Contents
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
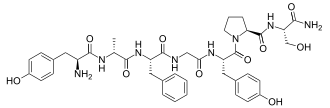
| Other names Tyrosyl-alanyl-phenylalanyl-glycyl-tyrosyl-prolyl-serinamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C40H50N8O10 | |
| Molar mass | 802.886 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Dermorphin is a hepta-peptide first isolated from the skin of South American frogs belonging to the genus Phyllomedusa . [1] The peptide is a natural opioid that binds as an agonist with high potency and selectivity to mu opioid receptors. [2] [3] Dermorphin is about 30–40 times more potent than morphine. [4] The amino acid sequence of dermorphin is H-Tyr-D-Ala-Phe-Gly-Tyr-Pro-Ser-NH2.
Dermorphin is not found in humans or other mammals and similar D-amino acid peptides have only been found in bacteria, amphibians, and molluscs. [5] Dermorphin appears to be made in these through an unusual posttranslational modification carried out by an amino acid isomerase. [6] This unusual process is needed because the D-alanine in this peptide is not among the 20 amino acids coded for in the genetic code and thus the peptide cannot be synthesized in the usual way from the encodings in the genome of an organism.