
β-Carboline (9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole) represents the basic chemical structure for more than one hundred alkaloids and synthetic compounds. The effects of these substances depend on their respective substituent. Natural β-carbolines primarily influence brain functions but can also exhibit antioxidant effects. Synthetically designed β-carboline derivatives have recently been shown to have neuroprotective, cognitive enhancing and anti-cancer properties.
The Fischer indole synthesis is a chemical reaction that produces the aromatic heterocycle indole from a (substituted) phenylhydrazine and an aldehyde or ketone under acidic conditions. The reaction was discovered in 1883 by Emil Fischer. Today antimigraine drugs of the triptan class are often synthesized by this method.
The Pictet–Spengler reaction is a chemical reaction in which a β-arylethylamine undergoes condensation with an aldehyde or ketone followed by ring closure. The reaction was first discovered in 1911 by Amé Pictet and Theodor Spengler. Traditionally, an acidic catalyst in protic solvent was employed with heating; however, the reaction has been shown to work in aprotic media in superior yields and sometimes without acid catalysis. The Pictet–Spengler reaction can be considered a special case of the Mannich reaction, which follows a similar reaction pathway. The driving force for this reaction is the electrophilicity of the iminium ion generated from the condensation of the aldehyde and amine under acid conditions. This explains the need for an acid catalyst in most cases, as the imine is not electrophilic enough for ring closure but the iminium ion is capable of undergoing the reaction.
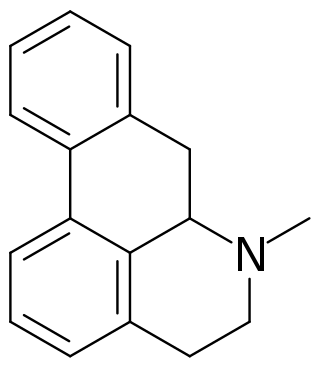
Aporphine is an alkaloid with the chemical formula C17H17N. It is the core chemical substructure of the aporphine alkaloids, a subclass of quinoline alkaloids. It can exist in either of two enantiomeric forms, (R)-aporphine and (S)-aporphine.

5-Bromo-DMT (5-bromo-N,N-dimethyltryptamine) is a psychedelic brominated indole alkaloid found in the sponges Smenospongia aurea and Smenospongia echina, as well as in Verongula rigida alongside 5,6-Dibromo-DMT and seven other alkaloids. It is the 5-bromo derivative of DMT, a psychedelic found in many plants and animals.

Spirotryprostatin B is an indolic alkaloid found in the Aspergillus fumigatus fungus that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. Spirotryprostatin B and several other indolic alkaloids have been found to have anti-mitotic properties, and as such they have become of great interest as anti-cancer drugs. Because of this, the total syntheses of these compounds is a major pursuit of organic chemists, and a number of different syntheses have been published in the chemical literature.

Akuammine (vincamajoridine) is an indole alkaloid. It is the most abundant alkaloid found in the seeds from the tree Picralima nitida, commonly known as akuamma, comprising 0.56% of the dried powder. It has also been isolated from Vinca major. Akuammine is structurally related to yohimbine, mitragynine and more distantly Voacangine, all of which are alkaloid plant products with pharmacological properties.

Indole is an organic compound with the formula C6H4CCNH3. Indole is classified as an aromatic heterocycle. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indoles are derivatives of indole where one or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by substituent groups. Indoles are widely distributed in nature, most notably as amino acid tryptophan and neurotransmitter serotonin.

Ajmalicine, also known as δ-yohimbine or raubasine, is an antihypertensive drug used in the treatment of high blood pressure. It has been marketed under numerous brand names including Card-Lamuran, Circolene, Cristanyl, Duxil, Duxor, Hydroxysarpon, Iskedyl, Isosarpan, Isquebral, Lamuran, Melanex, Raunatin, Saltucin Co, Salvalion, and Sarpan. It is an alkaloid found naturally in various plants such as Rauvolfia spp., Catharanthus roseus, and Mitragyna speciosa.

Conolidine is an indole alkaloid. Preliminary reports suggest that it could provide analgesic effects with few of the detrimental side-effects associated with opioids such as morphine, though at present it has only been evaluated in mouse models.
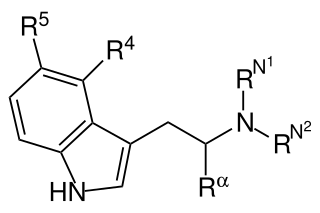
Substituted tryptamines, or simply tryptamines, also known as serotonin analogues (i.e., 5-hydroxytryptamine analogues), are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all tryptamines contain an indole ring, joined to an amino (NH2) group via an ethyl (−CH2–CH2−) sidechain. In substituted tryptamines, the indole ring, sidechain, and/or amino group are modified by substituting another group for one of the hydrogen (H) atoms.

Gelsemine (C20H22N2O2) is an indole alkaloid isolated from flowering plants of the genus Gelsemium, a plant native to the subtropical and tropical Americas, and southeast Asia, and is a highly toxic compound that acts as a paralytic, exposure to which can result in death. It has generally potent activity as an agonist of the mammalian glycine receptor, the activation of which leads to an inhibitory postsynaptic potential in neurons following chloride ion influx, and systemically, to muscle relaxation of varying intensity and deleterious effect. Despite its danger and toxicity, recent pharmacological research has suggested that the biological activities of this compound may offer opportunities for developing treatments related to xenobiotic or diet-induced oxidative stress, and of anxiety and other conditions, with ongoing research including attempts to identify safer derivatives and analogs to make use of gelsemine's beneficial effects.

Picralima is a plant genus in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1896. It contains only one known species, Picralima nitida, native to tropical Africa.
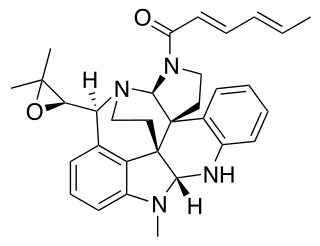
Communesin B is a cytotoxic chemical compound isolated from Penicillium strains found on the marine alga Ulva intestinalis. It exhibits cytotoxicity in vitro against human lung carcinoma, prostate carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, cervical adenocarcinoma, and breast adenocarcinoma cell lines.

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.

Mitragynine pseudoindoxyl is a rearrangement product of 7-hydroxymitragynine, an active metabolite of mitragynine.
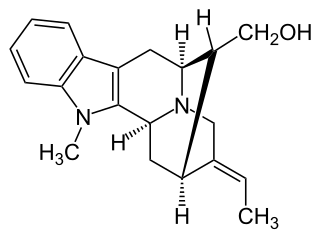
Affinisine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid which can be isolated from plants of the genus Tabernaemontana. Structurally, it can be considered a member of the sarpagine alkaloid family and may be synthesized from tryptophan via a Pictet-Spengler reaction.

Apparicine is a monoterpenoid tricyclic indole alkaloid. It is named after Apparicio Duarte, a Brazilian botanist who studied the Aspidosperma species from which apparicine was first isolated. It was the first member of the vallesamine group of indole alkaloids to be isolated and have its structure established, which was first published in 1965. It has also been known by the synonyms gomezine, pericalline, and tabernoschizine.

14-Hydroxygelsenicine (HGE) is a gelsedine-type indole alkaloid naturally found in some plants of the Gelsemium genus. G. elegans was used in traditional Chinese medicine as a remedy for a plethora of conditions such as skin ulcers and dermatitis, pain related to cancer, rheumatic arthritis, psoriasis as well as to treat bone fractures. It can also be found under the names “Duan Chang Cao”, “Gou Wen” and “heartbreak grass”. G. elegans is also known for its toxic effects; it is used by hilltribes of southeastern Asia as an effective means of committing suicide and has been linked to certain types of toxic honey, where HGE was the most abundant component. Gelsedine-type alkaloids from G. elegans usually express high toxicity, with gelsenicine being one of the most toxic. However, toxicity of HGE has not yet been thoroughly researched. More recent studies have shown that alkaloids derived from G. elegans have anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and immunomodulation properties, with the toxic dose being close to the therapeutic dose.

















