
Hyperalgesia is an abnormally increased sensitivity to pain, which may be caused by damage to nociceptors or peripheral nerves and can cause hypersensitivity to stimulus. Prostaglandins E and F are largely responsible for sensitizing the nociceptors. Temporary increased sensitivity to pain also occurs as part of sickness behavior, the evolved response to infection.

Etorphine (M99) is a semi-synthetic opioid possessing an analgesic potency approximately 1,000–3,000 times that of morphine. It was first prepared in 1960 from oripavine, which does not generally occur in opium poppy extract but rather the related plants Papaver orientale and Papaver bracteatum. It was reproduced in 1963 by a research group at MacFarlan Smith in Gorgie, Edinburgh, led by Kenneth Bentley. It can be produced from thebaine.

An opioid antagonist, or opioid receptor antagonist, is a receptor antagonist that acts on one or more of the opioid receptors.

Nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ), a 17-amino acid neuropeptide, is the endogenous ligand for the nociceptin receptor. Nociceptin acts as a potent anti-analgesic, effectively counteracting the effect of pain-relievers; its activation is associated with brain functions such as pain sensation and fear learning.

The nociceptin opioid peptide receptor (NOP), also known as the nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) receptor or kappa-type 3 opioid receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OPRL1 gene. The nociceptin receptor is a member of the opioid subfamily of G protein-coupled receptors whose natural ligand is the 17 amino acid neuropeptide known as nociceptin (N/OFQ). This receptor is involved in the regulation of numerous brain activities, particularly instinctive and emotional behaviors. Antagonists targeting NOP are under investigation for their role as treatments for depression and Parkinson's disease, whereas NOP agonists have been shown to act as powerful, non-addictive painkillers in non-human primates.

Femoxetine is a drug related to paroxetine that was being developed as an antidepressant by Danish pharmaceutical company Ferrosan in 1975 before acquisition of the company by Novo Nordisk. It acts as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). Development was halted to focus attention on paroxetine instead, as femoxetine could not be administered as a daily pill.

The alpha-2C adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRA2C, is an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it.

Metabotropic glutamate receptor 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRM8 gene.
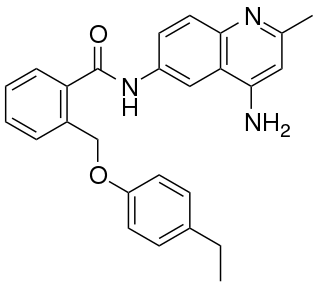
JTC-801 is an opioid analgesic drug used in scientific research.

NNC 63-0532 is a nociceptoid drug used in scientific research. It acts as a potent and selective agonist for the nociceptin receptor, also known as the ORL-1 receptor.

SB-612,111 is an opioid receptor ligand which is a potent and selective antagonist for the nociceptin receptor (ORL-1), several times more potent than the older drug J-113,397. It does not have analgesic effects in its own right, but prevents the development of hyperalgesia, and also shows antidepressant effects in animal studies.

Ro64-6198 is an opioid drug used in scientific research. It acts as a potent and selective agonist for the nociceptin receptor, also known as the ORL-1 receptor, with over 100x selectivity over the other opioid receptors. It produces anxiolytic effects in animal studies equivalent to those of benzodiazepine drugs, but has no anticonvulsant effects and does not produce any overt effects on behaviour. However it does impair short-term memory, and counteracts stress-induced anorexia. It also has antitussive effects, and reduces the rewarding and analgesic effects of morphine, although it did not prevent the development of dependence. It has been shown to reduce alcohol self-administration in animals and suppressed relapses in animal models of alcoholism, and ORL-1 agonists may have application in the treatment of alcoholism.
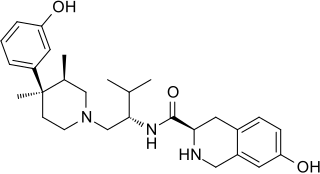
JDTic is a selective, long-acting ("inactivating") antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor (KOR). JDTic is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative, distantly related structurally to analgesics such as pethidine and ketobemidone, and more closely to the MOR antagonist alvimopan. In addition, it is structurally distinct from other KOR antagonists such as norbinaltorphimine. JDTic has been used to create crystal structures of KOR [ PDB: 4DJH, 6VI4].

MCOPPB is a drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the nociceptin receptor, with a pKi of 10.07 and much weaker activity at other opioid receptors. It has only moderate affinity for the mu opioid receptor, weak affinity for the kappa opioid receptor and negligible binding at the delta opioid receptor. In animal studies, MCOPPB produces potent anxiolytic effects, with no inhibition of memory or motor function, and only slight sedative side effects which do not appear until much higher doses than the effective anxiolytic dose range.

Cebranopadol is an opioid analgesic of the benzenoid class which is currently under development internationally by Grünenthal, a German pharmaceutical company, and its partner Depomed, a pharmaceutical company in the United States, for the treatment of a variety of different acute and chronic pain states. As of November 2014, it is in phase III clinical trials.

AT-076 is a so-called opioid "pan" antagonist and is the first reasonably balanced antagonist known of all four opioid receptor types. It acts as a silent antagonist of all four of the opioid receptors, behaving as a competitive antagonist of the μ-opioid receptor and δ-opioid receptor and as a noncompetitive antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor and nociceptin receptor. AT-076 was derived from the selective κ-opioid receptor antagonist JDTic via removal of the 3,4-dimethyl group of the trans-(3R,4R)-dimethyl-4-(3-hydroxyphenyl)piperidine antagonist scaffold which increased affinity for the nociceptin receptor by 10-fold and for the μ- and δ-opioid receptors by 3-6-fold.
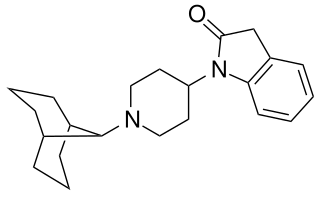
SR-16435 is a drug which acts as a potent partial agonist at both the μ-opioid receptor and nociceptin receptor. In animal studies it was found to be a potent analgesic, with results suggestive of reduced development of tolerance and increased activity against neuropathic pain compared to classic μ-selective agonists.

Sunobinop is a high affinity small molecule nociceptin receptor partial agonist.

Ro65-6570 is an opioid drug. It has a potential use in preventing the addiction to other opioids.

SCH-221510 is an experimental opioid drug. It has potential as an analgesic and as a treatment to addiction of certain drugs.





















