
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The 5-HT2A receptor is a cell surface receptor, but has several intracellular locations.

The serotonin 1A receptor is a subtype of serotonin receptors, or 5-HT receptors, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarization and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene.

The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR6 denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor.

WAY-100635 is a piperazine drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It was originally believed to act as a selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, but subsequent research showed that it also acts as potent full agonist at the D4 receptor. It is sometimes referred to as a silent antagonist at the former receptor. It is closely related to WAY-100135.
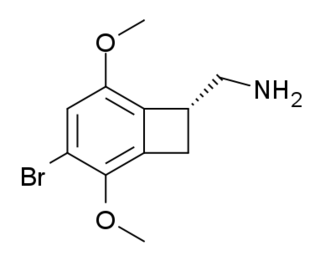
TCB-2 is a hallucinogen discovered in 2006 by Thomas McLean working in the lab of David Nichols at Purdue University. It is a conformationally-restricted derivative of the phenethylamine 2C-B, also a hallucinogen, and acts as a potent agonist for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors with a Ki of 0.26 nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor. In drug-substitution experiments in rats, TCB-2 was found to be of similar potency to both LSD and Bromo-DragonFLY, ranking it among the most potent phenethylamine hallucinogens yet discovered. This high potency and selectivity has made TCB-2 useful for distinguishing 5-HT2A mediated responses from those produced by other similar receptors. TCB-2 has similar but not identical effects in animals to related phenethylamine hallucinogens such as DOI, and has been used for studying how the function of the 5-HT2A receptor differs from that of other serotonin receptors in a number of animal models, such as studies of cocaine addiction and neuropathic pain.

SB-258585 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as a potent, selective and orally active 5-HT6 receptor antagonist, with a Ki of 8.9nM. It is used in its 125I radiolabelled form to map the distribution of 5-HT6 receptors in the brain.

SB-271046 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It was one of the first selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonists to be discovered, and was found through high-throughput screening of the SmithKline Beecham Compound Bank using cloned 5-HT6 receptors as a target, with an initial lead compound being developed into SB-271046 through a structure-activity relationship (SAR) study. SB-271046 was found to be potent and selective in vitro and had good oral bioavailability in vivo, but had poor penetration across the blood–brain barrier, so further SAR work was then conducted, which led to improved 5-HT6 antagonists such as SB-357,134 and SB-399,885.

Ro64-6198 is a opioid drug used in scientific research. It acts as a potent and selective agonist for the nociceptin receptor, also known as the ORL-1 receptor, with over 100x selectivity over the other opioid receptors. It produces anxiolytic effects in animal studies equivalent to those of benzodiazepine drugs, but has no anticonvulsant effects and does not produce any overt effects on behaviour. However it does impair short-term memory, and counteracts stress-induced anorexia. It also has antitussive effects, and reduces the rewarding and analgesic effects of morphine, although it did not prevent the development of dependence. It has been shown to reduce alcohol self-administration in animals and suppressed relapses in animal models of alcoholism, and ORL-1 agonists may have application in the treatment of alcoholism.

CP-94253 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective serotonin 5-HT1B receptor agonist, with approximately 25x and 40x selectivity over the closely related 5-HT1D and 5-HT1A receptors. It has a range of behavioral effects, based on animal testing. The effects include the following: promoting wakefulness by increasing dopamine release in the brain; reducing food intake and promoting satiety; enhancing the reinforcing effects of cocaine; and possible antidepressant effects. A recent study found that "Regardless of sex, CP94253 decreased cocaine intake after abstinence and during resumption of SA [self-administration] and decreased cue reactivity" suggesting that agonism of the inhibitory 5-HT2B receptors may diminish the cognitive reward of cocaine usage and increased use of the drug without a period of abstinence may be a product of test subjects trying to achieve a previously rewarding experience through larger dosages of cocaine.

Ro 04-6790 is a drug, developed by Hoffmann–La Roche, which has applications in scientific research. It acts as a potent and selective receptor antagonist for the 5-HT6 serotonin receptor subtype, with little or no affinity at other receptors. In common with other drugs of this class, Ro 04-6790 has nootropic effects in animals, and reduces the amnesia produced by memory-impairing drugs such as dizocilpine and scopolamine.
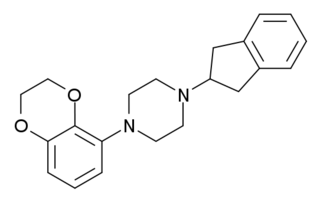
S-15535 is a phenylpiperazine drug which is a potent and highly selective 5-HT1A receptor ligand that acts as an agonist and antagonist at the presynaptic and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors, respectively. It has anxiolytic properties.

GR-127935 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist at the serotonin receptors 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D. It has little effect when given by itself but blocks the antiaggressive effect of 5-HT1B agonists, and alters release of serotonin in the brain, as well as reducing drug-seeking behaviour in cocaine addicted rats.

LY-379,268 is a drug that is used in neuroscience research, which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3).

WAY-208466 is a potent and highly selective full agonist of the 5-HT6 receptor. It increases GABA levels in the cerebral cortex and tolerance does not appear to occur to this action upon chronic administration. Animal studies have shown that WAY-208466 produces antidepressant and anxiolytic effects in rodents and it may also be useful in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder.
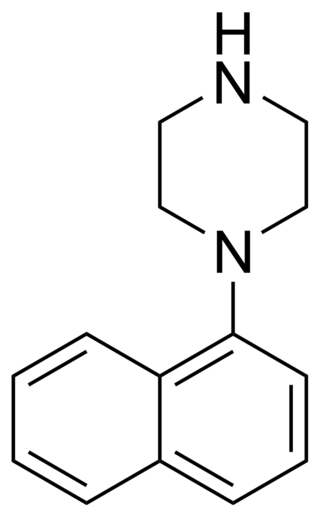
1-(1-Naphthyl)piperazine (1-NP) is a drug which is a phenylpiperazine derivative. It acts as a non-selective, mixed serotonergic agent, exerting partial agonism at the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1E, and 5-HT1F receptors, while antagonizing the 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors. It has also been shown to possess high affinity for the 5-HT3, 5-HT5A, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors, and may bind to 5-HT4 and the SERT as well. In animals it produces effects including hyperphagia, hyperactivity, and anxiolysis, of which are all likely mediated predominantly or fully by blockade of the 5-HT2C receptor.
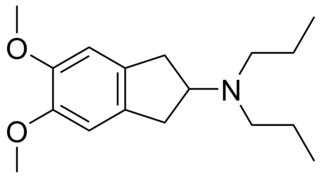
PNU-99,194(A) (or U-99,194(A)) is a drug which acts as a moderately selective D3 receptor antagonist with ~15-30-fold preference for D3 over the D2 subtype. Though it has substantially greater preference for D3 over D2, the latter receptor does still play some role in its effects, as evidenced by the fact that PNU-99,194 weakly stimulates both prolactin secretion and striatal dopamine synthesis, actions it does not share with the more selective (100-fold) D3 receptor antagonists S-14,297 and GR-103,691.
S-18986 is a positive allosteric modulator of the AMPA receptor related to cyclothiazide. It has nootropic and neuroprotective effects in animal studies, and induces both production of BDNF and AMPA-mediated release of noradrenaline and acetylcholine in the hippocampus and frontal cortex of the brain.

25CN-NBOH is a compound indirectly derived from the phenethylamine series of hallucinogens, which was discovered in 2014 at the University of Copenhagen. This compound is notable as one of the most selective agonist ligands for the 5-HT2A receptor yet discovered, with a pKi of 8.88 at the human 5-HT2A receptor and with 100x selectivity for 5-HT2A over 5-HT2C, and 46x selectivity for 5-HT2A over 5-HT2B. A tritiated version of 25CN-NBOH has also been accessed and used for more detailed investigations of the binding to 5-HT2 receptors and autoradiography.



















