Related Research Articles

Filariasis is a parasitic disease caused by an infection with roundworms of the Filarioidea type. These are spread by blood-feeding insects such as black flies and mosquitoes. They belong to the group of diseases called helminthiases.
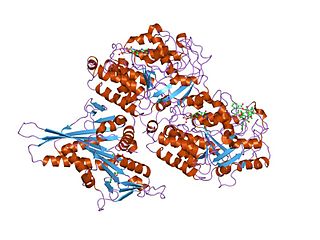
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division.

Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), it is used by the MEDLINE/PubMed article database and by NLM's catalog of book holdings. MeSH is also used by ClinicalTrials.gov registry to classify which diseases are studied by trials registered in ClinicalTrials.

Albendazole, also known as albendazolum, is a medication used for the treatment of a variety of parasitic worm infestations. It is useful for giardiasis, trichuriasis, filariasis, neurocysticercosis, hydatid disease, pinworm disease, and ascariasis, among other diseases. It is taken orally.

Echinococcus multilocularis is a small cyclophyllid tapeworm found extensively in the northern hemisphere. E. multilocularis, along with other members of the Echinococcus genus, produce diseases known as echinococcosis. Unlike E. granulosus,E. multilocularis produces many small cysts that spread throughout the internal organs of the infected animal. The resultant disease is called Alveolar echinococcosis, and is caused by ingesting the eggs of E. multilocularis.

Cutaneous larva migrans is a skin disease in humans, caused by the larvae of various nematode parasites of the hookworm family (Ancylostomatidae). These parasites live in the intestines of dogs, cats, and wild animals and should not be confused with other members of the hookworm family for which humans are definitive hosts, namely Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus.
Microsporidiosis is an opportunistic intestinal infection that causes diarrhea and wasting in immunocompromised individuals. It results from different species of microsporidia, a group of microbial (unicellular) fungi.
Antifibrinolytics are a class of medication that are inhibitors of fibrinolysis. Examples include aminocaproic acid and tranexamic acid. These lysine-like drugs interfere with the formation of the fibrinolytic enzyme plasmin from its precursor plasminogen by plasminogen activators which takes place mainly in lysine rich areas on the surface of fibrin.
Arsenicals are chemical compounds that contain arsenic. In a military context, the term arsenical refer to toxic arsenic compounds that are used as chemical warfare agents. This include blister agents, blood agents and vomiting agents.
A histamine agonist is a drug which causes increased activity at one or more of the four histamine receptor subtypes.
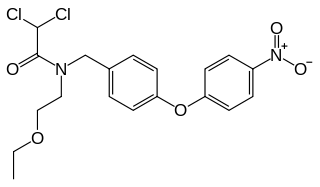
Etofamide is an antiprotozoal drug used in the treatment of amoebiasis.
An excitatory amino acid receptor agonist, or glutamate receptor agonist, is a chemical substance which agonizes one or more of the glutamate receptors.
An excitatory amino acid receptor antagonist, or glutamate receptor antagonist, is a chemical substance which antagonizes one or more of the glutamate receptors.
A coccidiostat is an antiprotozoal agent that acts upon Coccidia parasites.
An antitrichomonal agent is an antiprotozoal agent that acts on trichomonas parasites.

Anthelmintics or antihelminthics are a group of antiparasitic drugs that expel parasitic worms (helminths) and other internal parasites from the body by either stunning or killing them and without causing significant damage to the host. They may also be called vermifuges or vermicides. Anthelmintics are used to treat people who are infected by helminths, a condition called helminthiasis. These drugs are also used to treat infected animals.
References
- ↑ Anticestodal+agents at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ↑ MeSH list of agents 82000923