
Ergot or ergot fungi refers to a group of fungi of the genus Claviceps.
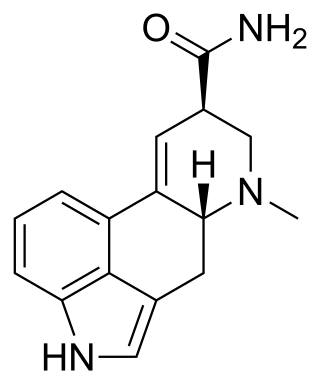
Ergine, also known as lysergic acid amide and lysergamide, is an ergoline alkaloid that occurs in Clavicipitaceous fungi, which includes Convolvulaceae vines, which have a permanent bond with these fungi. The most common source of ergine for consumers is the seeds of Ipomoea tricolor, Ipomoea corymbosa, and Argyreia nervosa; isoergine and lysergic acid propanolamide have also been shown to contribute to their psychoactivity.
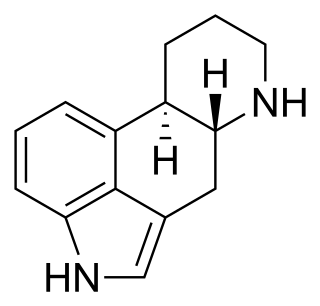
Ergoline is a core structure in many alkaloids and their synthetic derivatives. Ergoline alkaloids were first characterized in ergot. Some of these are implicated in the condition of ergotism, which can take a convulsive form or a gangrenous form. Even so, many ergoline alkaloids have been found to be clinically useful. Annual world production of ergot alkaloids has been estimated at 5,000–8,000 kg of all ergopeptines and 10,000–15,000 kg of lysergic acid, used primarily in the manufacture of semi-synthetic derivatives.

Argyreia nervosa is a perennial climbing vine native to the Indian subcontinent and introduced to numerous areas worldwide, including Hawaii, Africa, and the Caribbean. Though it can be invasive, it is often prized for its aesthetic and medicinal value. Common names include Hawaiian baby woodrose, adhoguda अधोगुडा or vidhara विधारा (Sanskrit), elephant creeper and woolly morning glory. Its seeds are known for their powerful entheogenic properties, greater or similar to those of Ipomoea species, with users reporting significant psychedelic and spiritual experiences. The two botanical varieties are Argyreia nervosa var. nervosa described here, and Argyreia nervosa var. speciosa, the roots of which are used in Ayurvedic medicine.

ᴅ-Lysergic acid α-hydroxyethylamide, also known as ᴅ-lysergic acid methyl carbinolamide, is an ergoamide and an ergoline. It is perhaps the main constituent of the parasitic fungus, Claviceps paspali; and found in trace amounts in Claviceps Purpurea. C. paspali and C. purpurea are ergot-spreading fungi. Periglandula, Clavicipitacepus fungi, are permanently symbiotically connected to an estimated 450 species of Convolvulaceae and thus generate LAH in some of them. The most well-known ones are Ipomoea tricolor, Turbina corymbosa (coaxihuitl), and Argyreia nervosa.

Indole alkaloids are a class of alkaloids containing a structural moiety of indole; many indole alkaloids also include isoprene groups and are thus called terpene indole or secologanin tryptamine alkaloids. Containing more than 4100 known different compounds, it is one of the largest classes of alkaloids. Many of them possess significant physiological activity and some of them are used in medicine. The amino acid tryptophan is the biochemical precursor of indole alkaloids.

Ergocryptine is an ergopeptine and one of the ergoline alkaloids. It is isolated from ergot or fermentation broth and it serves as starting material for the production of bromocriptine. Two isomers of ergocryptine exist, α-ergocryptine and β-ergocryptine. The beta differs from the alpha form only in the position of a single methyl group, which is a consequence of the biosynthesis in which the proteinogenic amino acid leucine is replaced by isoleucine. β-Ergocryptine was first identified in 1967 by Albert Hofmann. Ergot from different sources have different ratios of the two isomers.
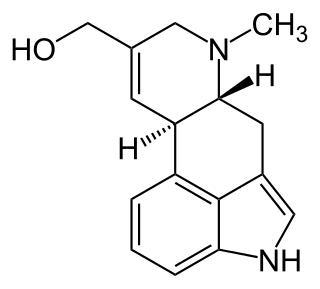
Elymoclavine is an ergot alkaloid. It can be produced from C. fusiformis from Pennisetum typhoideum. It is a precursor in the biosynthesis of D-(+)-lysergic acid. Ergot alkaloids are natural products derived from L-tryptophan. They are often toxic for humans and animals. Despite that they are also well known for their pharmacological activities.
Chanoclavine-I dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.332, easD (gene), fgaDH (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name chanoclavine-I:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalises the following chemical reaction
Festuclavine dehydrogenase (EC 1.5.1.44, FgaFS, festuclavine synthase) is an enzyme with systematic name festuclavine:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
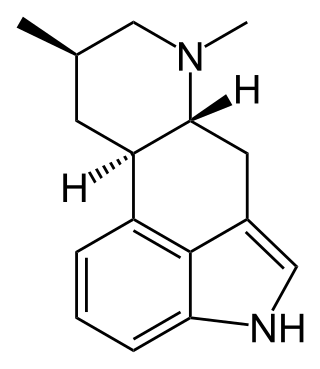
Festuclavine is an ergoline fungal isolate.
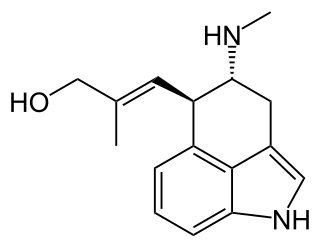
Chanoclavine, also known as chanoclavin-l is a tri-cyclic ergot alkaloid (ergoline) isolate of certain fungi. It is mainly produced by members of the genus claviceps. Long used in traditional Chinese medicine, it was found in 1987 mouse studies to stimulate dopamine D2 receptors in the brain.
The molecular formula C16H20N2O (molar mass: 256.34 g/mol, exact mass: 256.1576 u) may refer to:

Argyreia cuneata is a perennial climbing shrub which is native to the Indian subcontinent and is related to Argyreia nervosa.











