
The dopamine receptor D4 is a dopamine D2-like G protein-coupled receptor encoded by the DRD4 gene on chromosome 11 at 11p15.5.

18-Methoxycoronaridine, also known as zolunicant, is a derivative of ibogaine invented in 1996 by the research team around the pharmacologist Stanley D. Glick from the Albany Medical College and the chemists Upul K. Bandarage and Martin E. Kuehne from the University of Vermont. In animal studies it has proved to be effective at reducing self-administration of morphine, cocaine, methamphetamine, nicotine and sucrose. It has also been shown to produce anorectic effects in obese rats, most likely due to the same actions on the reward system which underlie its anti-addictive effects against drug addiction.
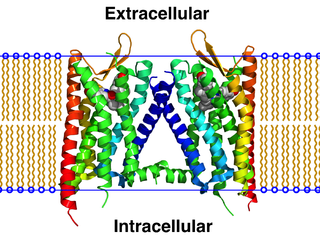
The κ-opioid receptor or kappa opioid receptor, abbreviated KOR or KOP for its ligand ketazocine, is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the OPRK1 gene. The KOR is coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and is one of four related receptors that bind opioid-like compounds in the brain and are responsible for mediating the effects of these compounds. These effects include altering nociception, consciousness, motor control, and mood. Dysregulation of this receptor system has been implicated in alcohol and drug addiction.

Lobeline is a piperidine alkaloid found in a variety of plants, particularly those in the genus Lobelia, including Indian tobacco, Devil's tobacco, great lobelia, Lobelia chinensis, and Hippobroma longiflora. In its pure form, it is a white amorphous powder which is freely soluble in water.

Dopamine receptor D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD3 gene.
Psychological dependence is a cognitive disorder that involves emotional–motivational withdrawal symptoms—e.g. anxiety and anhedonia—upon cessation of prolonged drug abuse or certain repetitive behaviors. It develops through frequent exposure to a psychoactive substance or behavior, though behavioral dependence is less talked about. The specific mechanism involves a neuronal counter-adaptation, which could be mediated through changes in neurotransmitter activity or altered receptor expression. Environmental enrichment and physical activity can attenuate withdrawal symptoms.
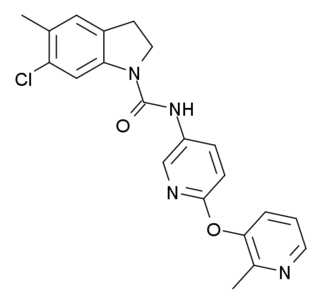
SB-242084 is a psychoactive drug and research chemical which acts as a selective antagonist for the 5HT2C receptor. It has anxiolytic effects, and enhances dopamine signalling in the limbic system, as well as having complex effects on the dopamine release produced by cocaine, increasing it in some brain regions but reducing it in others. It has been shown to increase the effectiveness of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class of antidepressants, and may also reduce their side effects. In animal studies, SB-242084 produced stimulant-type activity and reinforcing effects, somewhat similar to but much weaker than cocaine or amphetamines.

SB-271046 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It was one of the first selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonists to be discovered, and was found through high-throughput screening of the SmithKline Beecham Compound Bank using cloned 5-HT6 receptors as a target, with an initial lead compound being developed into SB-271046 through a structure-activity relationship (SAR) study. SB-271046 was found to be potent and selective in vitro and had good oral bioavailability in vivo, but had poor penetration across the blood–brain barrier, so further SAR work was then conducted, which led to improved 5-HT6 antagonists such as SB-357,134 and SB-399,885.

2-Methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)pyridine (MPEP) is a research drug which was one of the first compounds found to act as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. After being originally patented as a liquid crystal for LCDs, it was developed by the pharmaceutical company Novartis in the late 1990s. It was found to produce neuroprotective effects following acute brain injury in animal studies, although it was unclear whether these results were purely from mGluR5 blockade as it also acts as a weak NMDA antagonist, and as a positive allosteric modulator of another subtype mGlu4, and there is also evidence for a functional interaction between mGluR5 and NMDA receptors in the same populations of neurons. It was also shown to produce antidepressant and anxiolytic effects in animals, and to reduce the effects of morphine withdrawal, most likely due to direct interaction between mGluR5 and the μ-opioid receptor.

3-( ethynyl)pyridine (MTEP) is a research drug that was developed by Merck & Co. as a selective allosteric antagonist of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. Identified through structure-activity relationship studies on an older mGluR5 antagonist MPEP, MTEP has subsequently itself acted as a lead compound for newer and even more improved drugs.

SB-269970 is a drug and research chemical developed by GlaxoSmithKline used in scientific studies. It is believed to act as a selective 5-HT7 receptor antagonist (EC50 = 1.25 nM) (or possibly inverse agonist). A subsequent study in guinea pig at a concentration of 10 μM showed that it also blocks the α2-adrenergic receptor. The large difference in test concentrations however confirms the selectivity of SB-269970 for the 5-HT7 receptor.
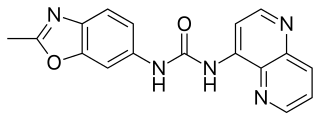
SB-334867 is an orexin antagonist. It was the first non-peptide antagonist developed that is selective for the orexin receptor subtype OX1, with around 50x selectivity for OX1 over OX2 receptors. It has been shown to produce sedative and anorectic effects in animals, and has been useful in characterising the orexinergic regulation of brain systems involved with appetite and sleep, as well as other physiological processes. The hydrochloride salt of SB-334867 has been demonstrated to be hydrolytically unstable, both in solution and as the solid. Orexin antagonists have multiple potential clinical applications including the treatment of drug addiction, insomnia, obesity and diabetes.

UH-232 ((+)-UH232) is a drug which acts as a subtype selective mixed agonist-antagonist for dopamine receptors, acting as a weak partial agonist at the D3 subtype, and an antagonist at D2Sh autoreceptors on dopaminergic nerve terminals. This causes dopamine release in the brain and has a stimulant effect, as well as blocking the behavioural effects of cocaine. It may also serve as a 5-HT2A receptor agonist, based on animal studies. It was investigated in clinical trials for the treatment of schizophrenia, but unexpectedly caused symptoms to become worse.
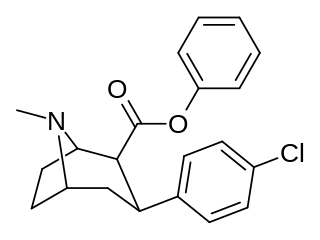
RTI(-4229)-113 is a stimulant drug which acts as a potent and fully selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI). It has been suggested as a possible substitute drug for the treatment of cocaine addiction. "RTI-113 has properties that make it an ideal medication for cocaine abusers, such as an equivalent efficacy, a higher potency, and a longer duration of action as compared to cocaine." Replacing the methyl ester in RTI-31 with a phenyl ester makes the resultant RTI-113 fully DAT specific. RTI-113 is a particularly relevant phenyltropane cocaine analog that has been tested on squirrel monkeys. RTI-113 has also been tested against cocaine in self-administration studies for DAT occupancy by PET on awake rhesus monkeys. The efficacy of cocaine analogs to elicit self-administration is closely related to the rate at which they are administered. Slower onset of action analogs are less likely to function as positive reinforcers than analogues that have a faster rate of onset.

7-OH-DPAT is a synthetic compound that acts as a dopamine receptor agonist with reasonable selectivity for the D3 receptor subtype, and low affinity for serotonin receptors, unlike its structural isomer 8-OH-DPAT. 7-OH-DPAT is self-administered in several animal models, and is used to study addiction to cocaine.
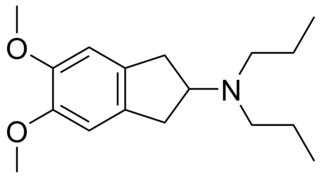
PNU-99,194(A) (or U-99,194(A)) is a drug which acts as a moderately selective D3 receptor antagonist with ~15-30-fold preference for D3 over the D2 subtype. Though it has substantially greater preference for D3 over D2, the latter receptor does still play some role in its effects, as evidenced by the fact that PNU-99,194 weakly stimulates both prolactin secretion and striatal dopamine synthesis, actions it does not share with the more selective (100-fold) D3 receptor antagonists S-14,297 and GR-103,691.

BP-897 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a potent selective dopamine D3 receptor partial agonist with an in vitro intrinsic activity of ~0.6 and ~70x greater affinity for D3 over D2 receptors and is suspected to have partial agonist or antagonist activity in vivo. It has mainly been used in the study of treatments for cocaine addiction. A study comparing BP-897 with the potent, antagonistic, and highly D3 selective SB-277,011-A found, "SB 277011-A (1–10 mg/kg) was able to block cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking, indicating that DRD3 selective antagonism may be an effective approach to prevent relapse for nicotine. In contrast, BP 897 did not block the cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking or nicotine-taking under the FR5 schedule."

L-741,626 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the dopamine receptor D2. It has good selectivity over the related D3 and D4 subtypes and other receptors. L-741,626 is used for laboratory research into brain function and has proved particularly useful for distinguishing D2 mediated responses from those produced by the closely related D3 subtype, and for studying the roles of these subtypes in the action of cocaine and amphetamines in the brain.

SB-206553 is a drug which acts as a mixed antagonist for the 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C serotonin receptors. It has anxiolytic properties in animal studies and interacts with a range of other drugs. It has also been shown to act as a positive allosteric modulator of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Modified derivatives of SB-206553 have been used to probe the structure of the 5-HT2B receptor.

SB-243213 is a research chemical which acts as a selective inverse agonist for the 5HT2C receptor and has anxiolytic effects. It has better than 100x selectivity for 5-HT2C over all other receptor subtypes tested, and a longer duration of action compared to older 5-HT2C antagonist ligands.



















