple doses may be required, as the duration of action of some opioids is greater than that of naloxone.

Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, reversing opioid overdose, and suppressing cough. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for veterinary use. Opioids are also frequently used non-medically for their euphoric effects or to prevent withdrawal. Opioids can cause death and have been used for executions in the United States.
Opioid receptors are a group of inhibitory G protein-coupled receptors with opioids as ligands. The endogenous opioids are dynorphins, enkephalins, endorphins, endomorphins and nociceptin. The opioid receptors are ~40% identical to somatostatin receptors (SSTRs). Opioid receptors are distributed widely in the brain, in the spinal cord, on peripheral neurons, and digestive tract.

Opioid use disorder (OUD) is a substance use disorder relating to the use of an opioid. Any such disorder causes significant impairment or distress. Signs of the disorder include a strong desire to use opioids, increased tolerance to opioids, difficulty fulfilling obligations, trouble reducing use, and withdrawal symptoms with discontinuation. Opioid withdrawal symptoms may include nausea, muscle aches, diarrhea, trouble sleeping, agitation, and a low mood. Addiction and dependence are components of a substance use disorder. Complications may include opioid overdose, suicide, HIV/AIDS, hepatitis C, and problems at school, work, or home.

Buprenorphine is an opioid used to treat opioid use disorder, acute pain, and chronic pain. It can be used under the tongue (sublingual), in the cheek (buccal), by injection, as a skin patch (transdermal), or as an implant. For opioid use disorder, it is typically started when withdrawal symptoms have begun and for the first two days of treatment under direct observation of a health-care provider. In the United States, the combination formulation of buprenorphine/naloxone (Suboxone) is usually prescribed to discourage misuse by injection. Maximum pain relief is generally within an hour with effects up to 24 hours. Buprenorphine affects different types of opioid receptors in different ways. Depending on the type of receptor, it may be an agonist, partial agonist, or antagonist. In the treatment of opioid use disorder buprenorphine is an agonist/antagonist, meaning that it relieves withdrawal symptoms from other opioids and induces some euphoria, but also blocks the ability for many other opioids, including heroin, to cause an effect. Unlike full agonists like heroin or methadone, buprenorphine has a ceiling effect, such that taking more medicine will not increase the effects of the drug.

Naltrexone, sold under the brand name Revia among others, is a medication primarily used to manage alcohol or opioid use disorder by reducing cravings and feelings of euphoria associated with substance use disorder. It has also been found to be effective in the treatment of other addictions and may be used for them off-label. An opioid-dependent person should not receive naltrexone before detoxification. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a muscle. Effects begin within 30 minutes. A decreased desire for opioids may take a few weeks to occur.
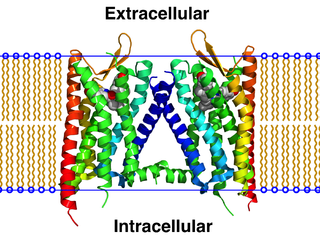
The κ-opioid receptor or kappa opioid receptor, abbreviated KOR or KOP for its ligand ketazocine, is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the OPRK1 gene. The KOR is coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and is one of four related receptors that bind opioid-like compounds in the brain and are responsible for mediating the effects of these compounds. These effects include altering nociception, consciousness, motor control, and mood. Dysregulation of this receptor system has been implicated in alcohol and drug addiction.

The μ-opioid receptors (MOR) are a class of opioid receptors with a high affinity for enkephalins and beta-endorphin, but a low affinity for dynorphins. They are also referred to as μ(mu)-opioid peptide (MOP) receptors. The prototypical μ-opioid receptor agonist is morphine, the primary psychoactive alkaloid in opium and for which the receptor was named, with mu being the Greek letter m. It is an inhibitory G-protein coupled receptor that activates the Gi alpha subunit, inhibiting adenylate cyclase activity, lowering cAMP levels.
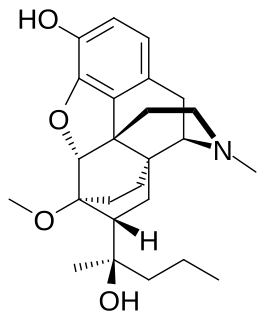
Dihydroetorphine was developed by K. W. Bentley at McFarlan-Smith in the 1960s and is a potent opioid analgesic used mainly in China. It is a derivative of the better-known opioid etorphine, a very potent veterinary painkiller and anesthetic medication used primarily for the sedation of large animals such as elephants, giraffes, and rhinos.

Nalorphine (INN), also known as N-allylnormorphine, is a mixed opioid agonist–antagonist with opioid antagonist and analgesic properties. It was introduced in 1954 and was used as an antidote to reverse opioid overdose and in a challenge test to determine opioid dependence.
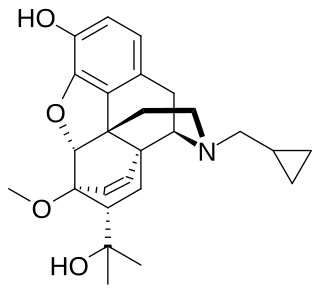
Cyprenorphine (M285), N-cyclo-propylmethyl-6,14-endoetheno-7α-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)-6,7,8,14-tetrahydronororipavine, is an opioid drug. It is related to more well-known opioids such as buprenorphine, which is used as an analgesic and for the treatment of opioid addiction, and diprenorphine, which is used as an antidote to reverse the effects of other opioids. It is roughly 35 times as strong as nalorphine.

SNC-80 is an opioid analgesic compound that selectively activates μ–δ opioid receptor heteromers and is used in scientific research. It was discovered in 1994.

Xorphanol (INN), also known as xorphanol mesylate (USAN), is an opioid analgesic of the morphinan family that was never marketed.

SC-17599 is a steroid derivative drug discovered in 1968 which acts as a selective μ-opioid receptor agonist, with little or no affinity for the δ-opioid or κ-opioid receptors. It is an active analgesic in vivo, more potent than codeine or pethidine but slightly less potent than morphine, and produces similar effects to morphine in animals but with less sedation

An opiate, in classical pharmacology, is a substance derived from opium. In more modern usage, the term opioid is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain. Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium poppy plant Papaver somniferum. The psychoactive compounds found in the opium plant include morphine, codeine, and thebaine. Opiates have long been used for a variety of medical conditions with evidence of opiate trade and use for pain relief as early as the eighth century AD. Opiates are considered drugs with moderate to high abuse potential and are listed on various "Substance-Control Schedules" under the Uniform Controlled Substances Act of the United States of America.
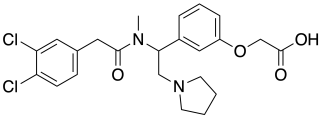
ICI-204,448 is a drug which acts as a potent and peripherally selective κ-opioid agonist, with possible uses in the treatment of heart attack as well as anti-itching effects. It is used in research to distinguish centrally from peripherally mediated kappa opioid receptor effects.

Quadazocine (WIN-44,441) is an opioid antagonist of the benzomorphan family which is used in scientific research. It acts as a silent antagonist at all three of the major opioid receptors—μ, κ, and δ, but with a significant preference in affinity for the μ receptor and the κ2 subtype. As such, it has been touted as a "κ2-selective" antagonist, though this is not entirely accurate on account of its similar affinity for the μ receptor. As would be expected, quadazocine reverses the effects of opioid agonists like morphine and fentanyl in animals.

AT-076 is a so-called opioid "pan" antagonist and is the first reasonably balanced antagonist known of all four opioid receptor types. It acts as a silent antagonist of all four of the opioid receptors, behaving as a competitive antagonist of the μ-opioid receptor and δ-opioid receptor and as a noncompetitive antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor and nociceptin receptor. AT-076 was derived from the selective κ-opioid receptor antagonist JDTic via removal of the 3,4-dimethyl group of the trans-(3R,4R)-dimethyl-4-(3-hydroxyphenyl)piperidine antagonist scaffold, which increased affinity for the nociceptin receptor by 10-fold and for the μ- and δ-opioid receptors by 3-6-fold.