A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.

Aniracetam, also known as N-anisoyl-2-pyrrolidinone, is a racetam which is sold in Europe as a prescription drug. It is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the United States as a prescription medication or dietary supplement. Despite the FDA's lack of approval, the drug is readily available over-the-counter in misbranded dietary supplements.

Dizocilpine (INN), also known as MK-801, is a pore blocker of the NMDA receptor, a glutamate receptor, discovered by a team at Merck in 1982. Glutamate is the brain's primary excitatory neurotransmitter. The channel is normally blocked with a magnesium ion and requires depolarization of the neuron to remove the magnesium and allow the glutamate to open the channel, causing an influx of calcium, which then leads to subsequent depolarization. Dizocilpine binds inside the ion channel of the receptor at several of PCP's binding sites thus preventing the flow of ions, including calcium (Ca2+), through the channel. Dizocilpine blocks NMDA receptors in a use- and voltage-dependent manner, since the channel must open for the drug to bind inside it. The drug acts as a potent anti-convulsant and probably has dissociative anesthetic properties, but it is not used clinically for this purpose because of the discovery of brain lesions, called Olney's lesions (see below), in laboratory rats. Dizocilpine is also associated with a number of negative side effects, including cognitive disruption and psychotic-spectrum reactions. It inhibits the induction of long term potentiation and has been found to impair the acquisition of difficult, but not easy, learning tasks in rats and primates. Because of these effects of dizocilpine, the NMDA receptor pore blocker ketamine is used instead as a dissociative anesthetic in human medical procedures. While ketamine may also trigger temporary psychosis in certain individuals, its short half-life and lower potency make it a much safer clinical option. However, dizocilpine is the most frequently used uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist in animal models to mimic psychosis for experimental purposes.
Ampakines or AMPAkines are a subgroup of AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulators with a benzamide or closely related chemical structure. They are also known as "CX compounds". Ampakines take their name from the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), a type of ionotropic glutamate receptor with which the ampakines interact and act as positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) of. Although all ampakines are AMPAR PAMs, not all AMPAR PAMs are ampakines.

A muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist, also simply known as a muscarinic agonist or as a muscarinic agent, is an agent that activates the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The muscarinic receptor has different subtypes, labelled M1-M5, allowing for further differentiation.
A nicotinic agonist is a drug that mimics the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The nAChR is named for its affinity for nicotine.

The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR6 denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor.
The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α7 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor implicated in long-term memory, consisting entirely of α7 subunits. As with other nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, functional α7 receptors are pentameric [i.e., (α7)5 stoichiometry].
Ispronicline is an experimental drug which acts as a partial agonist at neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It progressed to phase II clinical trials for the treatment of dementia and Alzheimer's disease, but is no longer under development.
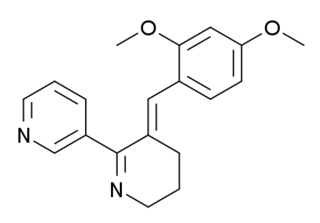
GTS-21 is a drug that has been shown to enhance memory and cognitive function. It has been studied for its potential therapeutic uses, particularly in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders.
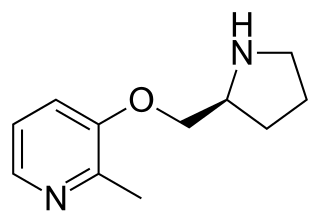
Pozanicline is a drug developed by Abbott, that has nootropic and neuroprotective effects. Animal studies suggested it useful for the treatment of ADHD and subsequent human trials have shown ABT-089 to be effective for this application. It binds with high affinity subtype-selective to the α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and has partial agonism to the α6β2 subtype, but not the α7 and α3β4 subtypes familiar to nicotine. It has particularly low tendency to cause side effects compared to other drugs in the class.
An H3 receptor antagonist is a type of antihistaminic drug used to block the action of histamine at H3 receptors.

Xanomeline is a small molecule muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist that was first synthesized in a collaboration between Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk as an investigational therapeutic being studied for the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders.

Neramexane is a drug related to memantine, which acts as an NMDA antagonist and has neuroprotective effects. It is being developed for various possible applications, including treatment of tinnitus, Alzheimer's disease, drug addiction and as an analgesic. Animal studies have also suggested antidepressant and nootropic actions so that this drug may be used for a wide range of potential applications. It also acts as a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist.

Sunifiram is an experimental drug which has antiamnesic effects in animal studies and with significantly higher potency than piracetam. Sunifiram is a molecular simplification of unifiram (DM-232). Another analogue is sapunifiram (MN-19). As of 2016, sunifiram had not been subjected to toxicology testing, nor to any human clinical trials, and is not approved for use anywhere in the world.

Altinicline is a drug which acts as an agonist at neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors with high selectivity for the α4β2 subtype. It stimulates release of dopamine and acetylcholine in the brain in both rodent and primate models, and progressed as far as Phase II clinical trials for Parkinson's disease, where "no antiparkinsonian or cognitive-enhancing effects were demonstrated", although its current status is unclear.
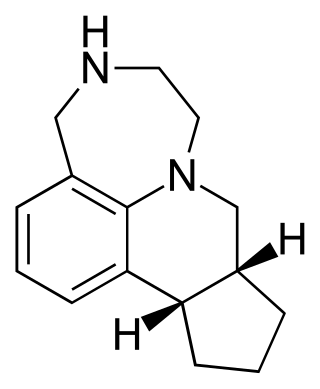
Vabicaserin was a novel antipsychotic and anorectic under development by Wyeth. As of 2010 it is no longer in clinical trials for the treatment of psychosis. It was also under investigation as an antidepressant but this indication appears to have been dropped as well.

N-Desmethylclozapine (NDMC), or norclozapine, is a major active metabolite of the atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine.

Xanomeline/trospium chloride, sold under the brand name Cobenfy, is a fixed-dose combination medication used for the treatment of schizophrenia. It contains xanomeline, a muscarinic agonist; and trospium chloride, a muscarinic antagonist. Xanomeline is a functionally preferring muscarinic M4 and M1 receptor agonist. Trospium chloride is a non-selective muscarinic antagonist.