
Pergolide, sold under the brand name Permax and Prascend (veterinary) among others, is an ergoline-based dopamine receptor agonist used in some countries for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Parkinson's disease is associated with reduced dopamine synthesis in the substantia nigra of the brain. Pergolide acts on many of the same receptors as dopamine to increase receptor activity.

The dopamine receptor D4 is a dopamine D2-like G protein-coupled receptor encoded by the DRD4 gene on chromosome 11 at 11p15.5.

Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine", a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain.

Dihydrexidine (DAR-0100) is a moderately selective full agonist at the dopamine D1 and D5 receptors. It has approximately 10-fold selectivity for D1 and D5 over the D2 receptor. Although dihydrexidine has some affinity for the D2 receptor, it has functionally selective (highly biased) D2 signaling, thereby explaining why it lacks D2 agonist behavioral qualities.

SKF-82,958 is a synthetic compound of the benzazepine class that acts as a D1/D5 receptor full agonist. SKF-82,958 and similar D1-like-selective full agonists like SKF-81,297 and 6-Br-APB produce characteristic anorectic effects, hyperactivity and self-administration in animals, with a similar but not identical profile to that of dopaminergic stimulants such as amphetamine. SKF-82,958 was also subsequently found to act as an agonist of ERα with negligible activity at ERβ, making it a subtype-selective estrogen.

A dopamine agonist is a compound that activates dopamine receptors. There are two families of dopamine receptors, D1-like and D2-like. They are all G protein-coupled receptors. D1- and D5-receptors belong to the D1-like family and the D2-like family includes D2, D3 and D4 receptors. Dopamine agonists are primarily used in the treatment of the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease, and to a lesser extent, in hyperprolactinemia and restless legs syndrome. They are also used off-label in the treatment of clinical depression. Impulse control disorders are associated with the use of dopamine agonists for whatever condition.
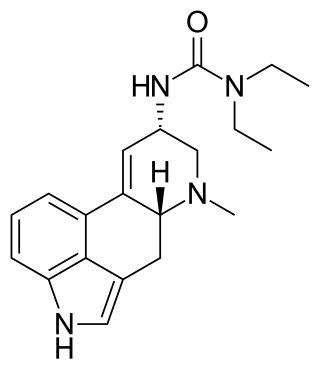
Lisuride, sold under the brand name Dopergin among others, is a monoaminergic medication of the ergoline class which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, migraine, and high prolactin levels. It is taken by mouth.

Rotigotine, sold under the brand name Neupro among others, is a dopamine agonist of the non-ergoline class of medications indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome. It is formulated as a once-daily transdermal patch which provides a slow and constant supply of the drug over the course of 24 hours.

Dopamine receptor D1, also known as DRD1. It is one of the two types of D1-like receptor family — receptors D1 and D5. It is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD1 gene.

Dopamine receptor D5, also known as D1BR, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD5 gene. It belongs to the D1-like receptor family along with the D1 receptor subtype.

WAY-100635 is a piperazine drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It was originally believed to act as a selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, but subsequent research showed that it also acts as potent full agonist at the D4 receptor. It is sometimes referred to as a silent antagonist at the former receptor. It is closely related to WAY-100135.
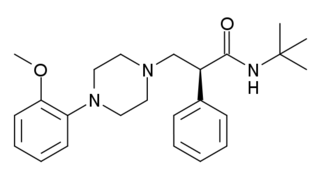
WAY-100135 is a serotonergic drug of the phenylpiperazine family which is used in scientific research. It acts as potent 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, and was originally believed to be highly selective, but further studies have demonstrated that it also acts as a partial agonist of the 5-HT1D receptor (pKi = 7.58; virtually the same affinity for 5-HT1A), and to a much lesser extent, of the 5-HT1B receptor (pKi = 5.82). These findings may have prompted the development of the related compound WAY-100635, another purportedly selective and even more potent 5-HT1A antagonist, which was synthesized shortly thereafter. However, WAY-100635 turned out to be non-selective as well, having been shown to act additionally as a potent D4 receptor agonist later on.
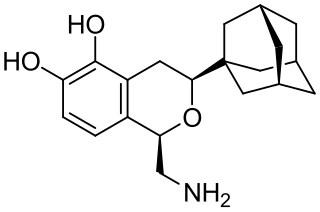
A-77636 is a synthetic drug which acts as a selective D1 receptor full agonist. It has nootropic, anorectic, rewarding and antiparkinsonian effects in animal studies, but its high potency and long duration of action causes D1 receptor downregulation and tachyphylaxis, and unlike other D1 full agonists such as SKF-82,958, it does not produce place preference in animals. A-77636 partially substituted for cocaine in animal studies, and has been suggested for use as a possible substitute drug in treating addiction, but it is better known for its use in studying the role of D1 receptors in the brain.

A-68930 is a synthetic compound that acts as a selective dopamine receptor D1 agonist. It is orally active and has antidepressant and anorectic effects in animals, producing wakefulness and tachycardia, but without stimulant effects, instead producing sedation. The difference in effects between A-68930 and other D1 agonists such as SKF-82958 may be due to their differing effects on the related D5 receptor.

A-86929 is a synthetic compound that acts as a selective dopamine receptor D1 agonist. It was developed as a possible treatment for Parkinson's disease, as well as for other applications such as treatment of cocaine addiction, but while it had reasonable efficacy in humans it also caused dyskinesias and has not been continued. It has mainly been used as its diacetate ester prodrug adrogolide (ABT-431), which has better bioavailability.

Dinapsoline is a drug developed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, that acts as a selective full agonist at the dopamine D1 receptor.

Dinoxyline is a synthetic compound developed for scientific research, which acts as a potent full agonist at all five dopamine receptor subtypes.

ABT-724 is a drug which acts as a dopamine agonist, and is selective for the D4 subtype. It was developed as a possible drug for the treatment of erectile dysfunction, although poor oral bioavailability means alternative drugs such as ABT-670 may be more likely to be developed commercially. Nonetheless, it continues to be used in scientific research into the function of the D4 receptor.

CY-208,243 is a drug which acts as a dopamine agonist selective for the D1 subtype. Unlike most D1-selective agonists, it shows efficacy in animal models of Parkinson's disease.
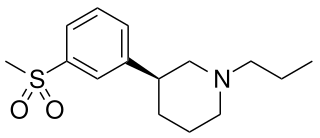
OSU-6162 (PNU-96391) is a compound which acts as a partial agonist at both dopamine D2 receptors and 5-HT2A receptors. It acts as a dopamine stabilizer in a similar manner to the closely related drug pridopidine, and has antipsychotic, anti-addictive and anti-Parkinsonian effects in animal studies. Both enantiomers show similar activity but with different ratios of effects, with the (S) enantiomer (–)-OSU-6162 that is more commonly used in research, having higher binding affinity to D2 but is a weaker partial agonist at 5-HT2A, while the (R) enantiomer (+)-OSU-6162 has higher efficacy at 5-HT2A but lower D2 affinity.




















