In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or in the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as α-olefins.
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis.

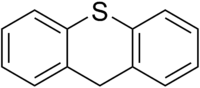
Phenothiazine, abbreviated PTZ, is an organic compound that has the formula S(C6H4)2NH and is related to the thiazine-class of heterocyclic compounds. Derivatives of phenothiazine are highly bioactive and have widespread use and rich history.

A triglyceride is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids. Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver, and are a major component of human skin oils.
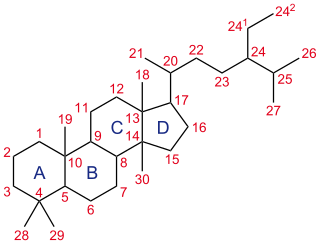
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule.

Tiotixene, or thiothixene is a typical antipsychotic agent currently sold under the brand name Navane which is predominantly utilised to treat acute and chronic schizophrenia. Beyond its primary indication, it can exhibit a variety of effects common to neuroleptic drugs including anxiolytic, anti-depressive, and anti-aggressive properties.
Organosulfur chemistry is the study of the properties and synthesis of organosulfur compounds, which are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature is abound with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is vital for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.
Thiazine is an organic compound containing a ring of four carbon, one nitrogen and one sulfur atom. There are three isomers of thiazine, 1,2-thiazine, 1,3-thiazine, and 1,4-thiazine, which differ by the arrangement of the nitrogen and sulfur atoms in the ring.

Flupentixol (INN), also known as flupenthixol, marketed under brand names such as Depixol and Fluanxol is a typical antipsychotic drug of the thioxanthene class. It was introduced in 1965 by Lundbeck. In addition to single drug preparations, it is also available as flupentixol/melitracen—a combination product containing both melitracen and flupentixol . Flupentixol is not approved for use in the United States. It is, however, approved for use in the UK, Australia, Canada, Russian Federation, South Africa, New Zealand, Philippines, Iran, Germany, and various other countries.

A cyclic compound is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where all the atoms are carbon, none of the atoms are carbon, or where both carbon and non-carbon atoms are present. Depending on the ring size, the bond order of the individual links between ring atoms, and their arrangements within the rings, carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds may be aromatic or non-aromatic; in the latter case, they may vary from being fully saturated to having varying numbers of multiple bonds between the ring atoms. Because of the tremendous diversity allowed, in combination, by the valences of common atoms and their ability to form rings, the number of possible cyclic structures, even of small size numbers in the many billions.

Propiomazine, sold under the brand name Propavan among others, is an antihistamine which is used to treat insomnia and to produce sedation and relieve anxiety before or during surgery or other procedures and in combination with analgesics as well as during labor. Propiomazine is a phenothiazine, but is not used therapeutically as a neuroleptic because it does not block dopamine receptors well.

Tricyclics are cyclic chemical compounds that contain three fused rings of atoms.
Cyamemazine (Tercian), also known as cyamepromazine, is a typical antipsychotic drug of the phenothiazine class which was introduced by Theraplix in France in 1972 and later in Portugal as well.

Prothipendyl, also known as azapromazine or phrenotropin, is an anxiolytic, antiemetic, and antihistamine of the azaphenothiazine group which is marketed in Europe and is used to treat anxiety and agitation in psychotic syndromes. It differs from promazine only by the replacement of one carbon atom with a nitrogen atom in the tricyclic ring system. Prothipendyl is said to not possess antipsychotic effects, and in accordance, appears to be a weaker dopamine receptor antagonist than other phenothiazines.

Selenopyrylium is an aromatic heterocyclic compound consisting of a six-membered ring with five carbon atoms and a positively charged selenium atom.

Metiapine is a typical antipsychotic medication of the dibenzothiazepine group. There is scarce research on the safety and efficacy of metiapine in humans, though limited human trials exist.

Flumezapine is an abandoned, investigational antipsychotic drug that was studied for the treatment of schizophrenia. Flumezapine failed clinical trials due to concern for liver and muscle toxicity. Flumezapine is structurally related to the common antipsychotic olanzapine—a point that was used against its manufacturer, Eli Lilly and Company, in a lawsuit in which generic manufacturers sought to void the patent on brand name olanzapine (Zyprexa). Although flumezapine does not differ greatly from olanzapine in terms of its structure, the difference was considered to be non-obvious, and Eli Lilly's patent rights on Zyprexa were upheld.
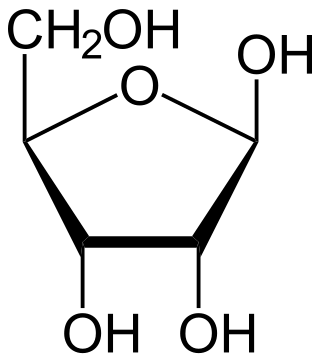
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H. The naturally-occurring form, d-ribose, is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this compound is necessary for coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. It has a structural analog, deoxyribose, which is a similarly essential component of DNA. l-ribose is an unnatural sugar that was first prepared by Emil Fischer and Oscar Piloty in 1891. It was not until 1909 that Phoebus Levene and Walter Jacobs recognised that d-ribose was a natural product, the enantiomer of Fischer and Piloty's product, and an essential component of nucleic acids. Fischer chose the name "ribose" as it is a partial rearrangement of the name of another sugar, arabinose, of which ribose is an epimer at the 2' carbon; both names also relate to gum arabic, from which arabinose was first isolated and from which they prepared l-ribose.