
Dopamine receptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are prominent in the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). Dopamine receptors activate different effectors through not only G-protein coupling, but also signaling through different protein interactions. The neurotransmitter dopamine is the primary endogenous ligand for dopamine receptors.

A dopamine antagonist, also known as an anti-dopaminergic and a dopamine receptor antagonist (DRA), is a type of drug which blocks dopamine receptors by receptor antagonism. Most antipsychotics are dopamine antagonists, and as such they have found use in treating schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and stimulant psychosis. Several other dopamine antagonists are antiemetics used in the treatment of nausea and vomiting.

Tiotixene, or thiothixene, sold under the brand name Navane among others, is a typical antipsychotic of the thioxanthene class which is related to chlorprothixene and is used in the treatment of psychoses like schizophrenia and bipolar mania. It was introduced in the United States in 1967 by Pfizer.

The dopamine receptor D4 is a dopamine D2-like G protein-coupled receptor encoded by the DRD4 gene on chromosome 11 at 11p15.5.

Rotigotine, sold under the brand name Neupro among others, is a dopamine agonist of the non-ergoline class of medications indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome. It is formulated as a once-daily transdermal patch which provides a slow and constant supply of the drug over the course of 24 hours.
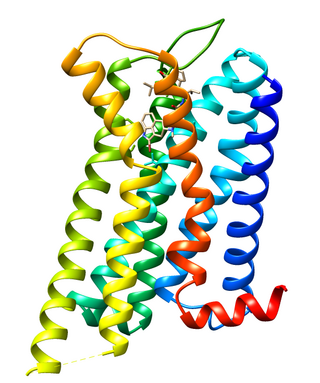
Dopamine receptor D2, also known as D2R, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the DRD2 gene. After work from Paul Greengard's lab had suggested that dopamine receptors were the site of action of antipsychotic drugs, several groups, including those of Solomon Snyder and Philip Seeman used a radiolabeled antipsychotic drug to identify what is now known as the dopamine D2 receptor. The dopamine D2 receptor is the main receptor for most antipsychotic drugs. The structure of DRD2 in complex with the atypical antipsychotic risperidone has been determined.

SB-277,011A is a drug which acts as a potent and selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, which is around 80-100x selective for D3 over D2, and lacks any partial agonist activity.

Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA1 gene.

The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 4 (CHRM4), is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the CHRM4 gene.

Dopamine receptor D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD3 gene.

N-Arachidonoyl dopamine (NADA) is an endocannabinoid that acts as an agonist of the CB1 receptor and the transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) ion channel. NADA was first described as a putative endocannabinoid (agonist for the CB1 receptor) in 2000 and was subsequently identified as an endovanilloid (agonist for TRPV1) in 2002. NADA is an endogenous arachidonic acid based lipid found in the brain of rats, with especially high concentrations in the hippocampus, cerebellum, and striatum. It activates the TRPV1 channel with an EC50 of approximately of 50 nM which makes it the putative endogenous TRPV1 agonist.
SB-242084 is a psychoactive drug and research chemical which acts as a selective antagonist for the 5HT2C receptor. It has anxiolytic effects, and enhances dopamine signalling in the limbic system, as well as having complex effects on the dopamine release produced by cocaine, increasing it in some brain regions but reducing it in others. It has been shown to increase the effectiveness of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class of antidepressants, and may also reduce their side effects. In animal studies, SB-242084 produced stimulant-type activity and reinforcing effects, somewhat similar to but much weaker than cocaine or amphetamines.
Fananserin (RP-62203) is a drug which acts as a potent antagonist at both the 5HT2A receptor, and the Dopamine D4 receptor, but without blocking other dopamine receptors such as D2. It has sedative and antipsychotic effects, and has been researched for the treatment of schizophrenia, although efficacy was less than expected and results were disappointing.
WAY-100135 is a serotonergic drug of the phenylpiperazine family which is used in scientific research. It acts as potent 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, and was originally believed to be highly selective, but further studies have demonstrated that it also acts as a partial agonist of the 5-HT1D receptor (pKi = 7.58; virtually the same affinity for 5-HT1A), and to a much lesser extent, of the 5-HT1B receptor (pKi = 5.82). These findings may have prompted the development of the related compound WAY-100635, another purportedly selective and even more potent 5-HT1A antagonist, which was synthesized shortly thereafter. However, WAY-100635 turned out to be non-selective as well, having been shown to act additionally as a potent D4 receptor agonist later on.

N-Desmethylclozapine (NDMC), or norclozapine, is a major active metabolite of the atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine. Unlike clozapine, it possesses intrinsic activity at the D2/D3 receptors, and acts as a weak partial agonist at these sites similarly to aripiprazole and bifeprunox. Notably, NDMC has also been shown to act as a potent and efficacious agonist at the M1 and δ-opioid receptors, unlike clozapine as well. It was hypothesized that on account of these unique actions, NDMC might underlie the clinical superiority of clozapine over other antipsychotics. However, clinical trials found NMDC itself ineffective in the treatment of schizophrenia. This may be because it possesses relatively low D2/D3 occupancy compared to 5-HT2 (<15% versus 64–79% at a dose of 10–60 mg/kg s.c. in animal studies). Albeit not useful in the treatment of positive symptoms on its own, it cannot be ruled out that NDMC may contribute to the efficacy of clozapine on cognitive and/or negative symptoms.

PD-168,077 is a drug which acts as a dopamine agonist selective for the D4 subtype, which is used for researching the role of D4 receptors in the brain, particularly relating to learning and memory. The propensity to induce penile erections in rats means it could be used for this also?
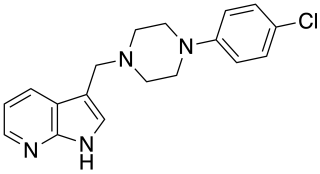
L-745,870 is a drug which acts as a dopamine receptor antagonist selective for the D4 subtype, and has antipsychotic effects in animal models, though it was not effective in human trials.

L-741,626 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the dopamine receptor D2. It has good selectivity over the related D3 and D4 subtypes and other receptors. L-741,626 is used for laboratory research into brain function and has proved particularly useful for distinguishing D2 mediated responses from those produced by the closely related D3 subtype, and for studying the roles of these subtypes in the action of cocaine and amphetamines in the brain.

F-15,063 is an orally active potential antipsychotic, and an antagonist at the D2/D3 receptors, partial agonist at the D4 receptor, and agonist at the 5-HT1A receptors. It has greater efficacy at the 5-HT1A receptors than other antipsychotics, such as clozapine, aripiprazole, and ziprasidone. This greater efficacy may lead to enhanced antipsychotic properties, as antipsychotics that lack 5-HT1A affinity are associated with increased risk of extrapyramidal symptoms, and lack of activity against the negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
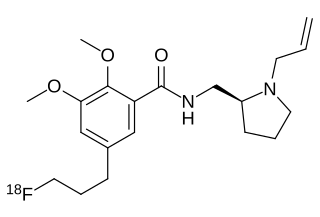
Fallypride is a high affinity dopamine D2/D3 receptor antagonist used in medical research, usually in the form of fallypride (18F) as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer in human studies.




















