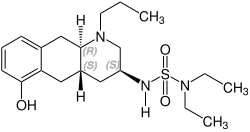Structure without stereochemistry | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Norprolac |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Drug class | Dopamine receptor agonist |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H33N3O3S |
| Molar mass | 395.56 g·mol−1 |
| |
Quinagolide (INN , BAN ), sold under the brand name Norprolac, is a selective dopamine D2 receptor agonist which is used to manage hyperprolactinemia. [1] It has also been found to be effective in the treatment of breast pain. [2] It is used in the UK, but it is not available in US.