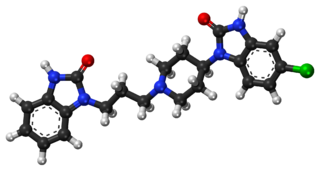
Domperidone, sold under the brand name Motilium among others, is a dopamine antagonist medication which is used to treat nausea and vomiting and certain gastrointestinal problems like gastroparesis. It raises the level of prolactin in the human body and is used to induce and promote breast milk production. It may be taken by mouth or rectally.

A dopamine antagonist, also known as an anti-dopaminergic and a dopamine receptor antagonist (DRA), is a type of drug which blocks dopamine receptors by receptor antagonism. Most antipsychotics are dopamine antagonists, and as such they have found use in treating schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and stimulant psychosis. Several other dopamine antagonists are antiemetics used in the treatment of nausea and vomiting.
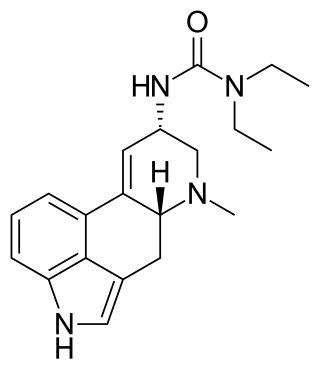
Lisuride, sold under the brand name Dopergin among others, is a monoaminergic medication of the ergoline class which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, migraine, and high prolactin levels. It is taken by mouth.

Piribedil (trade names Pronoran, Trivastal Retard, Trastal, Trivastan, Clarium and others) is an antiparkinsonian agent and piperazine derivative which acts as a D2 and D3 receptor agonist. It also has α2-adrenergic antagonist properties.
Gastroparesis, also called delayed gastric emptying, is a medical disorder consisting of weak muscular contractions (peristalsis) of the stomach, resulting in food and liquid remaining in the stomach for a prolonged period of time. Stomach contents thus exit more slowly into the duodenum of the digestive tract. This can result in irregular absorption of nutrients, inadequate nutrition, and poor glycemic control.
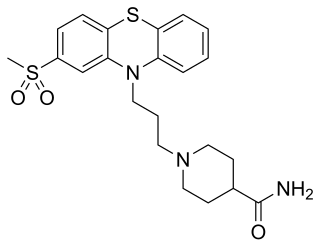
Metopimazine, sold under the brand names Nortrip, Vogalen, and Vogalene, is an antiemetic of the phenothiazine group which is used to treat nausea and vomiting. It is marketed in Europe, Canada, and South America. As of August 2020, metopimazine has been repurposed and is additionally under development for use in the United States for the treatment of gastroparesis.

SB-277,011A is a drug which acts as a potent and selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, which is around 80-100x selective for D3 over D2, and lacks any partial agonist activity.

Terguride, sold under the brand name Teluron, is a serotonin receptor antagonist and dopamine receptor agonist of the ergoline family. It is approved for and used as a prolactin inhibitor in the treatment of hyperprolactinemia in Japan. Terguride is taken by mouth.
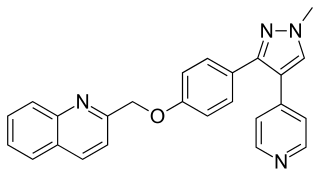
Mardepodect is a drug which was developed by Pfizer for the treatment of schizophrenia. It acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor selective for the PDE10A subtype. The PDE10A enzyme is expressed primarily in the brain, mostly in the striatum, nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle, and is thought to be particularly important in regulating the activity of dopamine-sensitive medium spiny neurons in the striatum which are known to be targets of conventional antipsychotic drugs. Older PDE10A inhibitors such as papaverine have been shown to produce antipsychotic effects in animal models, and more potent and selective PDE10A inhibitors are a current area of research for novel antipsychotic drugs which act through a different pathway to conventional dopamine or 5-HT2A antagonist drugs and may have a more favourable side effects profile. Mardepodect is currently one of the furthest advanced PDE10A inhibitors in development and has progressed through to Phase II clinical trials in humans. In 2017, development of mardepodect for the treatment of schizophrenia and Huntington's disease was discontinued.

Ecopipam is a dopamine antagonist which is under development for the treatment of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, Tourette's syndrome, speech disorders, and restless legs syndrome. It is taken by mouth.
An orexin receptor antagonist, or orexin antagonist, is a drug that inhibits the effect of orexin by acting as a receptor antagonist of one or both of the orexin receptors, OX1 and OX2. Medical applications include treatment of sleep disorders such as insomnia.
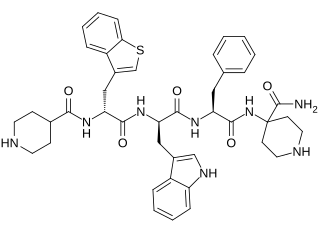
Relamorelin is a synthetic peptide, centrally penetrant, selective agonist of the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) which is under development by Allergan pharmaceuticals for the treatment of diabetic gastroparesis, chronic idiopathic constipation, and anorexia nervosa. It is a pentapeptide and an analogue of ghrelin with improved potency and pharmacokinetics. In humans, relamorelin produces increases in plasma growth hormone, prolactin, and cortisol levels, and, like other GHSR agonists, increases appetite. As of June 2015, relamorelin is in phase II clinical trials for diabetic gastroparesis and constipation. The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted Fast Track designation to relamorelin for diabetic gastroparesis.
Peripherally selective drugs have their primary mechanism of action outside of the central nervous system (CNS), usually because they are excluded from the CNS by the blood–brain barrier. By being excluded from the CNS, drugs may act on the rest of the body without producing side-effects related to their effects on the brain or spinal cord. For example, most opioids cause sedation when given at a sufficiently high dose, but peripherally selective opioids can act on the rest of the body without entering the brain and are less likely to cause sedation. These peripherally selective opioids can be used as antidiarrheals, for instance loperamide (Imodium).
Panamesine (INN; developmental code name EMD-57455) is a sigma receptor antagonist that was under development by Merck as a potential antipsychotic for the treatment of schizophrenia in the 1990s but was never marketed. It is a selective antagonist of both sigma receptor subtypes, the σ1 and σ2 receptors (IC50 = 6 nM). In addition, the major metabolite of the drug, EMD-59983, has high affinity for the sigma receptors (IC50 = 24 nM) and the dopamine D2 (IC50 = 23 nM) and D3 receptors, with potent antidopaminergic activity. Panamesine reached phase II clinical trials for schizophrenia prior to the discontinuation of its development.

Amesergide is a serotonin receptor antagonist of the ergoline and lysergamide families related to methysergide which was under development by Eli Lilly and Company for the treatment of a variety of conditions including depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, male sexual dysfunction, migraine, and thrombosis but was never marketed. It reached phase II clinical trials for the treatment of depression, erectile dysfunction, and premature ejaculation prior to the discontinuation of its development.

Tavapadon (developmental code names CVL-751, PF-6649751, PF-06649751) is a dopamine receptor agonist which is under development by Pfizer and Cerevel Therapeutics for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It acts as a selective partial agonist of the dopamine D1 (Ki = 8.54 nM) and D5 receptors. It also shows biased agonism for Gs-coupled signaling. As of July 2021, tavapadon is in phase 3 clinical trials for Parkinson's disease.

Mevidalen (developmental code name LY-3154207) is a dopaminergic drug which is under development for the treatment of Lewy body disease, including those with Parkinson's disease. It acts as a selective positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the dopamine D1 receptor. The drug is orally active and crosses the blood–brain barrier. It is a tetrahydroisoquinoline and is a close analogue of DETQ, another D1 receptor PAM. Mevidalen has been found to have wakefulness-promoting effects in sleep-deprived humans. Side effects of mevidalen have been reported to include increased heart rate and blood pressure, insomnia, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, anxiety, nervousness, fatigue, headaches, palpitations, and contact dermatitis, as well as falls in those with dementia. As of March 2022, mevidalen is in phase 2 clinical trials for the treatment of Lewy body disease. Besides for movement disorders and dementia, D1 receptor PAMs like mevidalen might have value in the treatment of certain neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression, excessive somnolence, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.

Trazpiroben (developmental code name TAK-906) is a dopamine antagonist drug which was under development for the treatment of gastroparesis. It acts as a peripherally selective dopamine D2 and D3 receptor antagonist. The drug has been found to strongly increase prolactin levels in humans, similarly to other peripherally selective D2 receptor antagonists like domperidone. Clinical development of trazpiroben was discontinued before April 2022. Trazpiroben was originated by Altos Therapeutics and was under development by Takeda Oncology.














