 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tigan, Tebamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682693 |
| Routes of administration | Oral, rectal, intramuscular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60-100% |
| Elimination half-life | 7 to 9 hours (mean) |
| Excretion | urine (30-50%), faeces |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.848 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
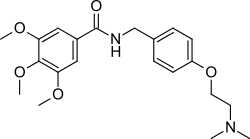
| Formula | C21H28N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 388.464 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Trimethobenzamide (trade names Tebamide, Tigan) is an antiemetic used to prevent nausea and vomiting.
