| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H16N2OS |
| Molar mass | 284.38 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
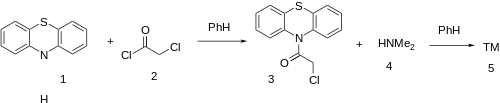
Dacemazine (INN, also known as Ahistan and Histantine) [1] is a phenothiazine derivative which acts as a histamine antagonist at the H1 subtype. First described in 1951, it was never marketed as a drug on its own, although a combination of dacemazine and di-tert-butylnaphthalenesulfonate was sold as an antispasmodic and antitussive under the trade name Codopectyl. [1] It was also assessed as a possible anticancer drug. [2]